- What Is IT Project Management?
- What Is IT Project Management Software?
- Benefits of IT Project Management Software
- Must-Have Features for IT Project Management Software
- How to Manage an IT Project
- Unique Challenges of IT Project Management
- IT Project Management Methodologies
- IT Project Management Tools
- Roles in IT Project Management
- IT Project Manager Job Description
- Is IT Project Management Certification Necessary?
What Is an IT Project?
An information technology (IT) project is a type of project that deals with IT infrastructure, information systems or computers. Examples of an IT project include web development, software development, mobile app development, network configuration, software implementation, hardware installation, database management, and IT emergency recovery.
What Is IT Project Management?
IT project management (ITPM) is the planning, scheduling, execution, monitoring and reporting of IT projects. While many industries focus exclusively on IT projects, IT is unique in that most, if not all, industries have some level of an IT component.
Related: 15 Free IT Project Management Templates for Excel, Word & More
Since they are often very wide in scope, IT project managers must deal with risk, interdependent integrations, software updates, scope creep and so on. Therefore, IT projects require more than the typical project management tools and skills to complete.
Specialized IT project management software complete with online Gantt charts, kanban boards, dashboards and reports provide the essential functions necessary for successful IT projects.
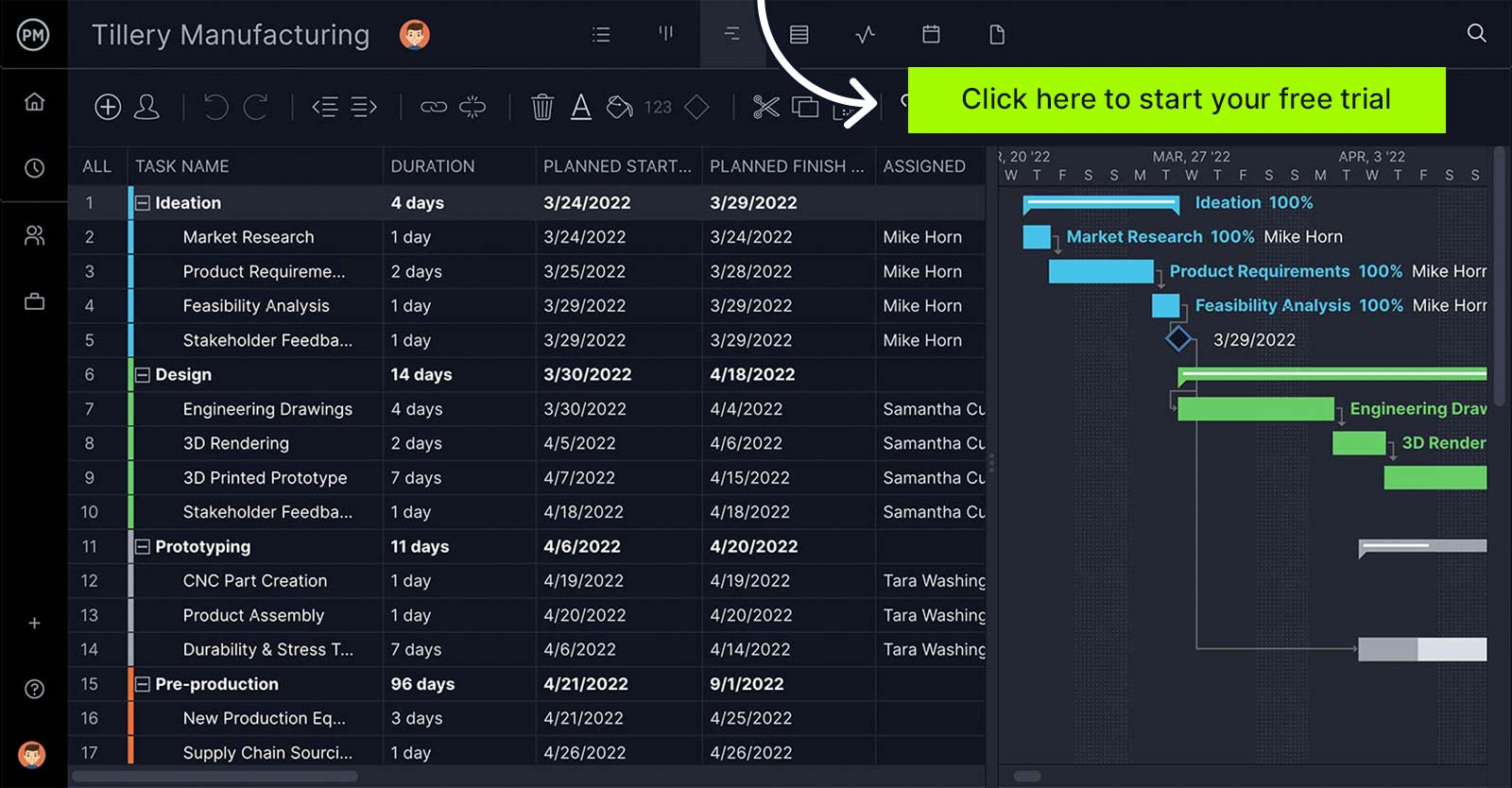
ProjectManager has everything you need to enhance IT planning, scheduling and rollouts. Learn more.
What Are the Six Phases of an IT Project?
The six phases of an IT project are based on the six phases of project management, which are used in conjunction with the IT phases to manage the project. They are as follows:
Initiation
During the first phase of an IT project, one must ask “why is this project needed?”—in other words, the objective of the project must be identified. Then, a project proposal, including a business plan, that meets the needs of the project must be written. In addition, a feasibility study might be conducted to ensure the proposal is airtight.
Definition
After the project proposal has been approved, the project moves into the definition phase. This is where the objectives of the project are finalized and the requirements for a successful project are identified. The project scope can also be outlined, and a project plan may be created during this phase. Budgets are also set, and resources are determined.
Get your free
IT project plan template
Use this free IT project plan template to manage your projects better.
Open the templateDesign
The design phase of an IT project is when the project team sets out to find the best solution for achieving their goal. This includes creating multiple designs and prototypes. Once a suitable design has been chosen, specifications for the development team are created and shared.
Development
The development phase is when the development team is assigned tasks and project management tools are selected. Additionally, technicalities are outlined, raw materials are requested and so on. The main goal of this phase is to make the entire plan as crystal clear as possible to avoid issues in the implementation phase.
Implementation
The implementation phase is where the final deliverable of the IT project is developed; unsurprisingly, this is often the longest phase of the project. The project team sets out to complete their tasks, while the manager monitors and controls the work, resources, cost, quality and risk.
Follow Up
Finally, once the implementation phase is complete, the final project is delivered to the customer/client/stakeholder. The follow up phase is all the work that comes after the project is delivered, and includes setting up support teams, training the end-users, creating a postmortem and ultimately ending the project.
Most IT projects and their phases are managed with a traditional, structured waterfall methodology. An agile framework, though, can minimize risk when adding functionality. DevOps deployment can be a good fit within an organizational culture. Rapid application development (RAD) is a low-investment, high-quality process.
What Does an IT Project Manager Do?
An IT project manager is responsible for overseeing an organization’s IT department and managing teams to execute IT projects on time and within budget. Some of the duties of an IT project manager include:
- Setting project goals and creating plans to meet them
- Maintaining the project schedule and budget, creating status reports
- Managing resources, including the team, equipment, etc.
- Assigning tasks to team members
- Developing strategy to deliver projects on time and within budget
- Using IT project management tools to track progress and performance
- Assessing project risks
- Developing IT risk management strategies
- Leading regular meetings with team and stakeholders
IT project managers are expected to have advanced knowledge of computers, operating systems, network and service desk administration. They must also be good communicators and be able to clearly explain complex technical issues. Other required skills include experience with scheduling, budgeting and resource planning.
While the skill sets of project managers across different industries are generally the same, an IT project manager is unique in that they’re focused solely on the IT needs of an organization. But like all project managers, the way an IT project manager handles their varied duties and responsibilities is with the help of robust IT project management software.
What Is IT Project Management Software?
IT project management software is used by managers to organize and control the processes of their IT projects. Like any software tool, it’s main purpose is to increase efficiency.
IT project management software boosts efficiency by giving users the features they need to monitor and track progress and performance. This keeps their IT projects on track to meet tight schedules and budgets.
Some key features common among IT project management tools include task and time tracking, real-time data, unlimited file storage, multiple project views to support hybrid methodologies, planning, scheduling and reporting. Microsoft Project is one of the most commonly used project management software, but it has major drawbacks that make ProjectManager a better choice for IT projects.
Benefits of IT Project Management Software
Regardless of what IT project management software you choose, you want one that is going to make your job easier. It should help you organize tasks and schedule their execution over a set schedule budget. You also want a tool that connects your team and stakeholders to keep them all on the same page.
There are many benefits to using IT project management software:
- Plan Waterfall Projects with Gantt charts
- Live Status with Real-Time Dashboards
- Manage Program or Portfolio of IT Projects
- Get Data Rich Reports With One Click
- Guide teams through digital transformation projects
- Track Time Spent on Tasks and Monitor Progress
- Customize Workflow on Kanban Boards
Must-Have Features for IT Project Management Software
The IT project management software that’s best for you will ideally have at least these six features.
Keep Tasks Organized on a Timeline
IT managers and teams need a visual tool to organize their tasks over a project timeline. Gantt charts help them prioritize, set the duration and even link dependent tasks that could block work later on during the execution of a project.
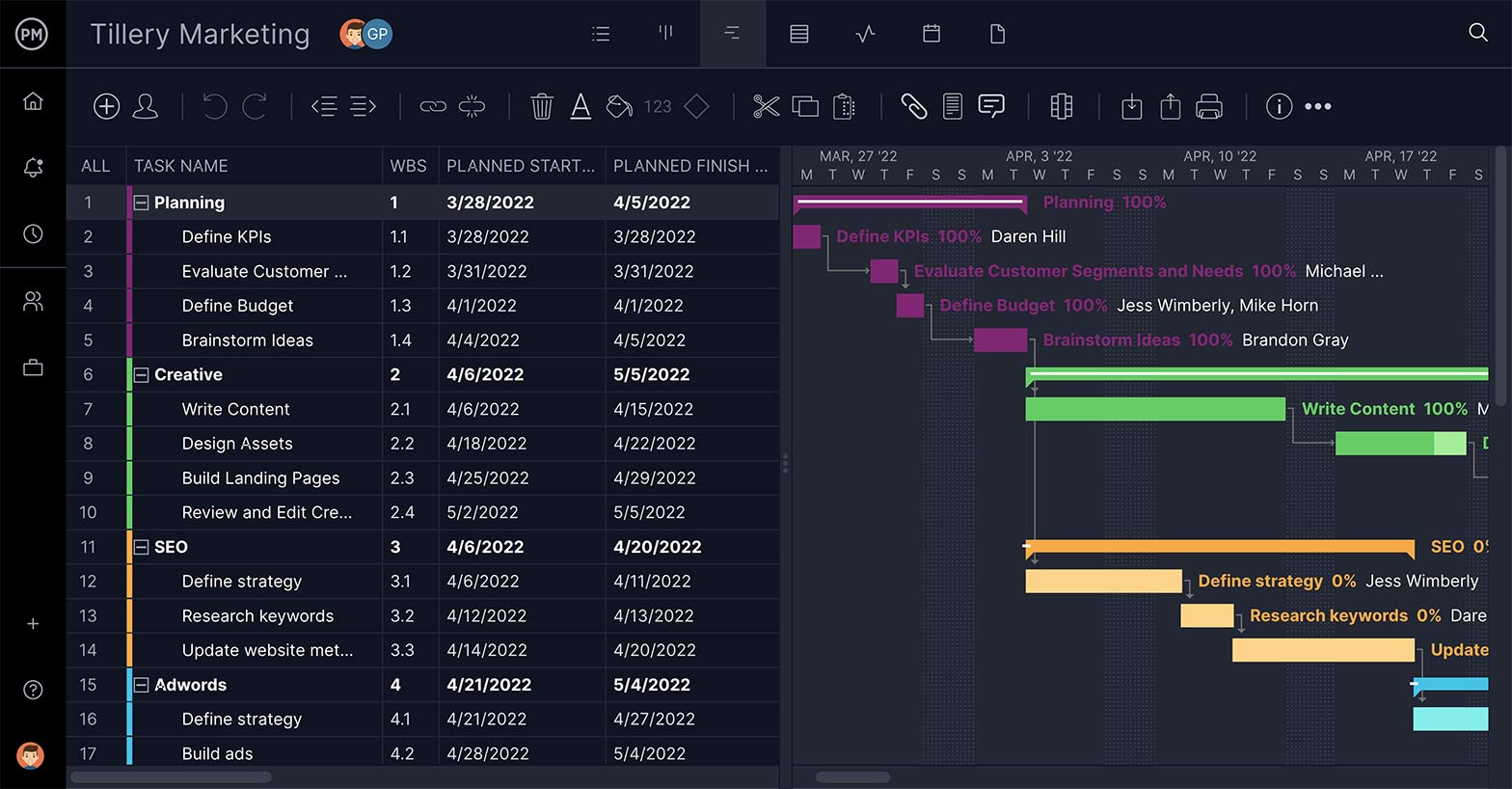
Make Better Data-Driven Decisions
Managing means constantly making choices. The more data you have, the better those decisions. Reports that pull info on progress, costs, variance, workload and much more can help you gather insightful information. Reports should be easy to generate, filter and share.
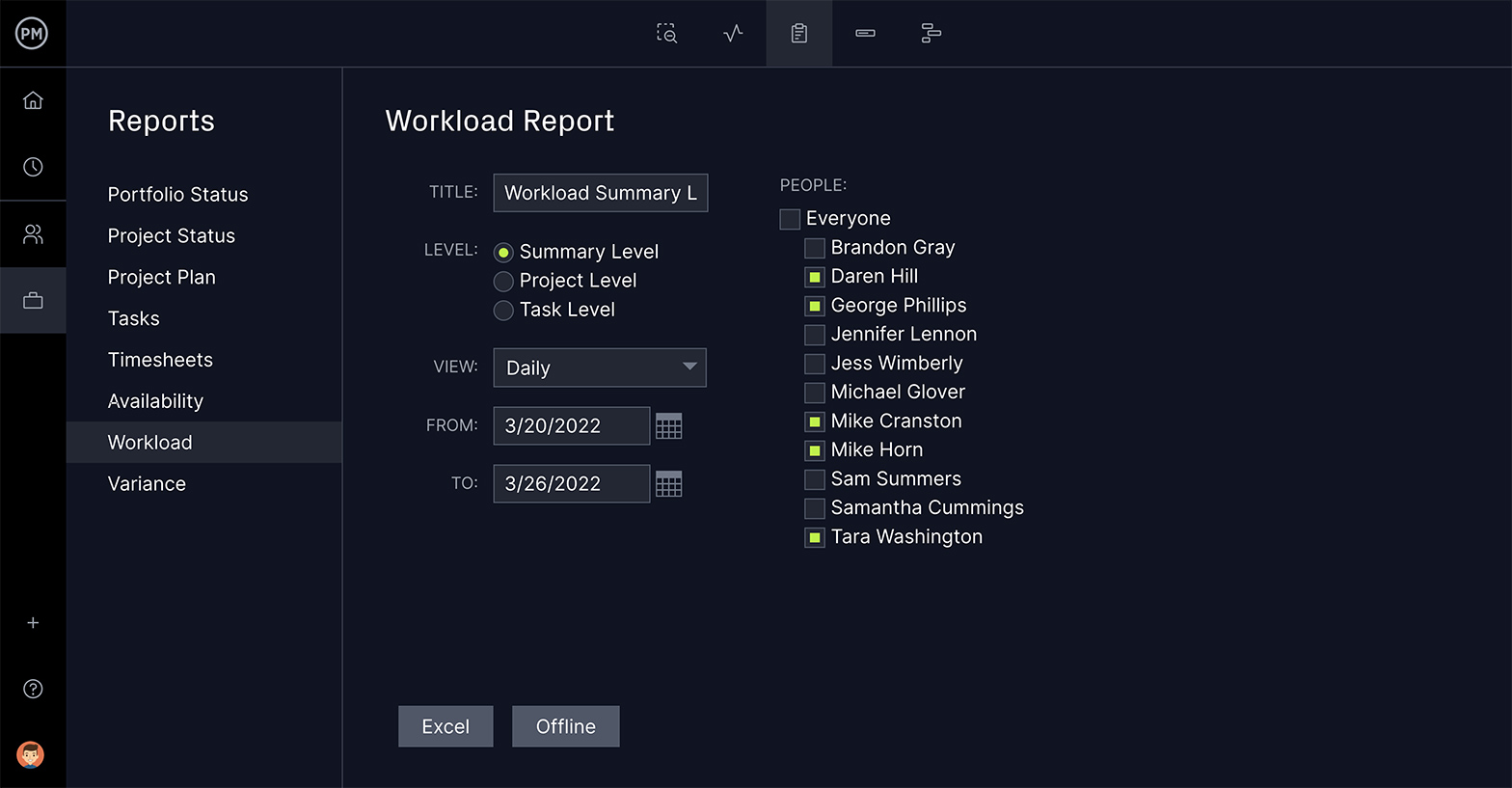
Get Live Status Reports
IT systems require that you keep a close eye on metrics, catch irregularities quickly and resolve them even quicker. A dashboard that is always collecting data and displaying it in easy-to-read graphs and charts will give you a high-level view of your IT’s health.

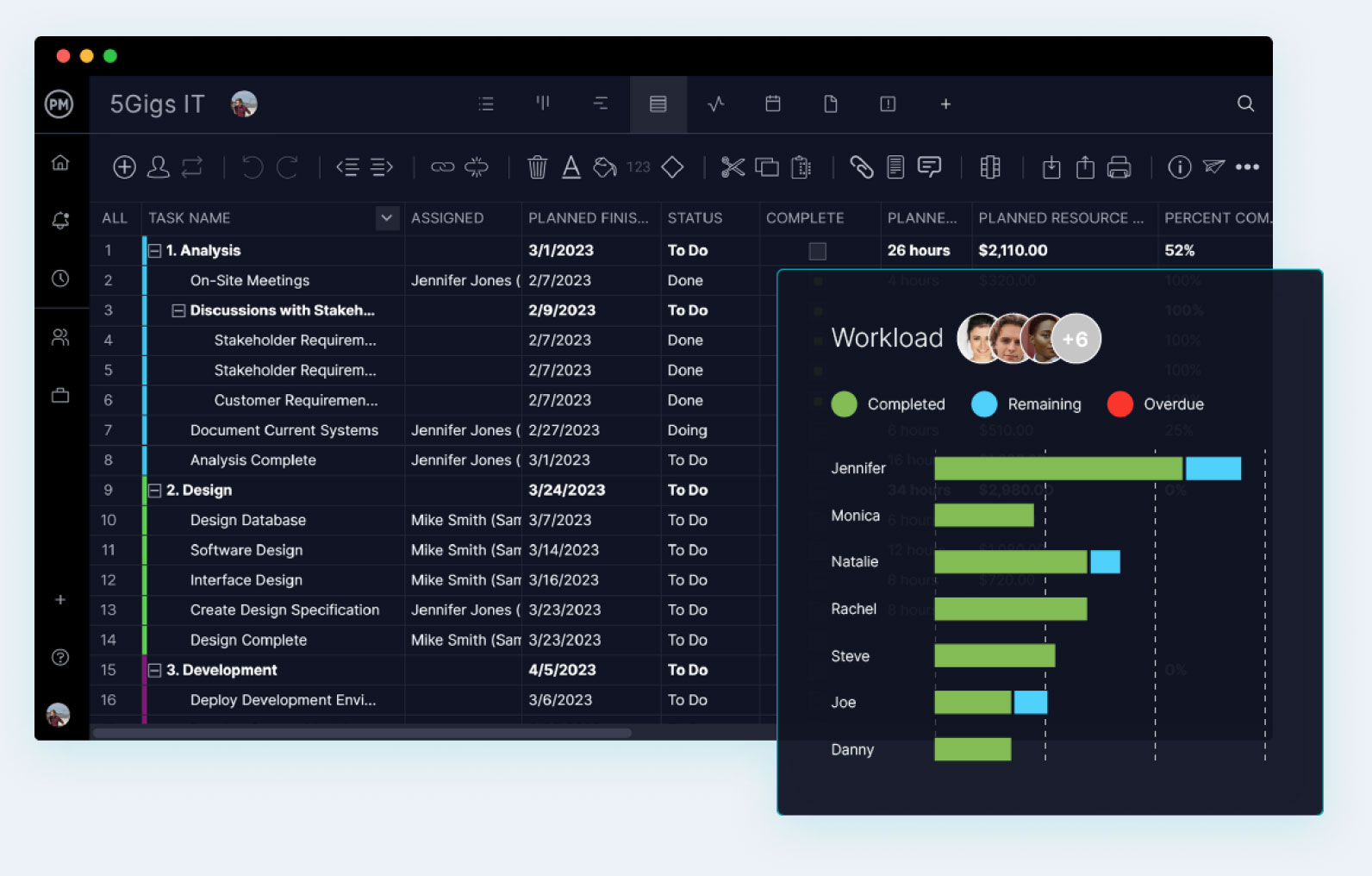
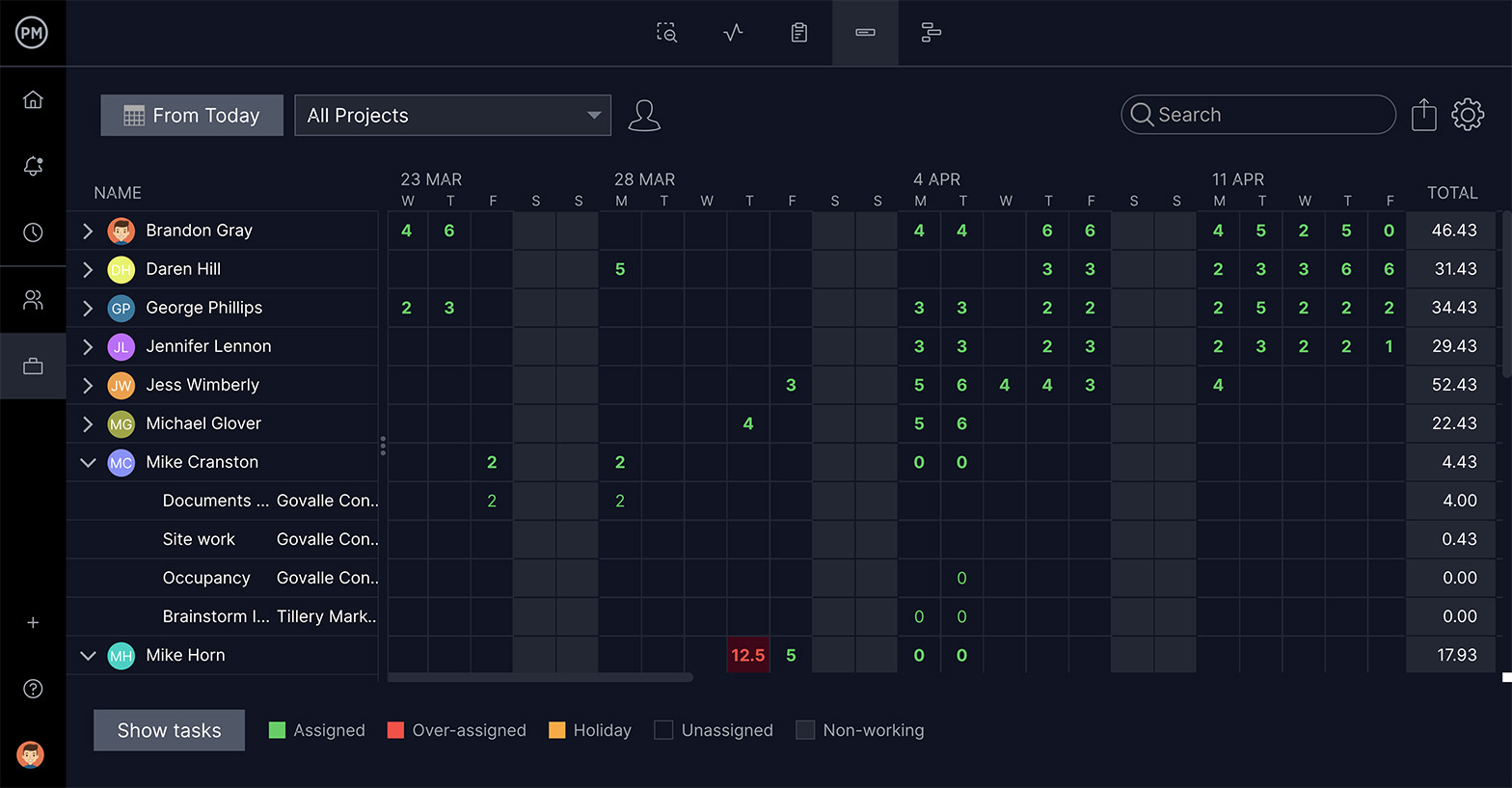
Assign the Right Amount of Tasks
Knowing what your IT teams are doing is essential to keeping them productive. If they have too many tasks, their work suffers. Using a workload management feature will allow you to see who is working on what, and balance that workload to have everyone equally allocated.
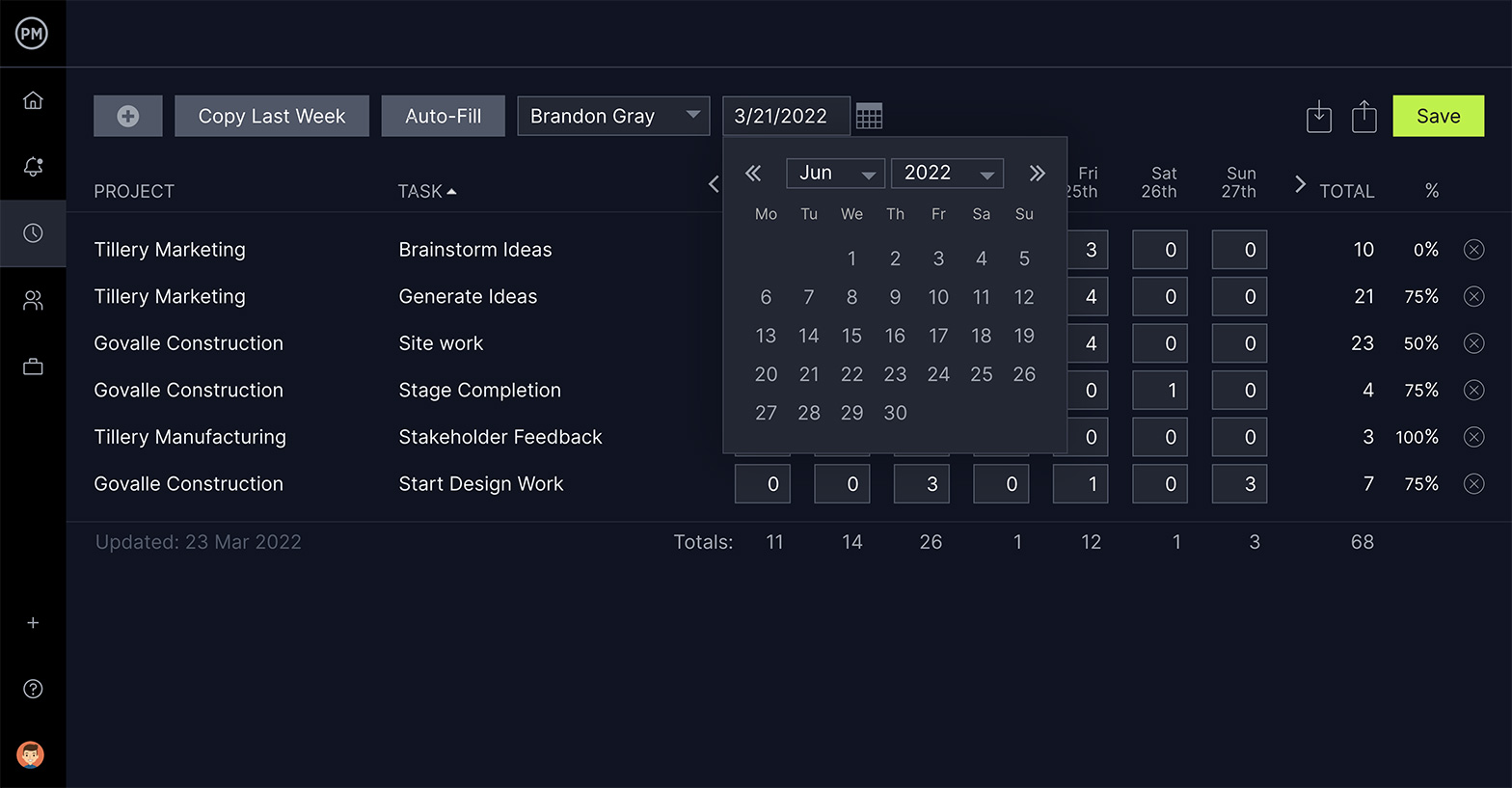
Track Your Team’s Logged Hours
Timesheets are more than a payroll tool—they’re another window into your team’s productivity. They allow you to monitor how many hours they’re spending on tasks, and you can reallocate resources as necessary to keep the work moving ahead as planned.
Know Immediately What’s Happening
IT systems are critical business processes. If they go down, money is lost. To avoid any slowdown (or worse), managers need a feature in their IT project management tool that alerts them in emergencies. It’s also helpful to get notified when anything is updated.
How to Manage an IT Project
While there are many ways to manage an IT project, some aspects are universal. The steps might be slightly different, but the general direction is the same.
We’ll walk you through these steps one-by-one, while illustrating how a project management software can help you along the way.
1. Collect Requirements
Before a project can begin, paperwork is required. You need to define scope, create a budget and determine the stakeholder requirements. All these documents can be attached to the project on our software, which has unlimited file storage.
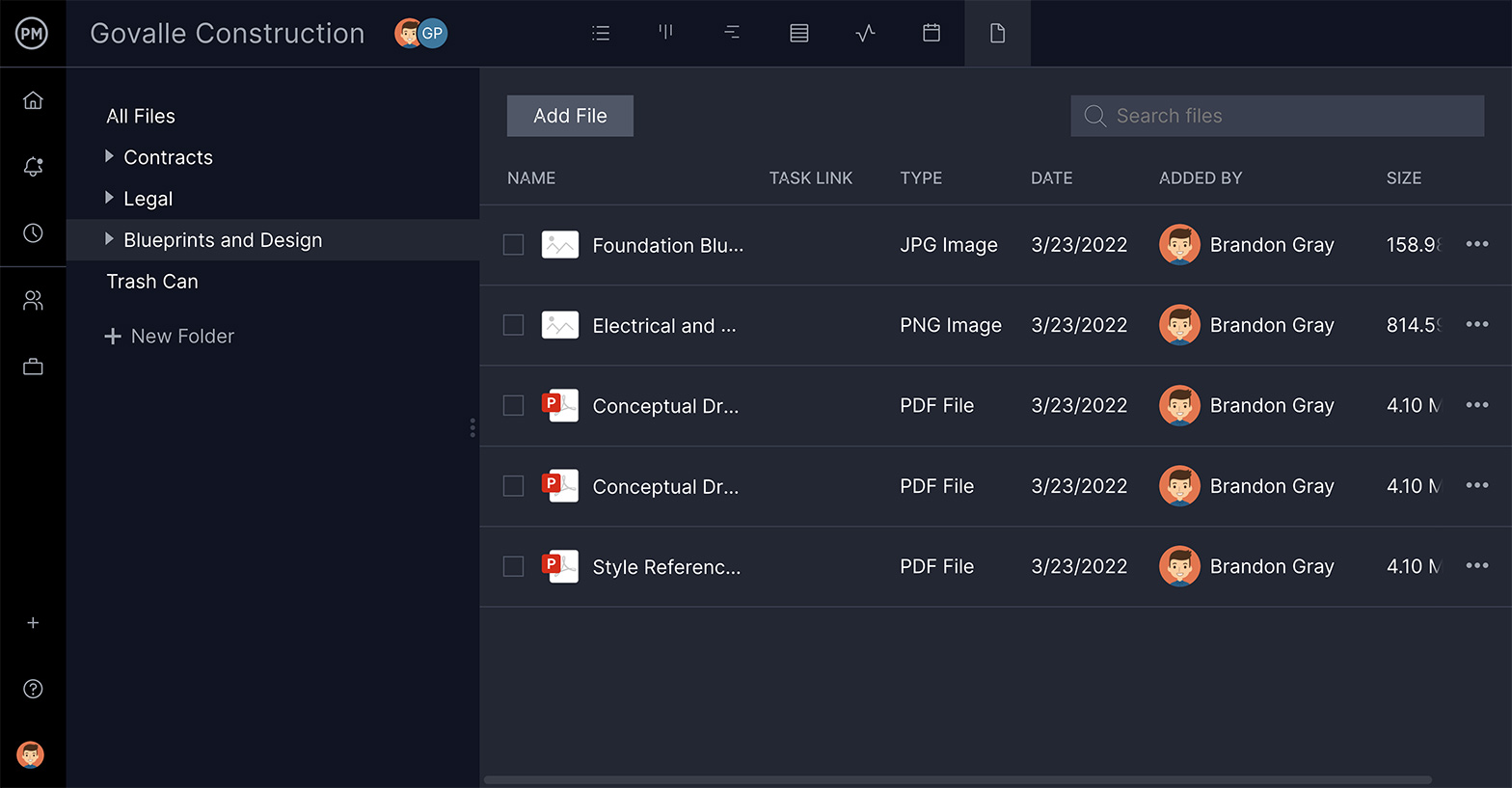
2. Select Team
Now that you’ve collected the project’s requirements, you can assemble a team with the skills and experience that fit the task at hand. Be sure to onboard them into your project management software, so communication happens in one place.
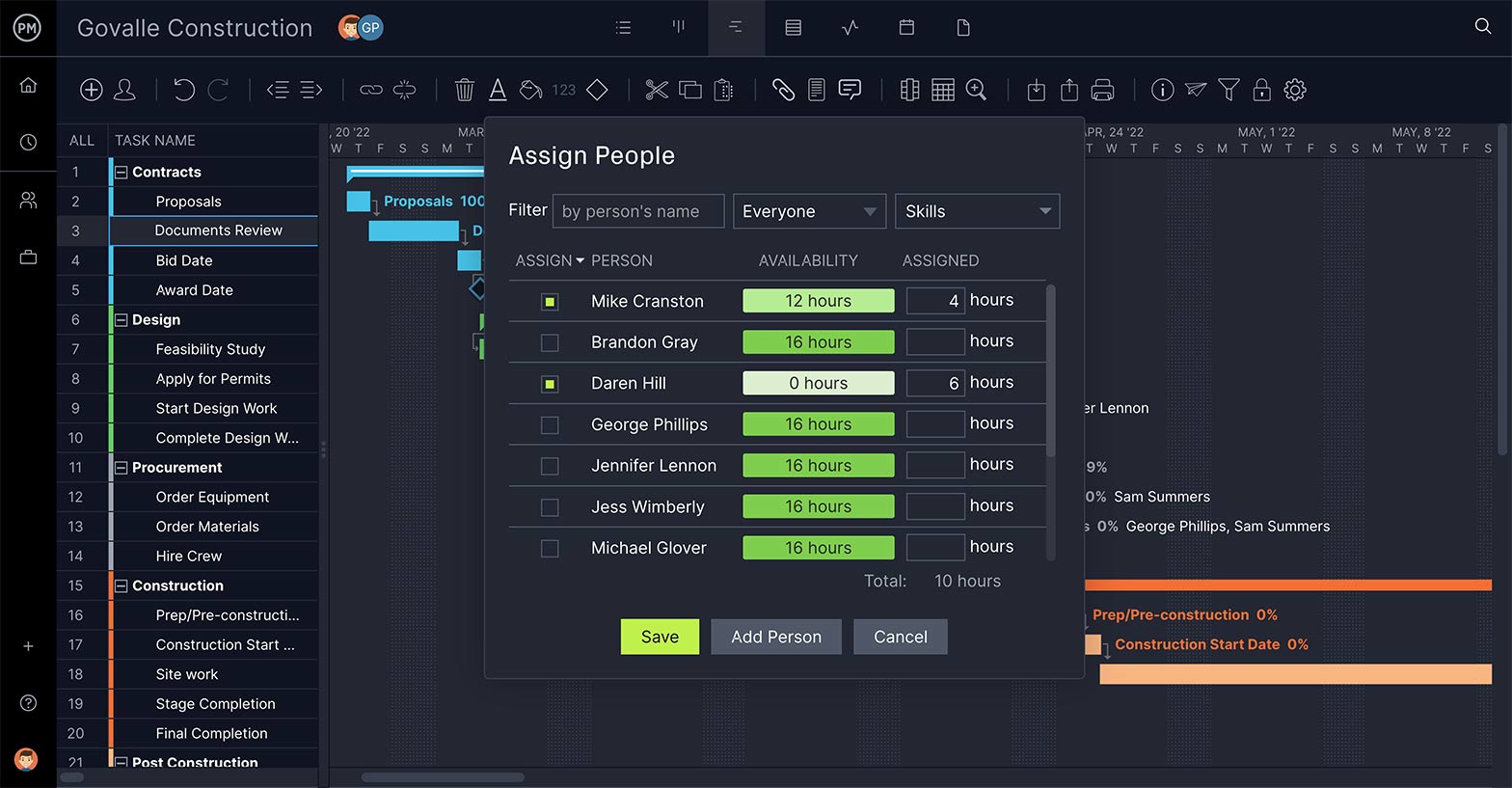
3. Use a Gantt Chart
Use a Gantt to add tasks to a timeline, link dependencies, set milestones and view the critical path. We offer a fully-featured online Gantt chart for project managers who work in a waterfall environment. The whole team doesn’t have to use this traditional planning tool though, as project data is shared across multiple project views: task lists, calendars and kanban boards.
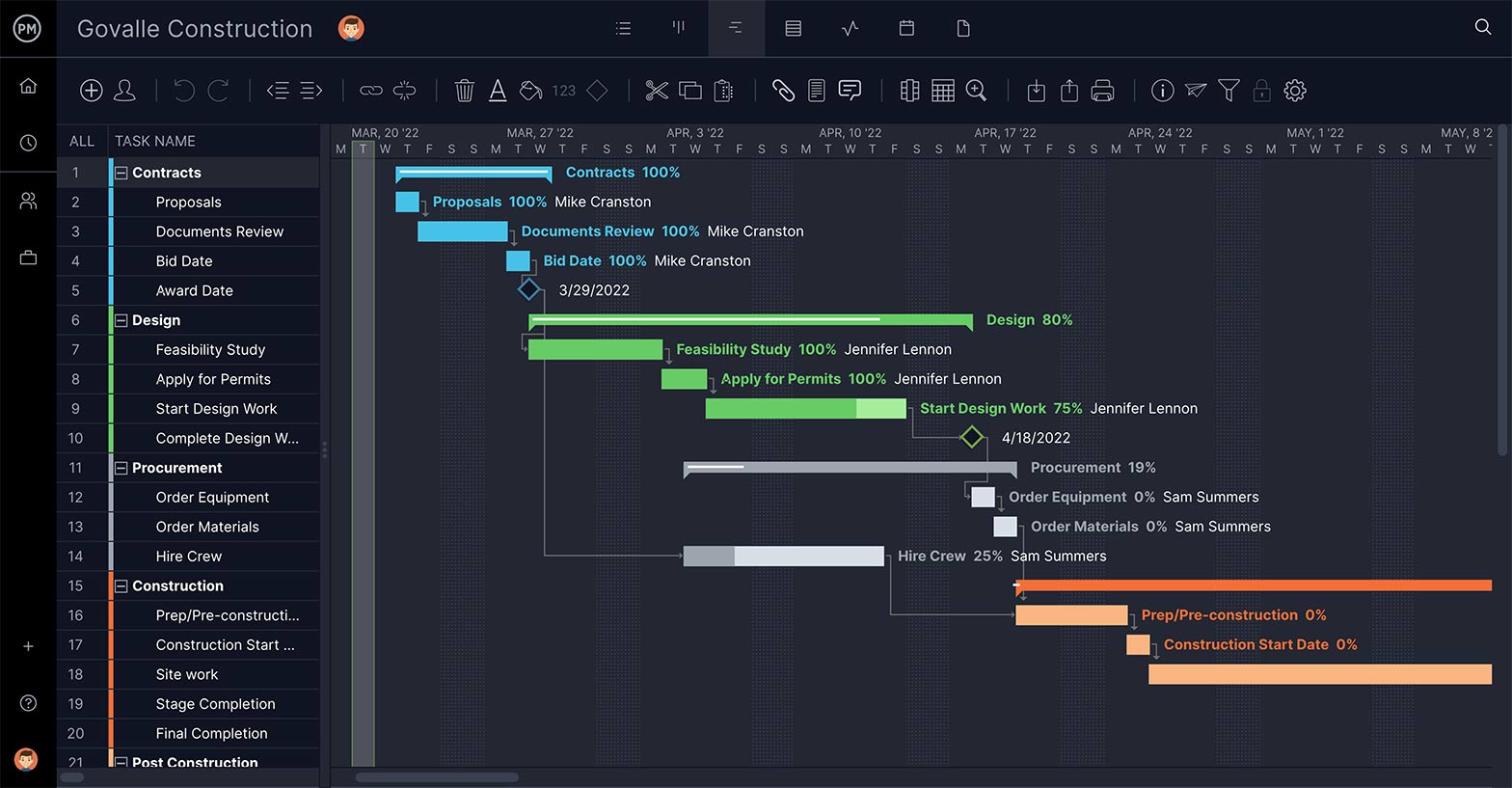
4. Use a Kanban Board
Use a kanban board to control workflow during project execution. With ProjectManager, you can create workflows, execute sprints and work in an agile framework without disturbing the Gantt plan.
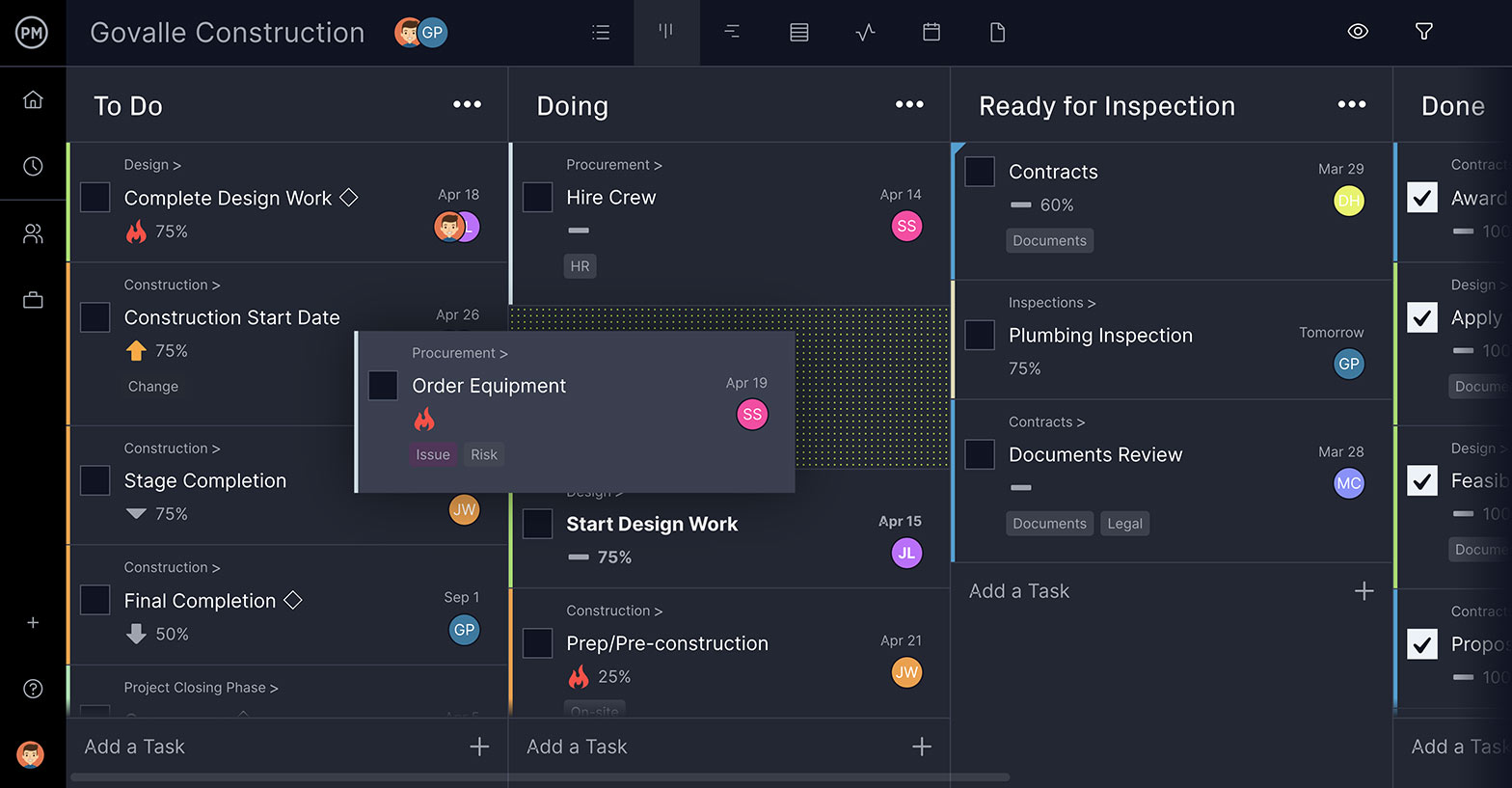
5. Monitor Progress
As the project moves forward, it’s important that the actual progress matches what was planned. Our software has a real-time dashboard that collects data as it’s updated. We automatically crunch the numbers and display them in charts that show costs, tasks, health and more. Project tracking has never been easier.

6. Manage Workload
IT projects require smart workload management. Are team members overtasked or have they too few assignments? To avoid slowing progress, our workload page shows you who’s on holiday and who has too much work: you can even reassign tasks right from the page.

7. Make Changes
Projects aren’t static. You have to pivot fast when there are change requests from stakeholders. Our software gives your plans and your team flexibility. For example, if a date changes, simply drag and drop the task to the new deadline on the Gantt chart. This change is then reflected throughout the software.
8. Get Reports
To track progress and keep stakeholders updated, our software has an in-depth reporting feature. There are many reports, that can be generated to help with IT project management. Make an in-depth status report with just a few clicks to get the information you need.

Ready to manage your IT project with ProjectManager? Start your 30-day free trial today!
Unique Challenges of IT Project Management
IT project management deals with a variety of issues. It ends up interfacing with many other aspects of an organization, such as business administration, human resources, finance and other departments within the organization and entities that are outside of the business. This presents a number of pressing problems with high stakes, for if the technology goes down, then an entire business can become paralyzed.
Changing Technology
There’s the challenge that IT is a volatile industry, with a rate of change that can be dizzying. Technology is notorious for becoming obsolete once it rolls off the assembly line, so IT project management must be prepared for this inevitable change.
Communication
Another hurdle that IT project management has to clear is communication between teams. This is a problem with all projects, frankly, but with IT there are often distributed teams who work remotely, often in different time zones, which only aggravates the situation. Having clear and effective communication channels is key for success on any IT project.
Transparency
Transparency is important, too, as the focus in IT is sharp. Having transparency across the project, with clear deadlines, helps teams better incorporate new technology or respond to change quickly and effectively.
Lack of Agreement on Methodology
But one of the biggest issues is that many organizations aren’t applying IT project management to their projects, which is like sailing a ship without a rudder. Without a process or methodology, whatever that might be, projects go off-track and over budget. Having an IT project manager who defines process, roles and tools is the first step to the success of an IT project.
IT Project Management Methodologies
There seem to be as many project management methodologies as there are projects. They break down into two larger camps, though: traditional and nontraditional methods. Let’s start with the traditional waterfall method, which breaks down the tasks in a project into a line of sequential project phases, and each of these phases depends on the delivery of the one before it.
Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall is the go-to methodology for most IT projects. While it is a project management method found in large projects outside of IT, it also lends itself to IT projects and has been proven a successful approach for formal and linear projects.
Waterfall has been around since it was codified in a paper published in 1970 by Dr. Winston W. Royce. The waterfall model has six stages:
- Requirements: First, the requirements are identified, analyzed and written up in a requirements document, defining what is being done and how it is to be done. This will be reviewed by stakeholders.
- Design: The next step is to document what was decided in the first stage in a design document, which notes everything needed to complete the project.
- Implementation: The IT project manager and team execute the design document, sticking to specifications, procedures and timelines.
- Testing: This is when deliverables from the project are measured against the standards set in the design document and stakeholders, like a quality check. If not met, then the process starts again. Our test case template can help with this process.
- Installation: If the tests are passed, then the project is ready for release to the end-user. The product should be fully operational at this point.
- Maintenance: Most IT projects don’t end with delivery: they often require support after installation, whether updates or upgrades, though often this is tasked to a separate team.
Agile Methodology
Software development has introduced an agile framework to projects, a more iterative approach that works in short sprints and open to pivoting throughout the project, rather than being rigidly aligned with the plan. Some IT teams have incorporated agile or some of its implementations into their own projects.
Hybrid Methodology
More popular than agile with IT teams is hybrid methodology, which combines waterfall and agile, creating a more flexible and yet structured approach that can lend itself to IT projects. This “best of both worlds” approach it can be the right path forward depending on the parameters of the project.
ProjectManager is the ideal IT project management software for waterfall or hybrid methodologies. It features online Gantt charts for waterfall enthusiasts and kanban boards for agile lovers. Plus, the real-time dashboard keeps the IT project manager updated on progress through metrics that can be filtered to show the data you want and then shared.
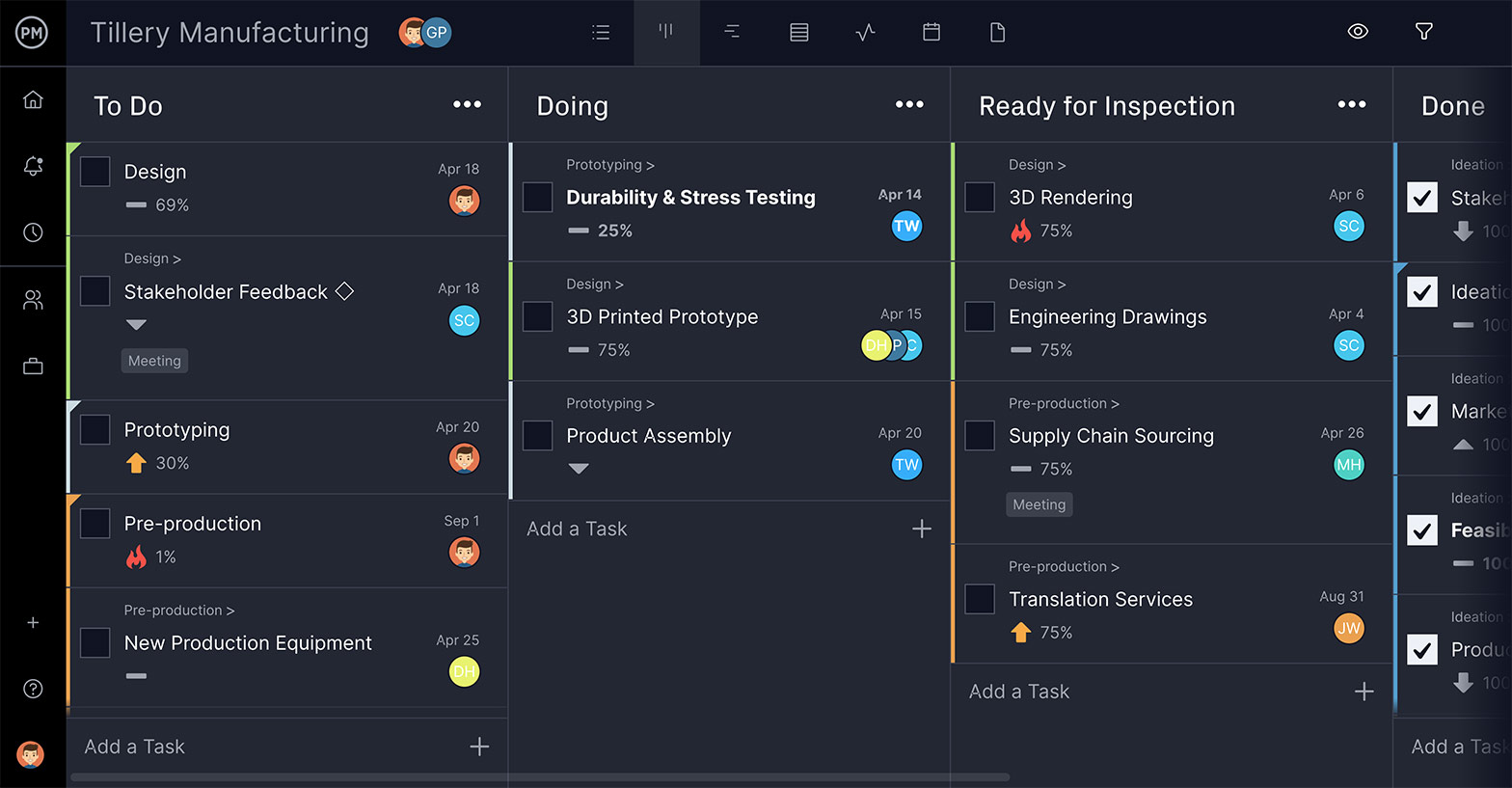
Other Methodologies
Less used in IT projects, but worth mentioning, is the critical path method and critical chain project management. The critical path method categorizes the tasks that must be completed to fulfill the project objective. This is done with a work breakdown structure (WBS), which is then mapped across a project duration or Gantt chart, with task dependencies linked to avoid blocking teams. This helps to know which tasks need to be done when.
The critical chain project management works backwards, recognizing deliverables and using past experience to map the tasks needed to complete the project. This is a very efficient way to use resources, while staying focused on the end-goal. However, delays can be common, and it’s not suited to work on a portfolio of projects.
IT Project Management Tools
The right IT project management tools will overcome the challenges of IT projects and give project managers better control and teams the features they need to collaborate and be more productive. Fortunately, ProjectManager is a project management software designed with IT project management in mind.
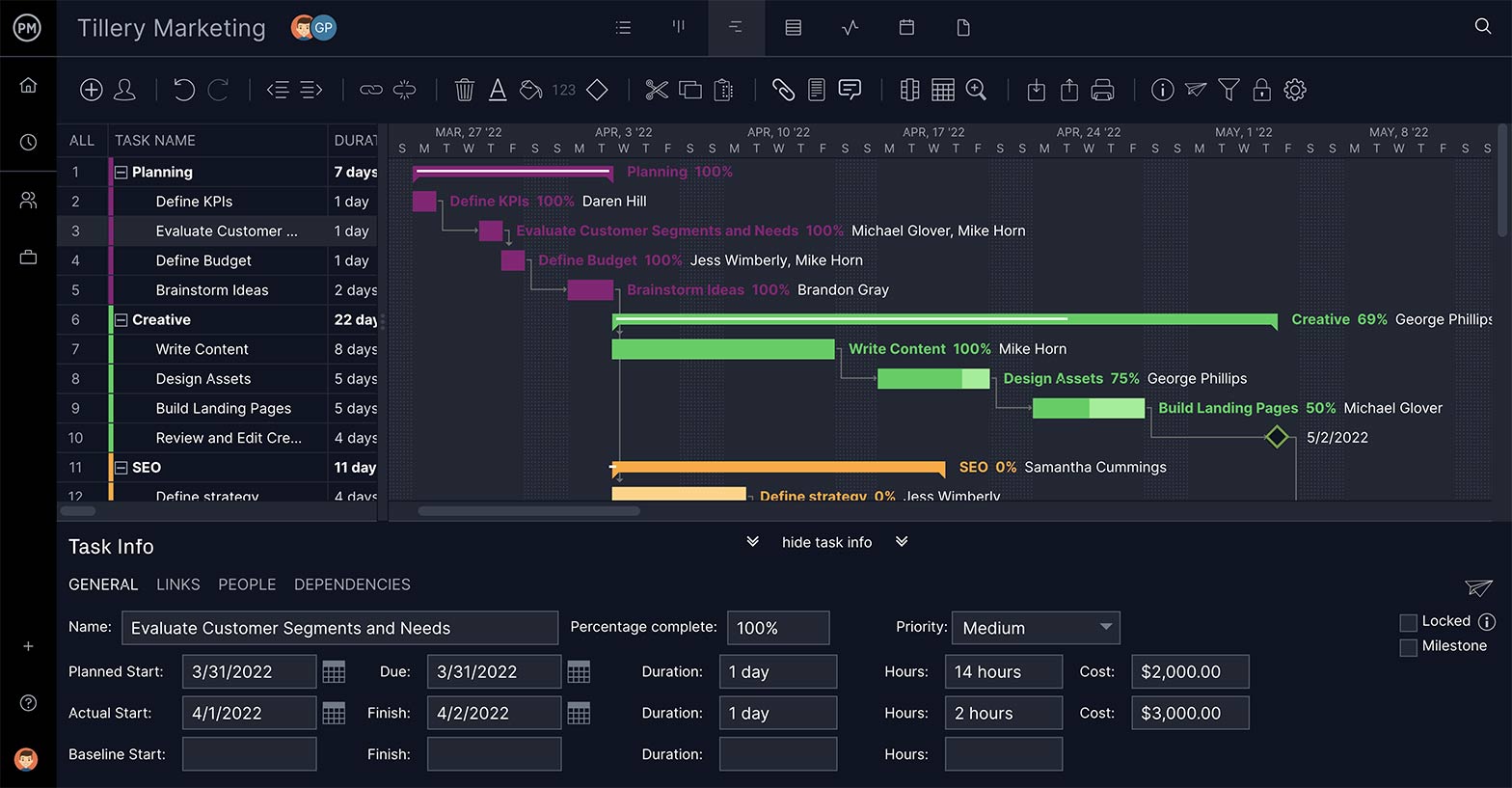
Gantt Charts for Waterfall Plans
The feature that fits with IT project management like a hand in a glove is ProjectManager’s online Gantt charts. Most of the methodologies above work on the timeline of a Gantt chart, and ours will allows you to link tasks that are dependent and even assign.
Teams love our online Gantt chart, especially IT teams that tend to work collaboratively and with autonomy. That’s because they can comment at the task level. Tasks can also have documents attached or images to add supporting materials and even sign-off once they’re completed.
Dashboards for Live Reporting
Because ProjectManager is a cloud-based project management software, status updates are instantly reflected throughout the program. That means your real-time dashboard is giving you project details as they happen.
The various metrics measuring cost, workload, time and more, can be filtered to show just the amount of data you need. Then these easy-to-read colorful graphs and charts can be shared to teams and stakeholders or printed out for presentations.

Roles in IT Project Management
Roles and responsibilities in IT project management mostly mirror those projects in other disciplines. There are stakeholders, who are those who have an interest in the project; teams, who are those with skills to execute the project plan; and the IT project manager, who is the person that is responsible for the planning, procurement and execution of the project.
Types of IT Teams
Where roles differ from more traditional projects is in the teams themselves. While more project management is executed by teams, whether remote or on site, they are largely part of the overall organization that is implementing the project. However, with IT project management there are three types of teams.
- First, there is the traditional project management team that is tasked with an IT project. These teams are not exclusive to IT and are led and staffed with a formal project management methodology.
- Second, there are professional services teams, who deliver technology to external customers. This is usually done with the implementation of software or installation of hardware. They are often led by a project manager, but can be headed by a services vice-president or director. However, they also use formal types of project management.
- Thirdly, there are internal IT teams. These are the teams that manage the delivery and maintenance of the technology in an organization. They roll out new systems, set up computers, monitors, phones and other devices for employees and manage the systems. They can be led by a project manager, though that person is usually defined within the company as a director or vice-president of IT.
The IT Project Manager
The IT project manager, due to the breadth of IT project management, has a wider range of responsibilities than most other project managers. They are not only dealing with leadership, resource allocation, scheduling and planning, monitoring and reporting, but must know about technology beyond the tools that they use to manage projects.
IT project managers are responsible for understanding firmware and being able to implement software integrations. They often build websites and databases, and manage these technologies as well. This includes building networks and maintaining security for data risks.
However, the basic structure of the IT project manager’s job remains being a clear communicator, setting realistic goals and applying the right methodology to achieve them. They must motivate and inform both teams and stakeholders, manage change and set the project schedule. The triple constraint of any project is still present. Therefore, the IT project manager, like any project manager, is concerned with setting deadlines and keeping to a budget. This is all managed through methodology.
IT Project Manager Job Description
An IT project manager can make a salary that ranges from $55,000 to $125,000, depending on industry and region. The more senior the position, however, the more compensated the person will be.
Responsibilities of an IT project manager are similar to any project manager, in that they lead the planning, execution and monitoring and reporting of the project. They are responsible for making sure resources are managed and the project comes in successfully, meaning on time, within budget and of the expected quality. They also report to upper management, stakeholders, clients, etc., while managing the IT staff.
The IT project manager is also responsible for staying updated on the latest technology and changes to the organization’s technology, through research and studying similar organizations and their IT structure. They make sure that the technology complements the organization’s overall goals, strategies and practices.
They also work to preserve the IT assets by implementing disaster recovery and back-up procedures, including any IT security and control structures. The IT project manager is responsible for the quality of all IT projects.
Skills and Qualifications
Some of the skills and qualifications of an IT project manager include:
- Technical management
- An understanding of technology
- An ability to stay on top of the ever-changing field
- Ability to analyze data
- Communications
- Staffing
- Problem-solving
- Data center management
- Budgets
- Strategic planning
- Quality management
Is IT Project Management Certification Necessary?
One way to stay up-to-date on all the skills and qualifications required of an IT project manager is certification. Certification is done by an outside agency that notes a standard of excellence, understanding of the discipline and experience.
Most IT project managers have at least a bachelor’s degree in business management or a more specific area, such as marketing, engineering or computer science. To further differentiate yourself, there are certifications, but they’re mostly general project manager certifications.
Types of Certifications
The Project Management Institute (PMI) offers a couple of industry-recognized project manager certifications, such as the Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) and the Project Management Professional (PMP). PMI also offers a PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA), Program Management Professional (PgMP) and Portfolio Management Professional (PfMP).
More technical certifications are The Open Group’s TOGAF 9 and OPEN CA certifications, as well as the IASA’s Certified IT Architech – Professional (CITA-P). These enterprise architect certifications merge a knowledge of technology with business goals.
IT governance certifications is offered by ITIL and ISACA, which have Certified in the Governance of Enterprise IT (CGEIT) and Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC).
IT Project Management Resources
Articles
Start your free 30-day trial
Deliver faster, collaborate better, innovate more effectively — without the high prices and months-long implementation and extensive training required by other products.
Start free trial