If you’re running a business or managing a project, the impact of a cybercriminal on your company can be catastrophic. They can steal customer data and ruin your reputation. It’s something many don’t recover from. And, unlike in the physical world, where bad neighborhoods are more clearly demarcated, IT risks can be like a trojan horse. They can appear friendly, but when your guard is down they ransack your data.
The threat can be internal, too, such as a disgruntled employee sabotaging everything you built for years in seconds. Bottom line: technology is useful, but it’s also vulnerable. That’s why organizations must do an IT audit to make sure their data and network are safe from attack. An IT security audit might be the only thing standing between success and failure.
What Is an IT Audit?
Audits sound bad. Nobody wants to get that letter announcing the IRS is about to open an audit on your financials. But an audit only means an official inspection of one’s accounts. An information technology audit is therefore an official examination of the IT infrastructure, policies and operations of an organization. It also adds an evaluation to suggest improvements. IT audits have been going on since the mid-1960s and continuously evolved since that point as technology advances. It’s an important part of a good IT project management procedure.
You can think of this as an IT security audit. The point is to see if the IT controls in place are properly protecting the company’s assets, ensuring the integrity of the data, and staying in line with the goals and objectives of the company. This means that everything that involves IT is inspected, from physical security to the overall business and financial concerns.
Get your free
IT Project Plan Template
Use this free IT Project Plan Template to manage your projects better.
Get the Template
Why Is It Important to Conduct an IT Audit?
An IT audit is crucial to guarantee that the IT operations, controls, infrastructure and processes of a company are safe from threats and working as intended. The main objective of an IT audit is to find areas of improvement and vulnerabilities to reduce the chances of IT risks and remain compliant with IT security standards. In addition to this key objective, there are other benefits from conducting regular IT audits, such as:
- Improving existing IT service management policies, guidelines and processes to better adjust to the business objectives of the organization.
- Finding new technologies such as software, hardware or networking that could help companies better store, manage and transfer their business data.
- Obtaining certifications such as SOC 2 allows companies to offer their products and services to new markets.
- Ensure employees across departments understand the IT best practices of the company.
- Avoid regulatory fines or potential business losses due to ineffective IT security practices.
Types of IT Audits
In broad strokes, an IT audit can be broken into two types; general control review and application control review. But, if you want to get more specific, here are five categories of a well-executed audit.
- Systems & applications: This focuses on the systems and applications within an organization. It makes sure they are appropriate, efficient, valid, reliable, timely and secure on all levels of activity.
- Information processing facilities: Verifies that the process is working correctly, timely and accurately, whether in normal or disruptive conditions.
- Systems development: To see if those systems that are under development are being created in compliance with the organization’s standards.
- Management of IT and enterprise architecture: Making sure that IT management is structured and processes in a controlled and efficient manner.
- Client/server, telecommunications, intranets and extranets: This spotlights telecommunication controls, such as a server and network, which is the bridge between clients and servers.All of this can be expedited with the help of IT project management software.
What Is an IT Auditor?
An IT auditor is responsible for inspecting the internal controls and risks associated with an organization’s IT infrastructure. Some of the main responsibilities of an IT auditor are identifying weaknesses, vulnerabilities and threats and suggesting solutions to prevent security breaches.
IT auditors help organizations meet security standards, obtain certifications and improve how data is managed. There are certifications for this skill, such as Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) and Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP).
IT Audit Process: How to Do an IT Audit
In a sense, an IT audit is a project and like any project, it involves planning, scheduling, reporting and tracking activities. Here’s a quick overview of each of the steps of the IT audit process.
1. Plan Your IT Audit
An IT audit is a thorough process so you need to plan carefully. Without a solid action plan, your audit might not achieve its key purpose which is to accurately find flaws, inefficiencies and vulnerabilities in the IT environment of your organization. To plan your IT audit, there are several steps you and your team should go through. Here are some of the most important of them.
- Select an IT auditor, it could be an in-house internal auditor or an external firm
- Set goals and objectives for your IT audit
- Define the scope of your IT audit
- Decide if your IT audit will be recurrent and if so, how often it will be conducted
- Define a timeframe for your IT audit as well as a detailed schedule to inspect each area of your IT department
- Establish roles and responsibilities for your employees as the audit is executed to make sure they’re on the same page
- Create an IT audit plan to make sure stakeholders understand the IT audit scope, objectives and schedule
2. Execute the IT Audit
Once you have a solid IT audit plan, you can move on to the execution phase of your audit. During this phase, team management is key to making sure your IT department and any other employees and stakeholders involved collaborate with the IT auditor so that everything goes according to plan and the IT audit can be completed on time.
Related: IT project management templates
3. Make IT Audit Reports
As explained above, an IT audit is a process that seeks to find inefficiencies, vulnerabilities, threats and opportunities for improvement for your business’ IT operations, so documenting these findings is key for success. Once the IT audit is complete, it is critical to create a thorough audit report that compiles all the observations and suggestions from the IT auditor. This is one of the most important steps of any audit, as the findings are only useful to the organization if they’re well documented.
4. Follow Up
Ideally, the IT audit report should be an informative document with lots of suggestions to improve how your company manages its IT practices. Now, it’s time to plan how to put the audit findings into practice by taking actions such as training employees, procuring assets and implementing IT risk management frameworks.

IT Audit Checklist
Now that we’ve defined the major steps of the IT auditing process, let’s review some of the key areas that should be inspected during an IT audit.
IT Security Controls
- Antivirus software
- Network firewall
- Passwords encryption
- Two-factor authentication
- Physical security measures
- Unauthorized access alerts
- Employee IT security training
Standards & Procedures
- Employees are required to sign IT security acknowledgment agreements
- IT assets are disposed of safely to avoid data breaches
- Documents with sensitive data are shredded or disposed of safely
- Data backups are done and reviewed frequently
- Data is backed up in multiple locations
- There’s a well-defined IT disaster recovery plan
Documentation & Reporting
- Security protocols are well-documented
- Security protocols are updated as IT infrastructure changes
- IT logs are safely stored and reviewed frequently
- IT incidents are documented thoroughly
Performance Monitoring
- Outage events are recorded
- Hard drive, RAM and cloud storage are monitored
- Network performance is measured consistently
- IT expenses are tracked and minimized
Systems Development
- There are clear guidelines for managing the system design and development process
- System testing protocols are established
- There’s a post-implementation review process in place
While the items outlined above are a good starting point, there are many more variables that you should consider when planning and executing your IT audit so that it adjusts to the particular needs of your organization.
IT Audit Best Practices
The process of conducting an IT audit is complex and touches on all aspects of your information system. There are overreaching general management issues and policies to consider. There’s also security architecture and design, systems and networks, authentication and authorization and even physical security. It involves continuity planning and disaster recovery, like any good risk management.
There are, too, some overriding best practices that can steer you through the maze, so you start and finish effectively. These five tips will help you conduct an IT security audit properly.
- Scope: By knowing the scope of the audit ahead of time, you’re more likely to have an audit that runs without problems. For one thing, you’ll want to involve all relevant stakeholders when planning. Speak to those who are working in the IT environment. They can help you understand what risks you’re looking to identify and understand the current capabilities of the system. This way you’ll have a better idea if there’s a need to adopt new technologies or not. Also, know the applicable laws and regulations to make sure you’re compliant.
- Outside resources: You might have a team assembled in-house who are able to run the IT security audit themselves or you might need to seek outside contractors to help with parts or the whole thing. This must be determined beforehand. You might have an IT audit manager or need to hire a consultant, who can then train the team on what to keep an eye out for in-between IT audits.
- Implementation: Know the inventory you have and put these systems down in a list organized by priority. Know industry standards, methods and procedures to make sure you’re keeping up with the most current practices. Evaluate your audit to see if assets are protected and risks mitigated.
- Feedback: IT audit reports can feel like they’re in a different language if you’re not an IT professional. For the audit to be effective, the audit must be clear to those who are decision-makers. The IT auditor should give the report in person and field any questions so that when done there is no question about the work and whatever vulnerabilities were discovered.
- Repeat: An IT audit isn’t a one-time event, of course, but in between audits there is still work to do. That includes offering recommendations going forward and using IT software that can automatically monitor systems, users and assets. It’s a good idea to have a plan set up to review applicable laws, regulations and new developments quarterly, as the technology space is notoriously fast-moving.
How ProjectManager Facilitates the IT Audit Process
When doing an IT audit, there are many tasks that probably require a team to execute. Sounds like a project. While there are software packages that are designed to monitor IT security, an audit is a different animal and can benefit from a project management software to control it effectively.
Every audit can be broken down into a series of tasks, just as you use a work breakdown structure (WBS) to take a large project and break it up into smaller, more manageable pieces. A task list can be prioritized and then that spreadsheet uploaded into ProjectManager, where it’s transformed from a static sheet to a dynamic tool.
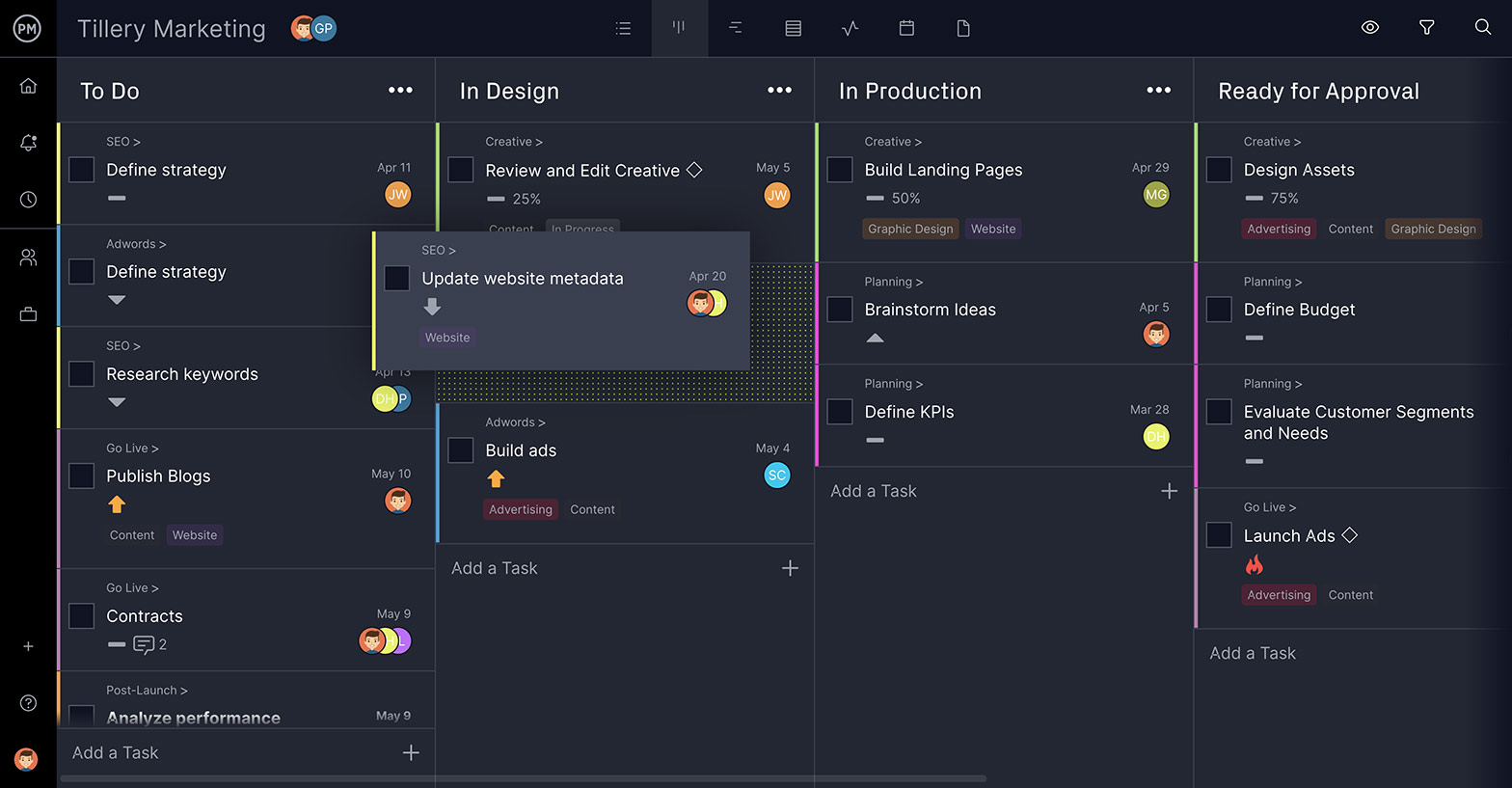
Visualize the Workflow With Kanban Boards
Once imported, the task list can be viewed in a variety of ways. There is the kanban view to manage workflows. The various tasks are individual cards, which are organized by columns that state whether the work is to be started, in progress or done. These cards can be assigned to one or more team members, who can comment directly on them to collaborate. Files and images can also be attached.
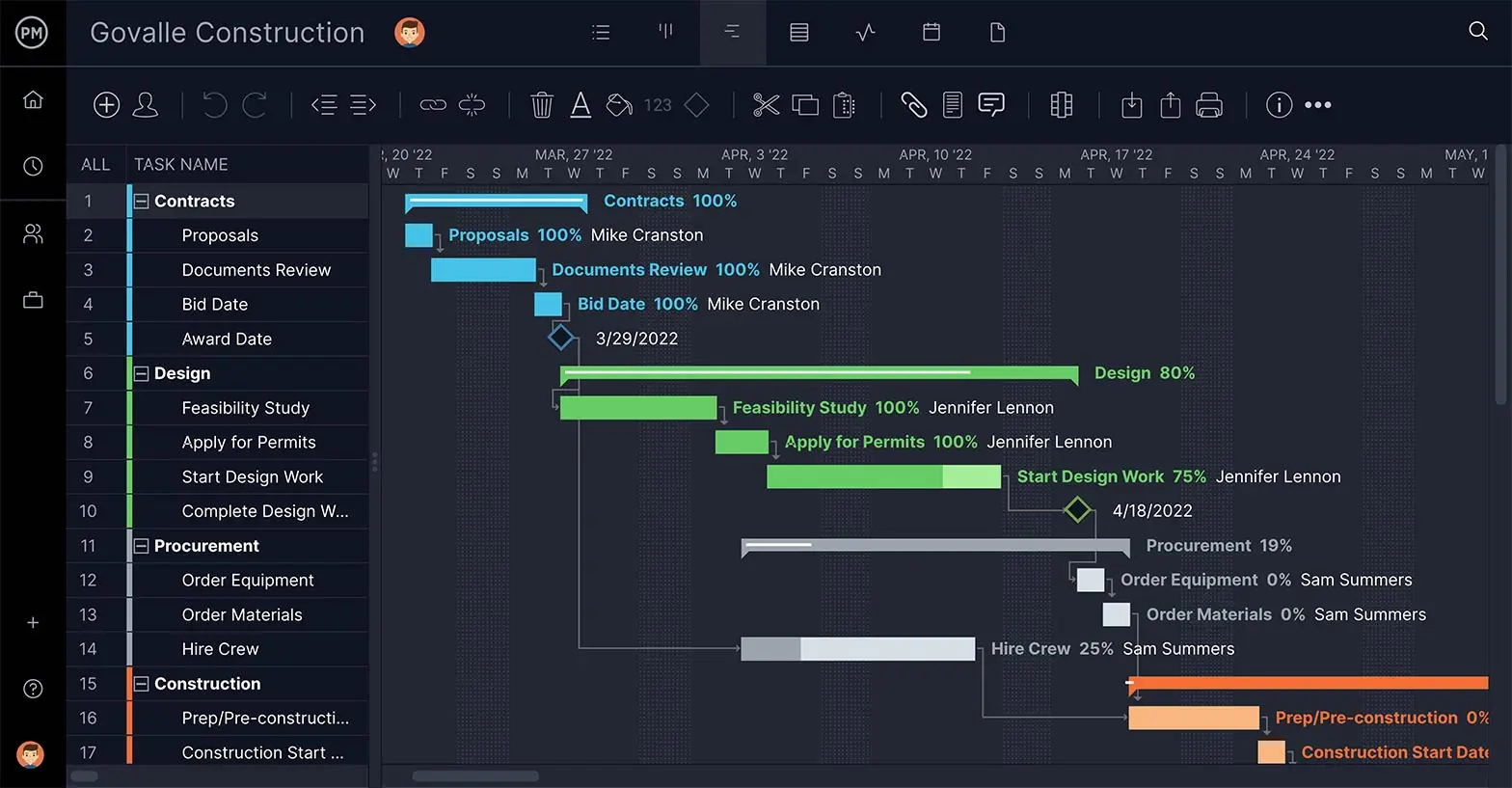
Make an Audit Schedule With Gantt Charts
Another view is the Gantt chart. This shows your task list to the left and populates those tasks across a timeline to the right. The tasks can again be assigned, collaborated on and tracked. ProjectManager is a cloud-based software, so all status updates are instantly reflected. Task dependencies can be linked to avoid blocking team members and if deadlines need to change that can be done with a simple drag and drop of the task timeline.
Project Dashboards for Monitoring the Audit
In terms of monitoring the progress of the IT security audit and reporting back to management, ProjectManager has a real-time dashboard. It keeps the project leader abreast of what’s going to and crunches the numbers automatically, displaying project metrics in clear and colorful graphs and charts. These can then be filtered to reflect the data you want and shared or printed out for a presentation.

ProjectManager also has many free templates to assist with various phases of any project. Our IT risk assessment template is a great place to start when doing an IT audit.
Information technology is part of almost every organization. The benefits are great, but so are the risks. ProjectManager is a cloud-based project management software that helps IT professionals manage the complex tasks involved in an IT audit. Try it free today with this 30-day trial.

