- What Is a Project Schedule?
- How to Make a Project Schedule: In-Depth
- How to Maintain Your Project Schedule During Execution
- What Are Project Scheduling Tools?
- Benefits of Online Scheduling Tools
- Must-Have Scheduling Software Features
- Creating a Project Schedule in ProjectManager
- Best Practices for the Project Scheduling Process
- Project Schedule vs Project Plan
- Project Scheduling Key Terms
- Get a Free 30-Day Trial of Our Project Scheduling Software
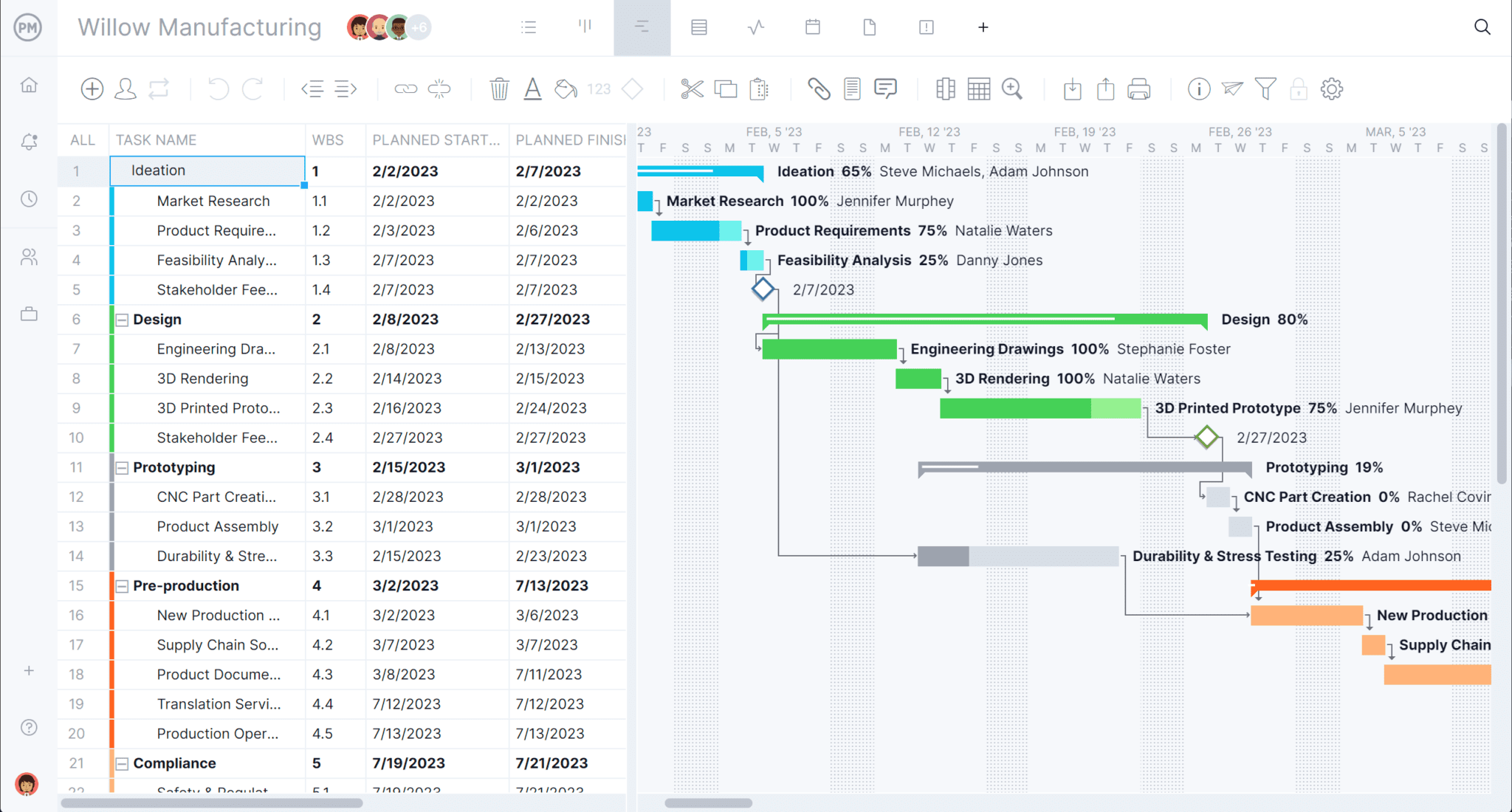
What Is a Project Schedule?
A project schedule is a timetable that organizes tasks, resources and due dates in an ideal sequence so that a project can be completed on time. A project schedule is created during the planning phase and includes the following:
- A project timeline with start dates, end dates and milestones
- The work necessary to complete the project deliverables
- The costs, resources and dependencies associated with each task
- The team members that are responsible for each task
Project schedules are created and tracked with project scheduling software, which has key features that allow project managers to monitor the progress of tasks, resources and costs in real time. They can also assign work, link dependent tasks, view dashboards, allocate resources and more.
ProjectManager, for example, has online Gantt charts for scheduling tasks and resources, but also team management features and reporting tools for a comprehensive project management platform.
What’s Included in a Project Schedule?
Project schedules are created during the project planning phase and are crucial to the creation of a project plan, where the schedule plan, schedule baseline, deliverables and requirements are identified. The project schedule is designed to guide the project team throughout the execution phase of the project.
Then, during the execution phase, the schedule baseline is compared against the actual project progress. The following are included in the creation of a project schedule:
- Deliverables
- Tasks
- Task start and end dates
- Task dependencies
- Project calendar
- Work packages
- Task duration and project timeline
- Budgets
- Resource availability
- Schedule risk analysis
Project Schedule Steps
When creating a schedule you can use a project schedule template, which offers project schedule examples and a project schedule spreadsheet for free. But a template can only take you so far. A project schedule is not just a standard timetable that works for every project.
There are different project scheduling techniques and project planning tools involved in the scheduling process. Also, every project has different resources, timetables, scope considerations and other unique variables that must be considered in the schedule management plan.
Using project management software integrates the schedule into other project management tools, such as Gantt charts, dashboards and reports to monitor progress, as well as kanban boards to manage workflows. Whichever path you choose, these are the steps to create a project schedule:
- Create the schedule plan for your project
- Define who has authority over the schedule
- Identify start and end dates for project activities and tasks
- Figure out task dependencies
- Sequence activities and tasks chronologically to create a project calendar
- Estimate needed resources and resource availability
- Determine duration of activities and tasks
- Build project schedule
- Monitor and control the schedule throughout the project life cycle
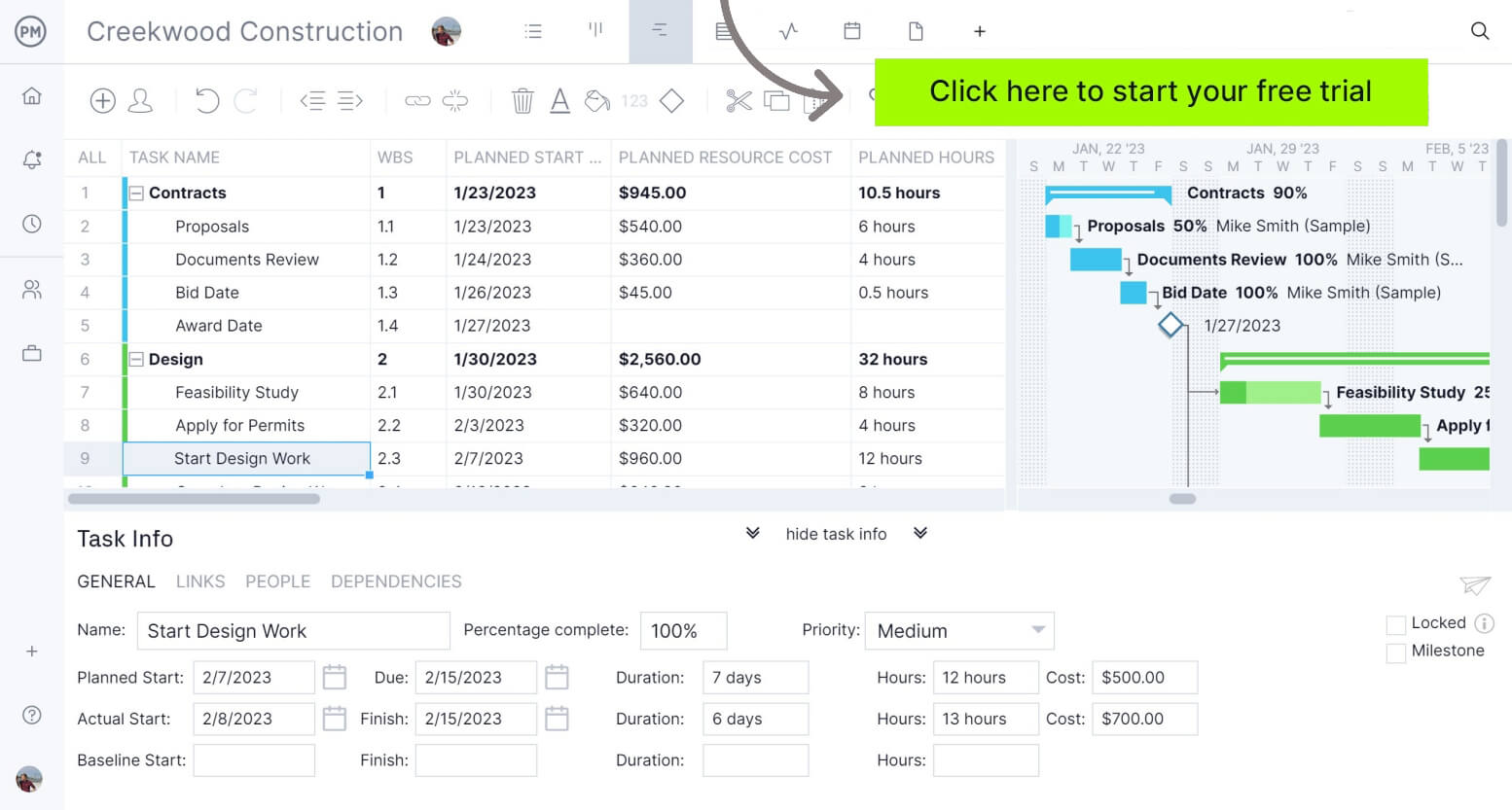
Free Project Schedule Template
Need help getting started with your project schedule? Try ProjectManager’s free schedule template and practice adding tasks, phases, dependencies, resources and more in a live Gantt environment.
On the left-hand side the various phases of the project are outlined. These can be color-coded to make it easier to distinguish one phase from another. Under each phase are the tasks associated with it, including assignees, due dates and other resources needed to execute the scheduled tasks.
The visual timeline to the right is where things get interesting. You can see the entire project in one place, dependent tasks can be linked and milestones added to indicate important dates.
What Are the Project Scheduling Techniques?
Estimating the duration of project tasks as accurately as possible is key to creating a realistic schedule. To do this requires the use of various project scheduling techniques.
Project managers can interview their team and other stakeholders to get their perspective on how long certain tasks can take, and can refer to historic data from similar past projects.
Additionally, project managers can use project scheduling techniques to increase the accuracy of their time estimates and minimize schedule risk. The critical path method (CPM) is an equation that shows the longest possible timeline for the project. The Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) also visualizes the flow of tasks for better estimates but shows task dependencies as well.
Project managers will also use schedule compression techniques such as project crashing and fast tracking which can reduce the schedule duration without impacting the project scope. Simulation, resource-leveling heuristics, creating a task list, using a project calendar and using a Gantt chart are all other tools that can help with estimation, collection and tracking of project tasks.
A work breakdown structure (WBS) shows how many tasks and deliverables there are to get to your final deliverable. It’s a network diagram that has your project goal on top with “branches” underneath that show all the steps needed to get you there. This tool makes sure you don’t leave out anything when devising your schedule. A workback schedule is another technique that allows you to break down the project scope and identify all the tasks, activities, deliverables and milestones.
Regardless of your preferred scheduling methods, you need a tool designed to accommodate them equally. ProjectManager’s Gantt charts allow you to create timelines, apply a work breakdown structure and automatically calculate the critical path. Need to cut down on the white noise and view specific information? Filter for exactly what you want to see, whether it be incomplete tasks, overdue tasks, tasks assigned to certain team members or anything else you like.
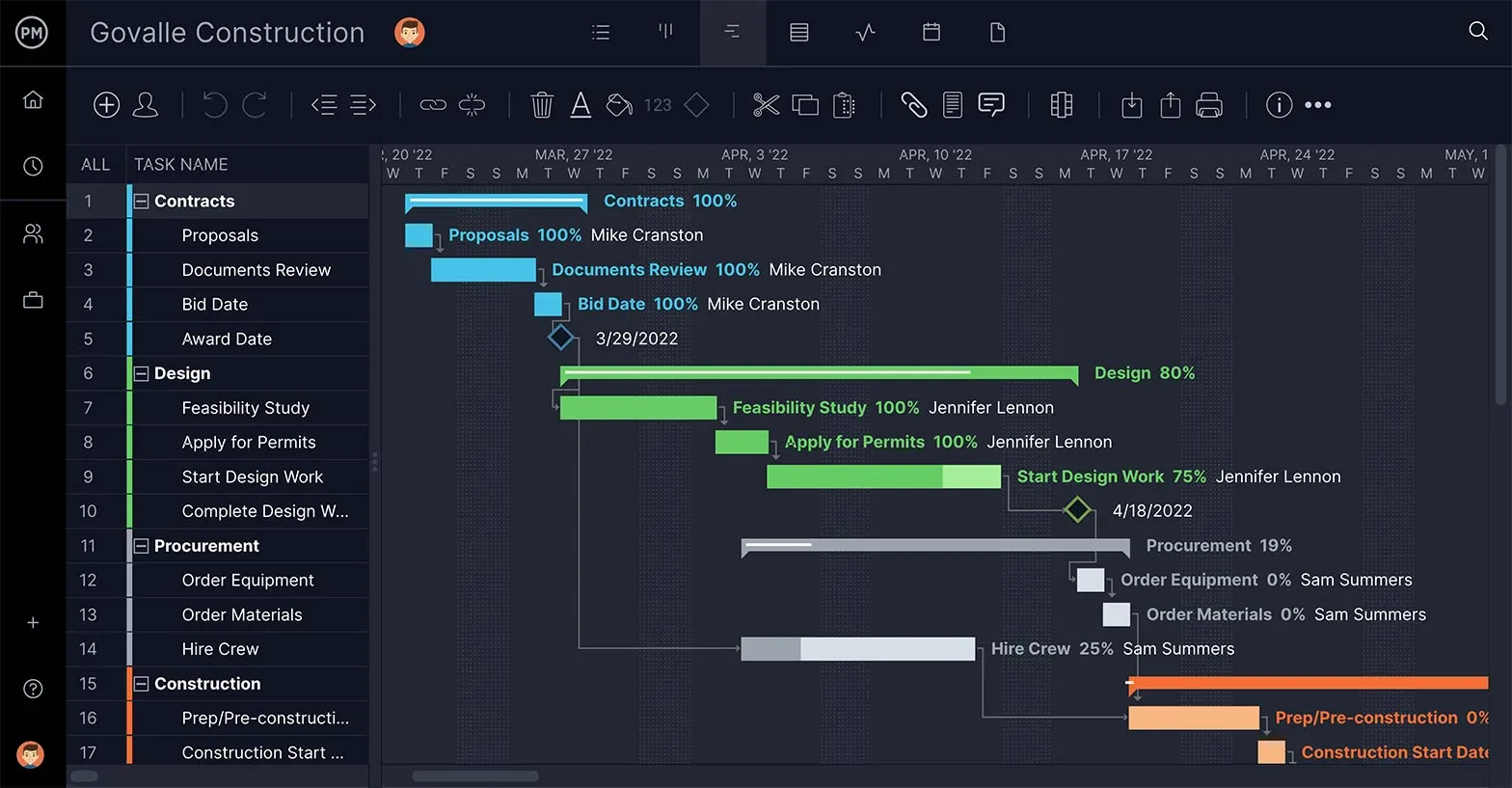
How to Make a Project Schedule: In-Depth
Project scheduling occurs during the planning phase of the project life cycle. When beginning to put together a schedule for your project, you should ask yourself four things to start:
- What needs to be done?
- When will it be done?
- Who will do it?
- Where will it be done?
The answers to these four questions will greatly inform your project schedule moving forward, as you’ll use this information to plan start and end dates, link activities, set the duration, create milestones and manage resources.
Follow these steps to create a project schedule of your own!
1. Create the Project Scope
The project scope statement is created during the initial planning. It’s a document that contains the specific goals, deliverables, features, budget, etc of your project. All of the tasks needed to complete the project successfully are listed here (which requires understanding the stakeholder’s requirements.)
Be thorough when putting a task list together, you don’t want to leave anything out. By using a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) you can organize these activities and lay them out in order of completion. Understanding task dependencies and their sequence are very important for schedule management.
2. Establish the Sequence of Tasks
Tasks are the small jobs that lead to the final deliverable, and it’s fairly crucial to map out the sequence of those tasks before diving into them. Oftentimes a task will be dependent on another to start or finish. You don’t want to get halfway through a task before you realize you can’t complete it due to hanging objectives.
3. Group Tasks
Once you’ve collected your tasks and have them in proper order, you should take the opportunity to divide your tasks by importance. You need to know which is critical to the project implementation schedule and must be done first and those less important that can be done if there’s time. You could use a priority matrix to facilitate this process.
Then, break your tasks down with milestones that relate to the five project phases—initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and close. Organizing your tasks with milestones makes it easier to track progress, and gives your teams a sense of accomplishment that boosts morale and productivity.
4. Link Task Dependencies
Some tasks can be done simultaneously, but some tasks are dependent on others to start or finish before they can start or finish. These task dependencies must be mapped out in your schedule to keep you aware of them, or you risk bottlenecks and blocking your team.
5. Find the Critical Path
The critical path is a method for scheduling tasks in a project to find those which are critical to the success of the project. This allows you to make smart choices about tasks that can be ignored if time and costs become constrained. This method is commonly used for schedule risk analysis. Software that can find the critical path for you can make this step a lot easier.
6. Assign Resources
Resource management and project scheduling are closely related. Every task on your schedule should have the related resources and costs associated with completing it. Tasks aren’t done on their own, and without mapping the resource availability to each task you’re in danger of going wildly over budget. With resources attached to tasks, you can more accurately plan your team’s time and keep their workload balanced.
How to Manage Your Project Schedule During Execution
Once you’ve got all the pieces of your schedule together, the last thing you want to do is manually punch it into a static document like a Google sheets or a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. A schedule maker can automate much of the process for you.
There are project scheduling tools on the market that are great for simple scheduling duties, but when you’re leading a project, big or small, you need a tool that can adapt to the variety of scheduling issues you’re going to need to track. Watch the video below to learn how scheduling software can help you lead your project to a successful conclusion, or continue on to read our full walkthrough.
What Are Project Scheduling Tools?
Project scheduling tools are used to help managers organize and execute their project’s tasks and resources within a given budget. Software offerings range from rudimentary to sophisticated and provide users with a wide spectrum of features that facilitate the scheduling of their project.
Software devoted to scheduling a project can assist in the larger role of planning and estimation of the duration of each task. Outside of scheduling, software can also include tools that manage costs, budget, resource allocation, collaboration, communication and reporting.
Benefits of Online Scheduling Tools
Using online scheduling software means that project managers can make data-driven time management and resource management decisions. When they see that there’s a bottleneck or some block preventing team members from moving forward on their tasks, they can quickly reallocate resources and keep the project on track.
Managers and teams can work better together with the right online scheduling software and manage resources and budgets to keep the project running smoothly. Those are the big benefits, but not the only ones when using online scheduling software. Here are others:
- Build detailed plans for your projects
- View all your work on task lists and project calendars
- Get status updates to stakeholders
- Create task lists for yourself and your teams
- Manage start and end dates for your tasks
- Manage workload and reallocate work
- Monitor performance in real time
- Edit with drag-and-drop scheduling
Must-Have Scheduling Software Features
Scheduling software that has the following features will give you the most power to effectively manage your project.
Get Tasks Organized on a Timeline
Projects have lots of tasks, and they need to be organized on a timeline to create a workable schedule. Gantt charts are a visual tool that can collect all your tasks, prioritize them, link those that are dependent on one another and even break the larger project into manageable phases.
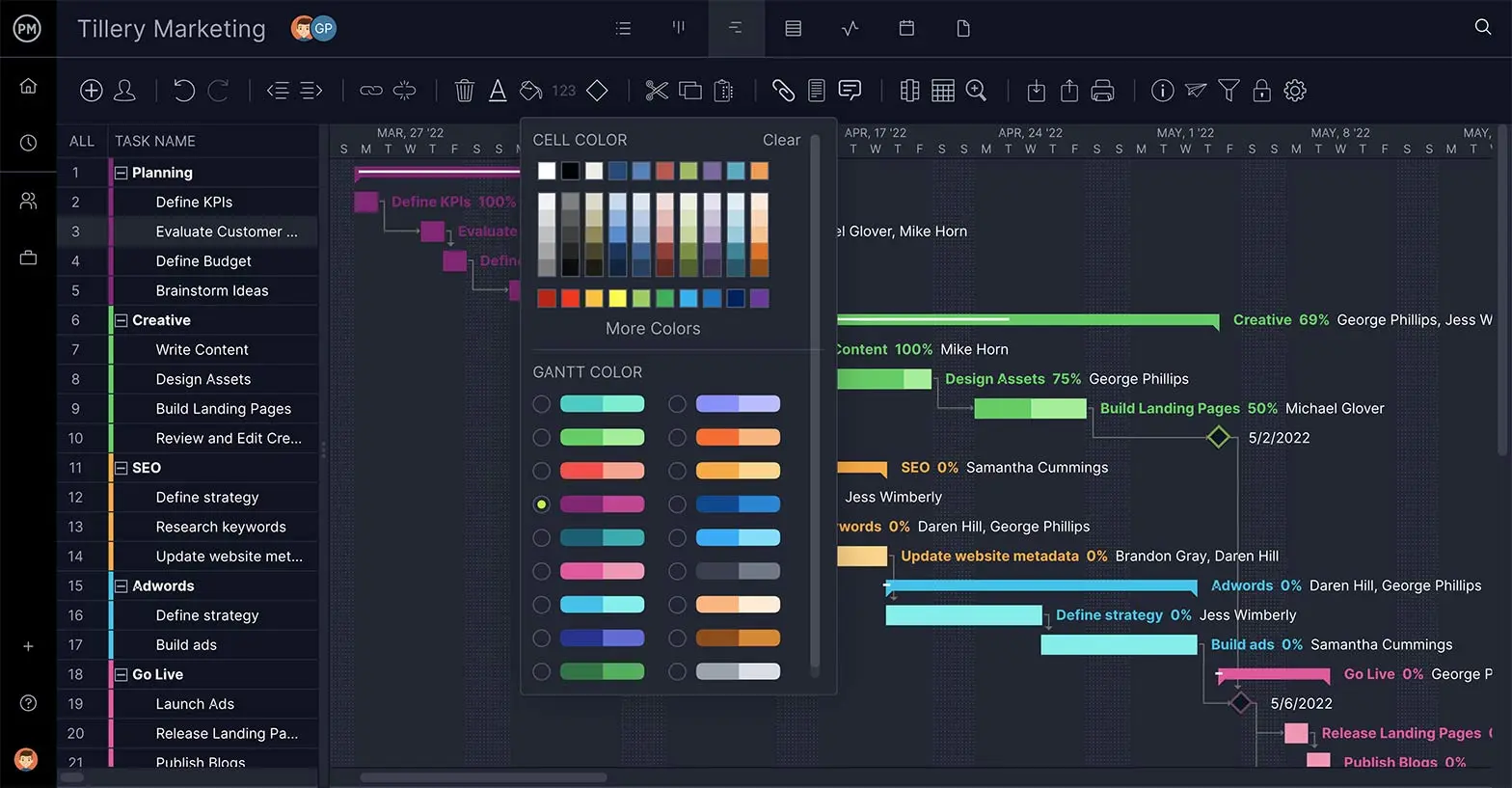
Monitor High-Level Progress
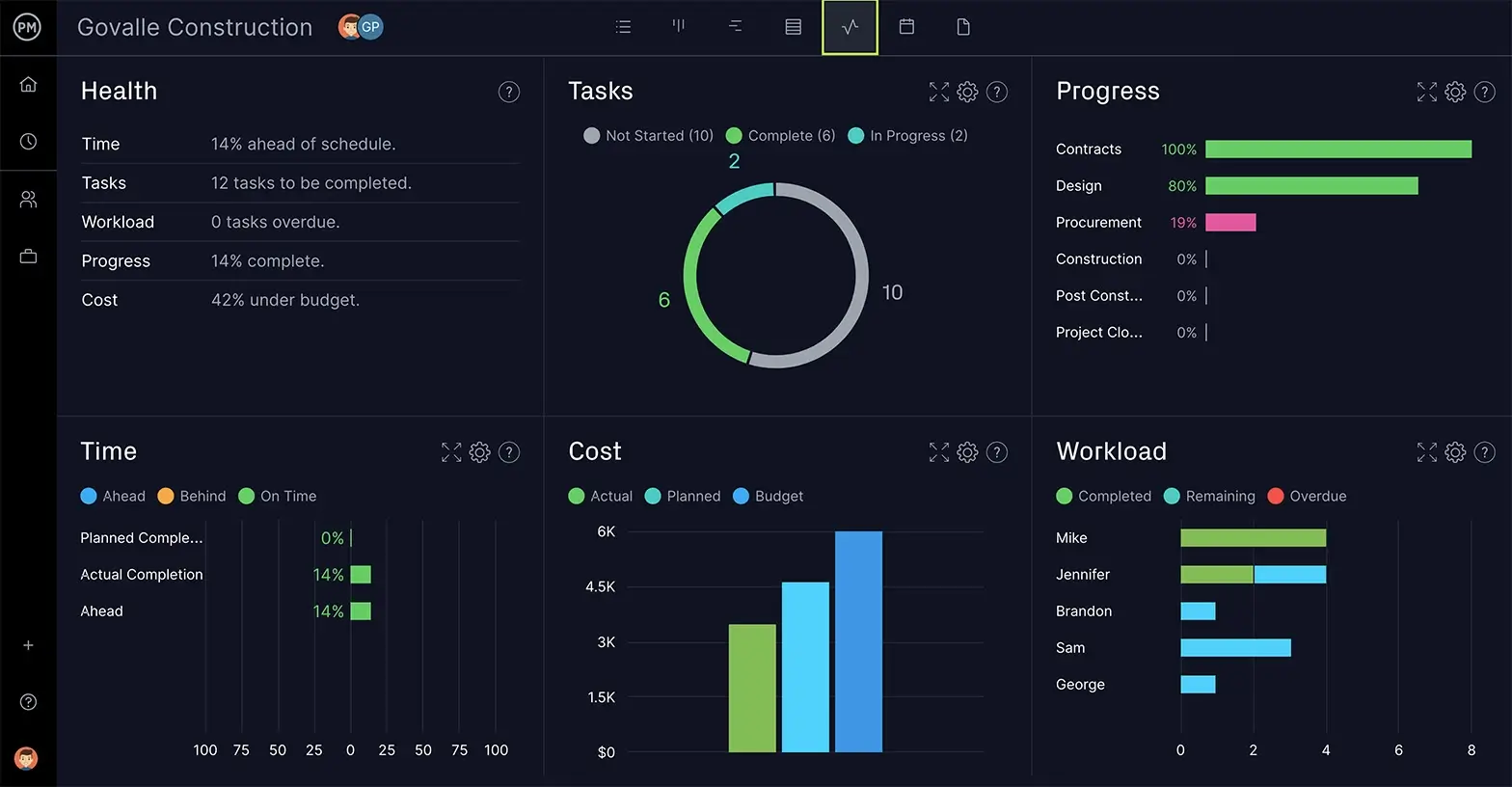
Once your project schedule is executed, you need to keep a close watch on performance to stay on track. Dashboards are a window into progress that act like an instant status report, showing percentage of tasks complete, project variance, workload and more.
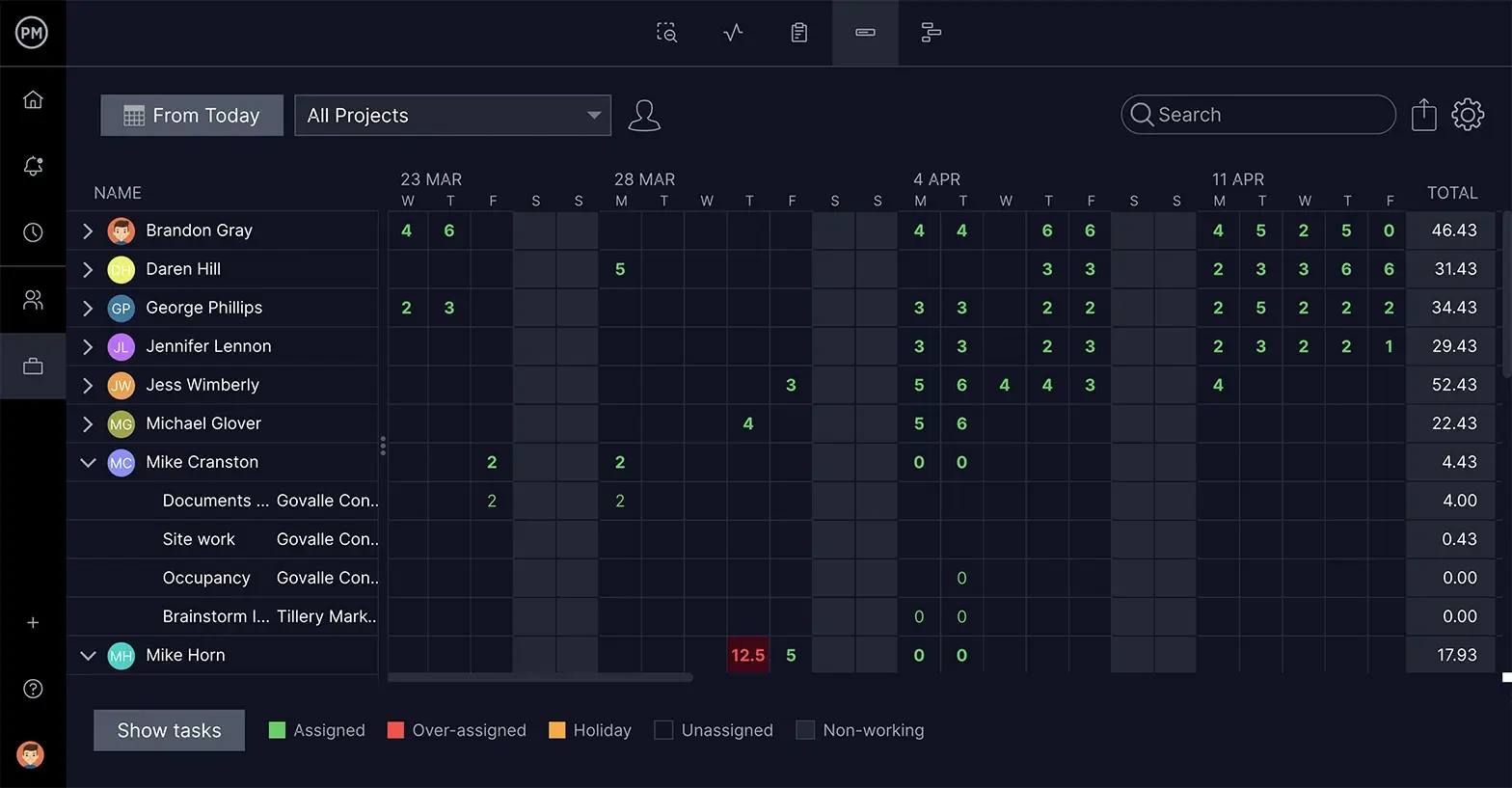
Balance Your Team’s Tasks
Keeping on schedule means allocating your resources smartly. Knowing how many tasks your team is assigned is crucial. If some are overallocated and others have too few tasks, the schedule suffers—as well as morale. You want to be able to reallocate their assignments.
Generate Fast and Insightful Data
Stakeholders have a vested interest in the success of a project, and must be regularly updated on its progress. You do that by quickly creating reports on tasks, costs, project variance, etc., and sharing them at stakeholder presentations. Filtering shows the information you want to see.
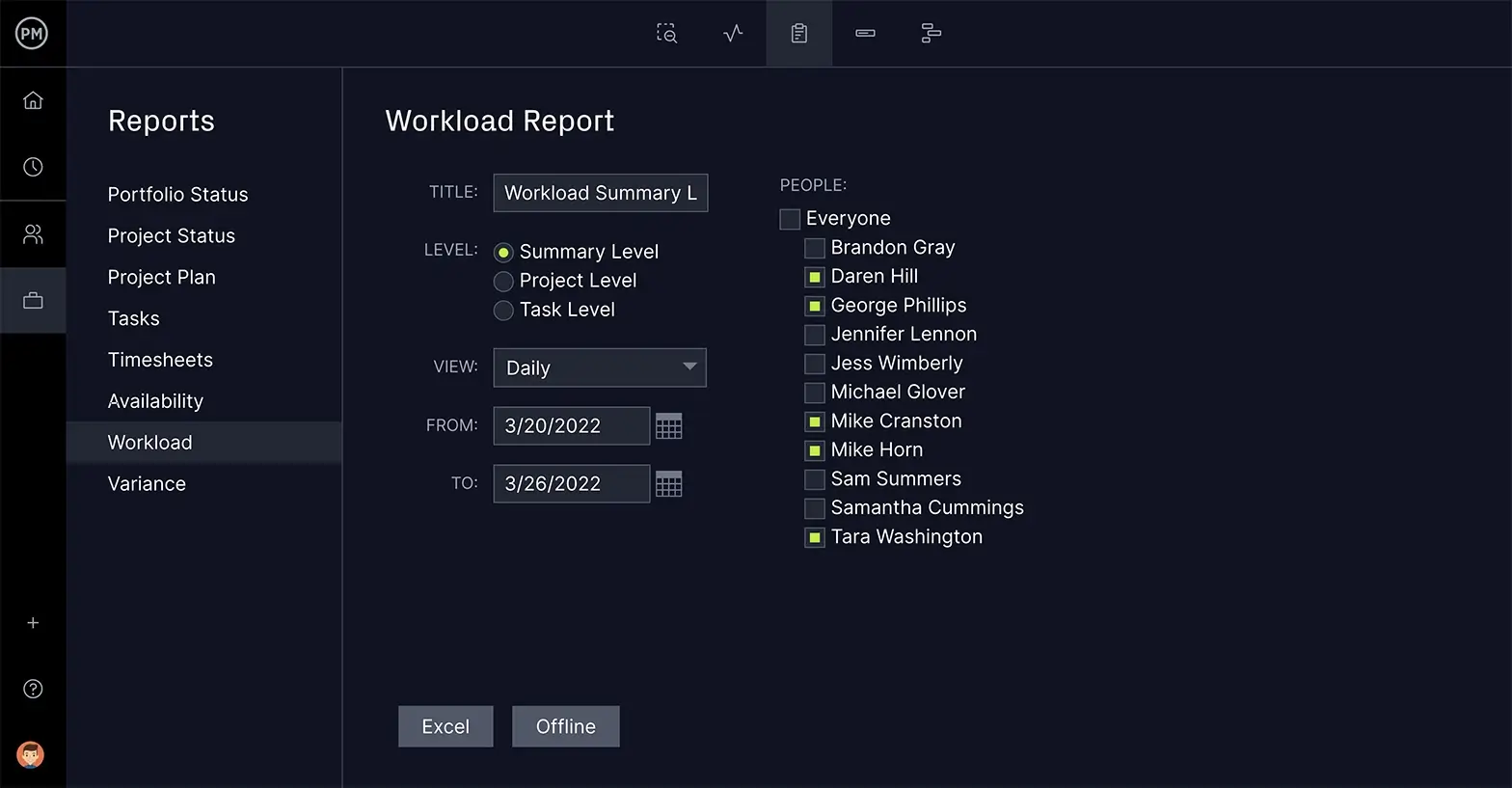
Facilitate Teams to Work More Productively
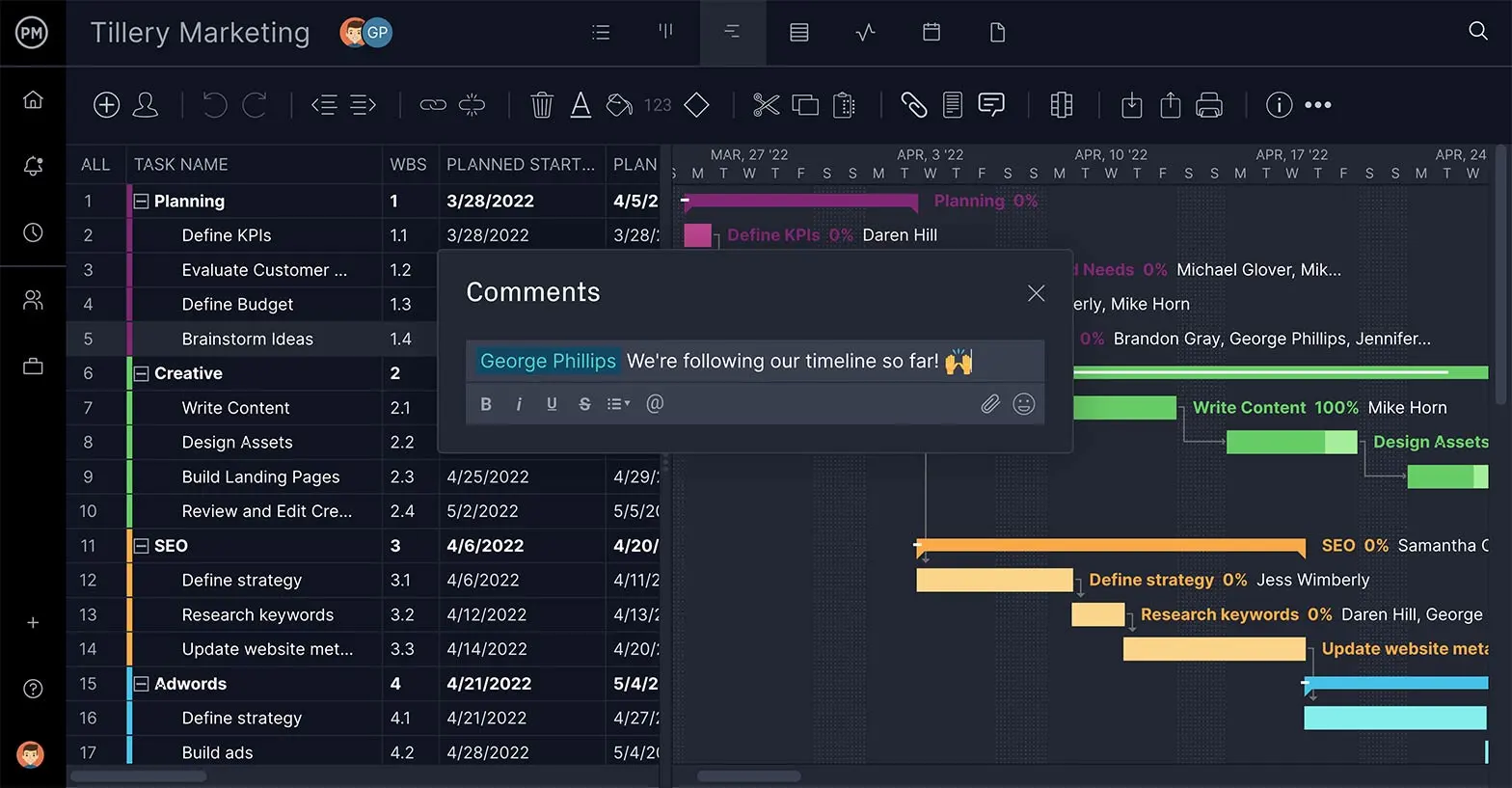
Teams need the right tools to execute the schedule on time and within your budget. Getting them to work better together is important. Look for features that allow team members to comment at the task level, attach files and share data with each other.
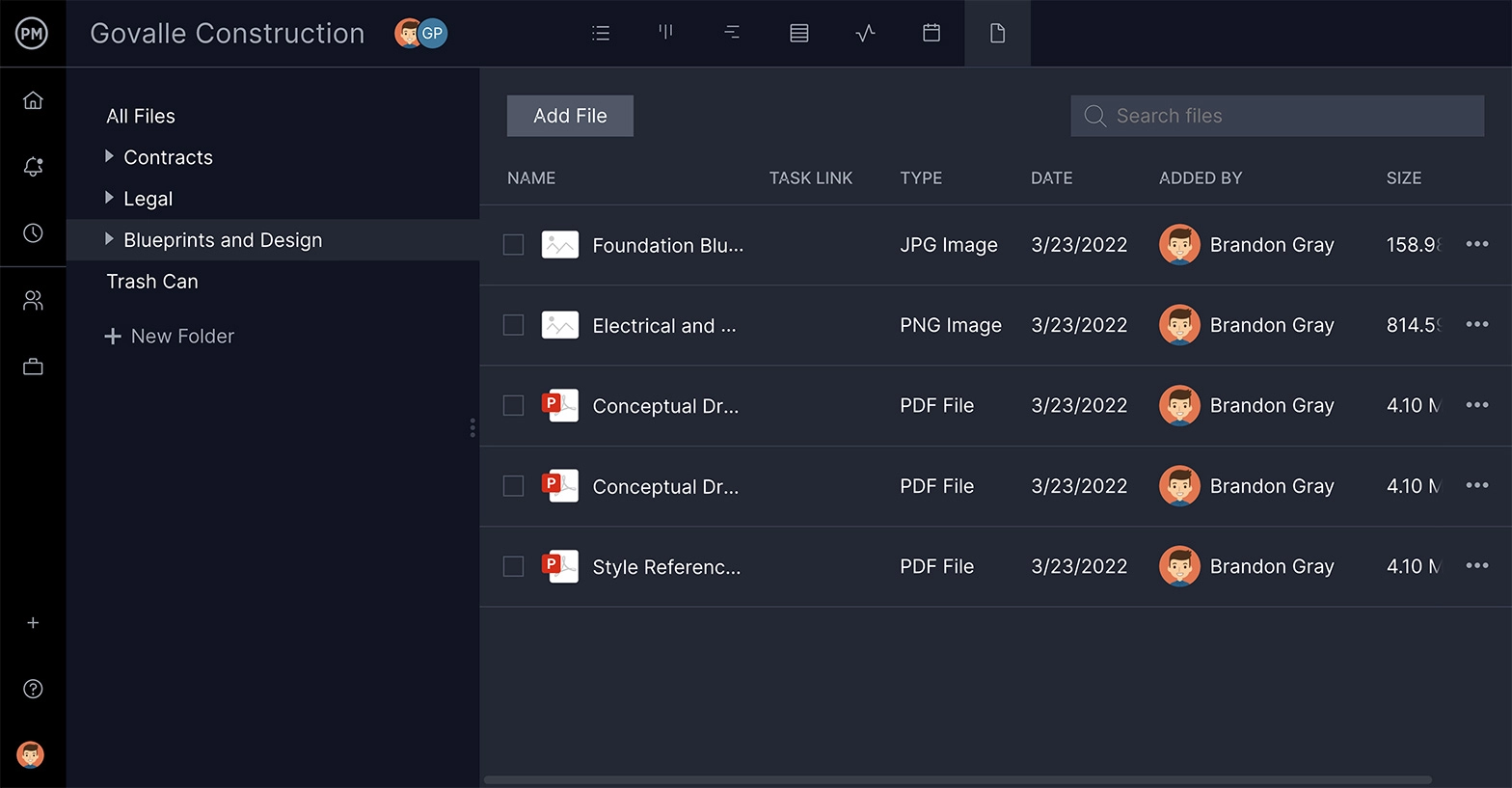
Have a Centralized Repository
Projects have a lot of paperwork. These documents are referred to throughout the life cycle of the project, and need to be easily accessible. Having a scheduling tool with unlimited file storage means you can keep everything in one place, and get to it fast when you need it.
Creating a Project Schedule in ProjectManager
Project scheduling software organizes your tasks on a timeline, considers the resources you have to complete the project and manages all those parts to keep the project on track.
ProjectManager is an award-winning scheduling software that integrates plans, timelines, budgets, communication and more to give you greater control over your project schedule. Sign up for a free 30-day trial of our software, and follow along to build an ideal project schedule.
Initiate Your Project
Set up the project before you start scheduling. In this initial phase, you set up your schedule plan, budget, resource schedule and the general timeline in which you have to produce your final deliverable.
Add the budget to create a baseline to compare to what you actually spend when executing.the project.
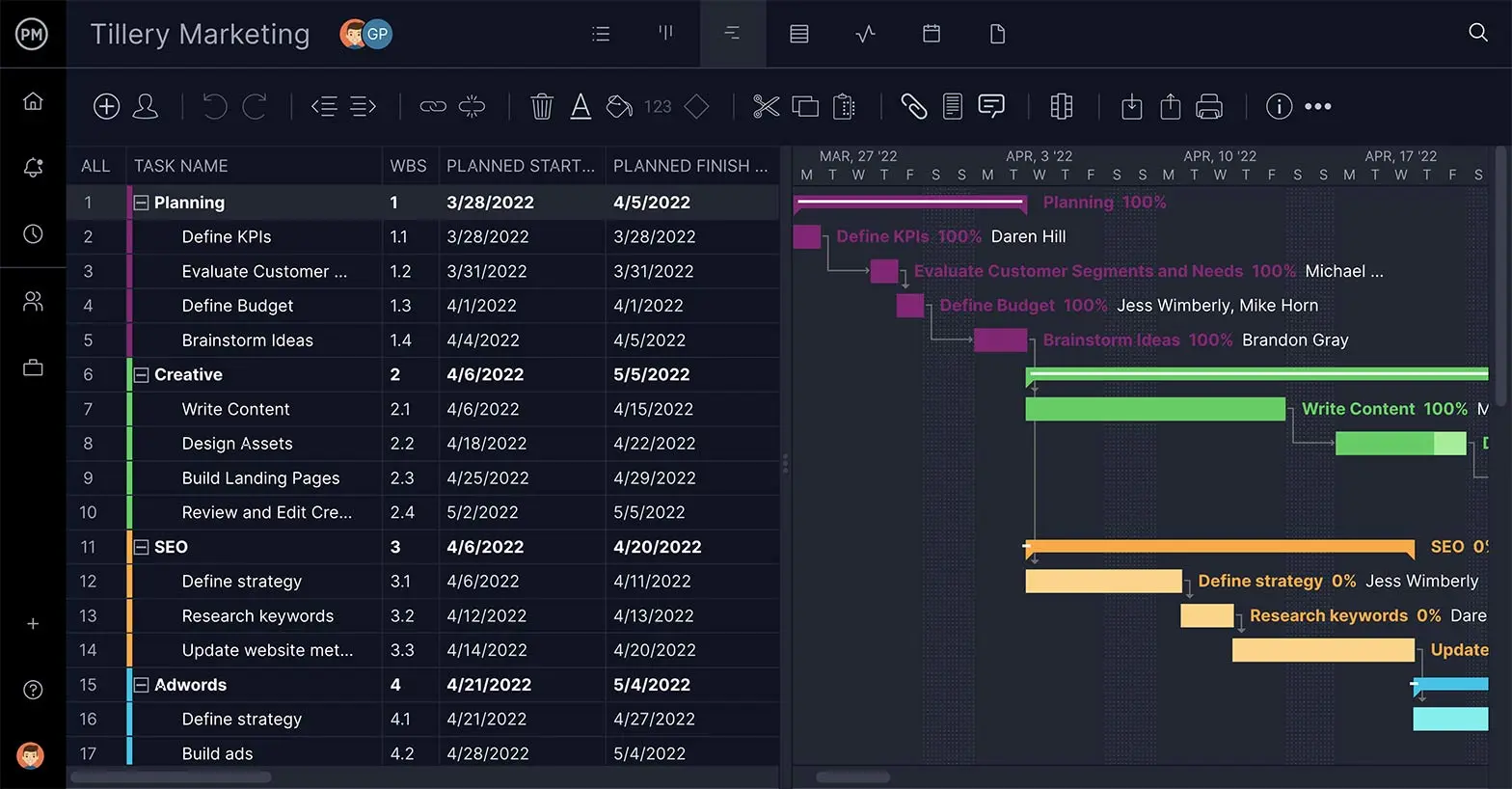
Define Tasks
Project scheduling is all about managing your tasks. As we covered earlier, tasks are the small jobs that lead to your final deliverable. Defining those tasks is the first step towards proper project management.
Import a task list from any spreadsheet, or use our built-in templates to get started. Add durations and due dates to those tasks to set them on a timeline on the Gantt.
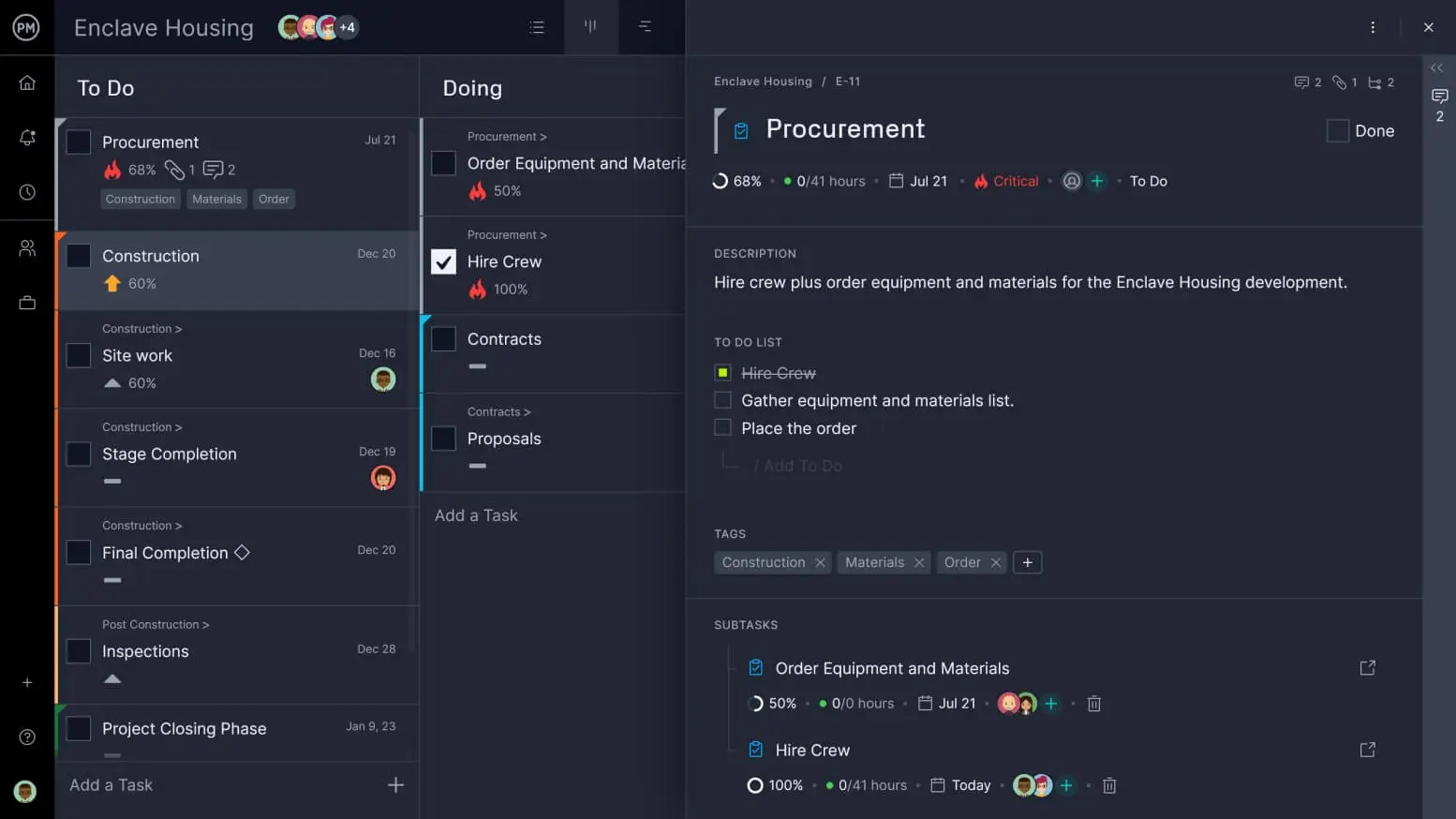
Block Calendar
ProjectManager allows you to manage your project calendar in real time. Take note of the dates that your team can or cannot work. These are your holidays, paid time off and other such dates that must be established before you can create your schedule.
Set holidays in the software, both global and local, to know your team’s availability. This is most helpful in managing remote teams. Outlining your typical working days is the best first step if you don’t have the other information readily available.

Set Task Dependencies
Avoiding bottlenecks and getting the work done on time are the primary reasons you’re thoroughly scheduling your project. You’ll want to link dependent tasks to ensure the work flows smoothly.
Connect the dependent tasks in your project by dragging one task on the Gantt onto the other. A line will appear, and from there, you can set what type of dependency these two tasks have.
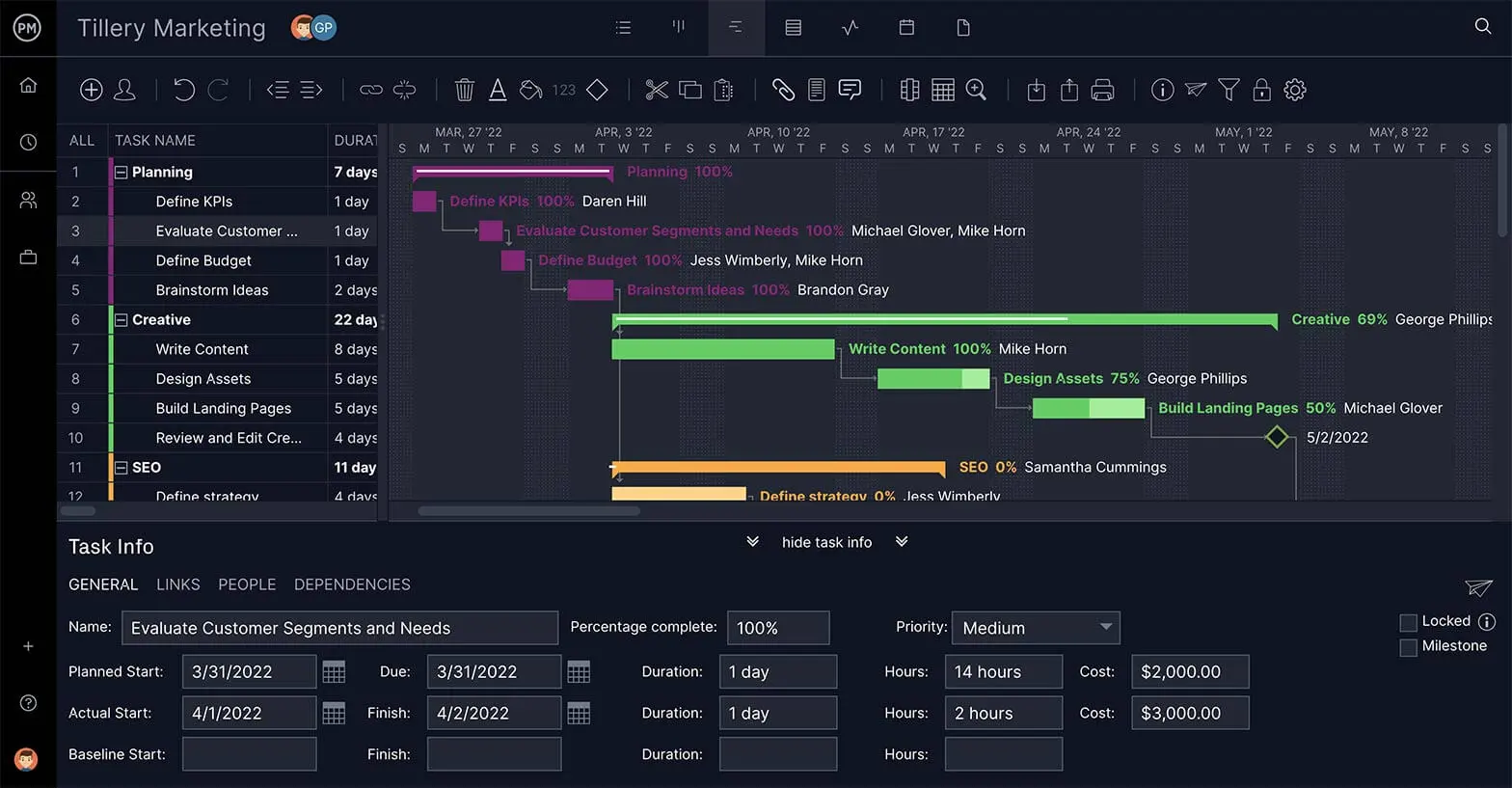
Assign Team
Teams are your most valuable resource. They do the work that gets the project to the finish line. For optimal efficiency, you need to get the right team member working on the right set of tasks.
Assign team members tasks from any of the multiple project views. For further direction, you can attach detailed descriptions, priority levels and costs associated with tasks to help your team track and complete them.

Monitor Progress
Once the schedule is set and the project is in the execution phase, managers will want to stay attuned with what’s going on without getting in the way of their team. Tracking project metrics allows you to catch issues and resolve them before they become projects.
Get a high-level view of the project with our real-time dashboard. We collect project data on time, cost, workload and more, and automatically calculate and display it in colorful, easy-to-read graphs and charts.
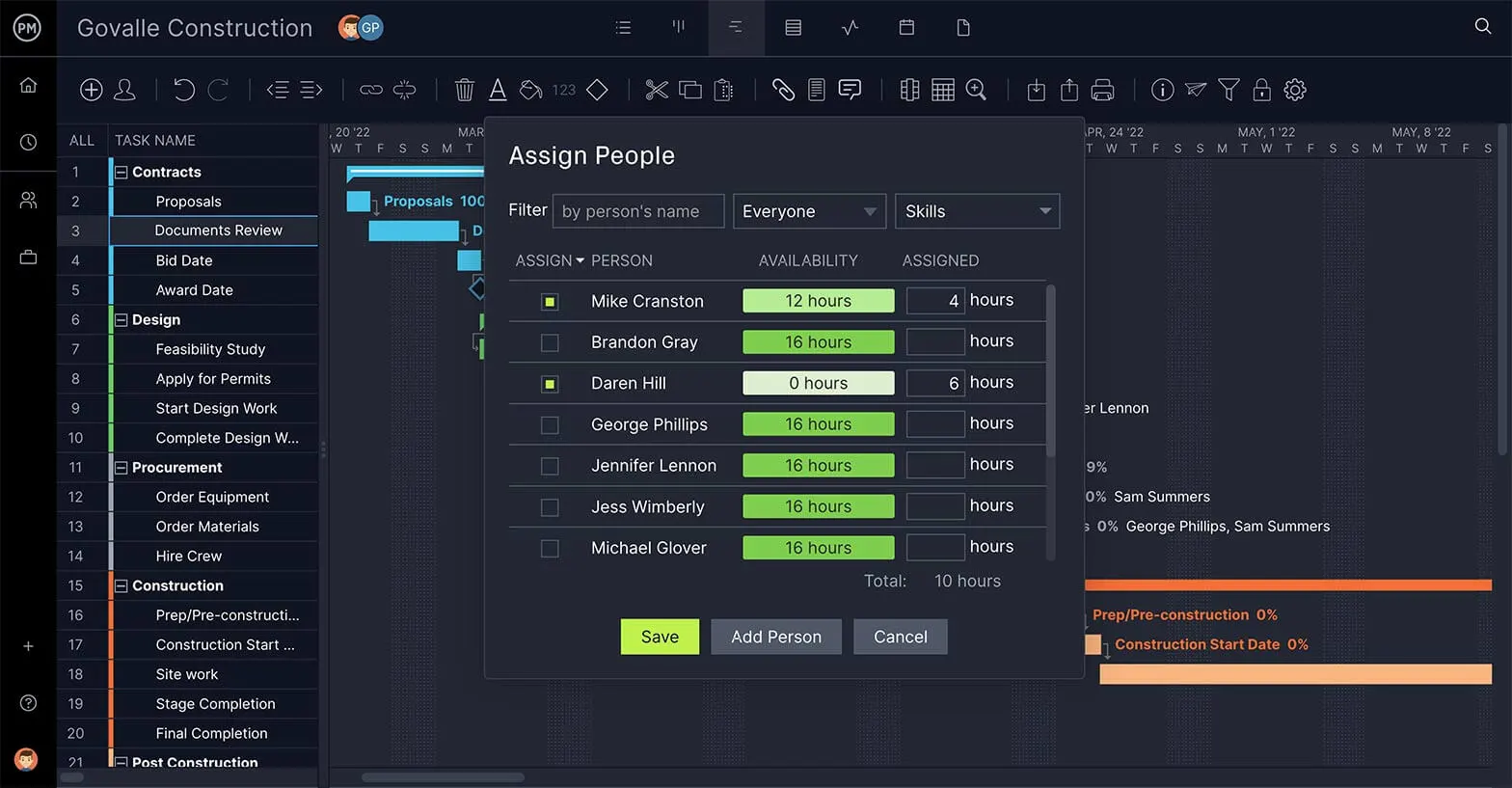
Manage Resources
Knowing your resources and keeping them balanced leads to a more productive and happy project team.
Use our workload page to see how many tasks your team is assigned. The color-coded chart makes it easy to see who is overallocated, and you can reallocate their workload without leaving the page.

Adjust Plan
Schedules are living documents. As internal and external forces play on a project, you need a fast and easy way to adapt. Being flexible helps you prevent slippage.
Drag and drop tasks to new start or end dates on our online Gantt chart to easily edit your schedule. All changes are instantly reflected throughout the software.

Keep Stakeholders in the Loop
Stakeholders are the people with a vested interest in the project. They need to know what’s happening, and keeping them informed of your project progress is one of your key responsibilities.
Generate reports on project variance, tasks and more with a single click. You can quickly filter through results when presenting the report to stakeholders to assist in responding to their questions.

Best Practices for the Project Scheduling Process
Keeping your project on track and within budget requires a good schedule. That means creating a schedule that is both reliable and that meets the requirements of your project. To make sure your schedule is the best it can be, follow these best practices.
Thoroughly Collect Project Tasks
The last thing you want is to miss a critical task after you’ve created your project schedule. Making sure every task is accounted for and lands in the right place to get the project done on time is hard enough, without trying to squeeze in tasks missed. A work breakdown structure is a great tool to make sure you capture every step on the road to your deliverable.
Be Realistic
When developing your project schedule, it’s important to set reasonable durations for your tasks. It should be measurable, of course; short, if possible, but with room for changes if needed. To do this, you need to take a deep look at your resources and your team’s capacity to complete the work. The more you do this on the front end of a project, the less issues you’ll have once it starts. Remember that you can use project management tools and techniques such as the critical path method (CPM) or PERT charts to help you estimate time more accurately.
Have Float in Your Schedule
Float is the amount of time a task can extend before it negatively impacts the final deliverable. You want to have some amount of float in your schedule to give you the wiggle room you’ll need as changes occur. But you don’t want too much float! That’s usually an indication that there is something amiss with your schedule.
Constantly Assess the Critical Path
The critical path is the way to see which of your tasks are essential to reaching the final deliverable, and which can be sidelined if time and cost become issues by charting the project’s earliest possible completion. But know that the critical path can change during the execution of your project, so you need to go back and check it regularly.
Keep Track of Project Scope
Things change is a project. That’s unavoidable. Not responding to these changes, however, is irresponsible. Monitoring your project scope, and adjusting tasks and schedules to keep your project on track, is what managing a schedule is all about. Take note of how scope changes impact your project timeline, and if the change gets in the way of meeting your final deliverable.
Project Schedule vs Project Plan
To wrap this up, we’ll end with some disambiguation between two related concepts; though related, a project schedule and a project plan are two different things. The project plan is the larger, grand-scheme blueprint on how the project will run. The project schedule focuses on the details on how that will get done.
The project plan is an outline that explains how the project will be managed. The project plan comes first, and the project schedule often falls under its larger project umbrella. You can’t create a project schedule without first having the large strokes of the project painted out in your project plan. Once the plan is approved, then the schedule can be added, with specific dates, duration, assignments, resources, etc.
The project schedule is made up of the specific tasks and due dates for each. It’s a timeline for the project for when the tasks will be started and completed. The schedule is more an estimation based on historical data, experience, etc. The schedule is fluid, and changes throughout the project. The plan remains the same. It defines the project goal, scope, resources needed, costs, etc. Only once these have been established can work on a schedule begin.
Another difference between the project plan and schedule is that the plan doesn’t necessitate the use of project management tools. Since the project plan is mostly a series of documents, you can just use a word processing program. However, project schedules usually run on project management software tools, with features such as Gantt charts.
Project Scheduling Key Terms
- Project Scheduling: Project scheduling is a project management process that consists of creating and managing a schedule to organize the tasks, deliverables and milestones of a project on a timeline. The project schedule defines the duration, start and end dates for activities and is used by project managers for resource management, task management and team management purposes
- Schedule Plan: A schedule plan or schedule management plan, is a component of the project plan that defines how the schedule will be developed, monitored and controlled. It also establishes the scheduling methodology and scheduling tools used to develop the project schedule. The complexity of the schedule plan varies depending on the project. The schedule plan is also referred to as the schedule management plan.
- Schedule Baseline: A schedule baseline is the approved version of the project schedule in the schedule plan. Once the project execution phase starts, the actual start and end dates of tasks will be compared to those established in the schedule baseline to measure performance and keep the project on track. The project schedule may differ from the schedule baseline because it changes as the project progresses.
- Schedule Performance Index: The schedule performance index is part of earned value management and its a measurement that lets you know whether you’re on or behind schedule.
- Schedule Variance: Schedule variance (SV) measures whether a project is on track by calculating the difference between actual progress against your projections.
- Resource Schedule: Consists in including resource availability and capacity planning considerations when developing a schedule. That means planning tasks on a timeline based on the resources and constraints associated with each.
- Project Calendar: A project calendar establishes the working days and hours that are available for scheduled tasks. It allows project managers to make schedule management decisions based on the time available on the calendar. A project calendar is part of the schedule plan.
- Schedule Crashing: Schedule crashing is a project scheduling technique that consists in shortening the project schedule duration by expediting the execution of critical path activities by adding more resources, such as team members or equipment. The goal is to reduce the schedule duration without affecting the project scope.
- Priority matrix: A priority matrix is a time management tool that allows project managers to prioritize tasks by evaluating the impact and effort associated with them. It’s similar to the Eisenhower matrix in terms of structure, but the priority matrix scales and quadrants are designed for project management.
- Workback Schedule: A workback schedule is a project scheduling technique that allows project managers to break down the life cycle of a project by analyzing its timeline in reverse order. Similar to reverse engineering, this process allows them to have a different perspective about the project’s stages, tasks, deliverables and milestones.
Get a Free 30-Day Trial of Our Project Scheduling Software
Scheduling is one of the more difficult jobs in project management, but coordinating delivery dates on your estimates can be streamlined and made more efficient when you employ the tools in ProjectManager, a cloud-based software.
From interactive Gantt charts, resource and workload management that can be easily integrated to a real-time reporting dashboard, you’ve never had a tighter hand on your project schedule.
See why tens of thousands of project teams use our tool to keep on schedule. Take a 30-day free trial of our software today to try these powerful tools for yourself.
Project Scheduling Resources
Software
Templates
Articles
- Project Management Trends (2022)
- 6 Tips for Better Schedule Management
- How to Create a Project Management Schedule (Example Included)
- The Ultimate Guide to the Critical Path Method
- The Ultimate Guide to Gantt Charts
- How to Make a Construction Schedule
- How to Schedule Multiple Projects
- ¿Cómo Hacer el Cronograma de Actividades de un Proyecto?
- Wie erstellt man einen Projektzeitplan?
- O que é um cronograma do projeto?
Start your free 30-day trial
Deliver faster, collaborate better, innovate more effectively — without the high prices and months-long implementation and extensive training required by other products.
Start free trial