IT change management is a structured approach to handling changes in an organization’s IT environment. Proper IT change management ensures that modifications to systems, applications or infrastructure are implemented with minimal disruption. By establishing standardized procedures, IT teams can manage risks, maintain compliance and keep services running smoothly. Understanding IT change management is crucial for organizations aiming to improve operational efficiency, reduce errors and enhance communication across IT and business teams while aligning changes with overall business goals.
Implementing IT change management allows organizations to track changes systematically, document decisions and measure outcomes. This improves accountability and helps teams respond to incidents faster. By using IT change management, organizations can anticipate potential issues, reduce downtime and ensure that changes are tested, approved and communicated effectively across stakeholders.
What Is IT Change Management?
IT change management is the process of planning, implementing and reviewing changes to an organization’s IT systems in a controlled and structured way. It minimizes risk to critical systems while ensuring that changes are executed efficiently. This includes tracking requests, analyzing potential impacts, scheduling modifications and documenting outcomes to maintain accountability and compliance.
Project management software greatly enhances the IT change management process by centralizing requests, providing automated workflows and offering real-time visibility into change status. Teams can assign tasks, set approvals and monitor deadlines, ensuring that changes follow standard procedures and are implemented smoothly across departments.
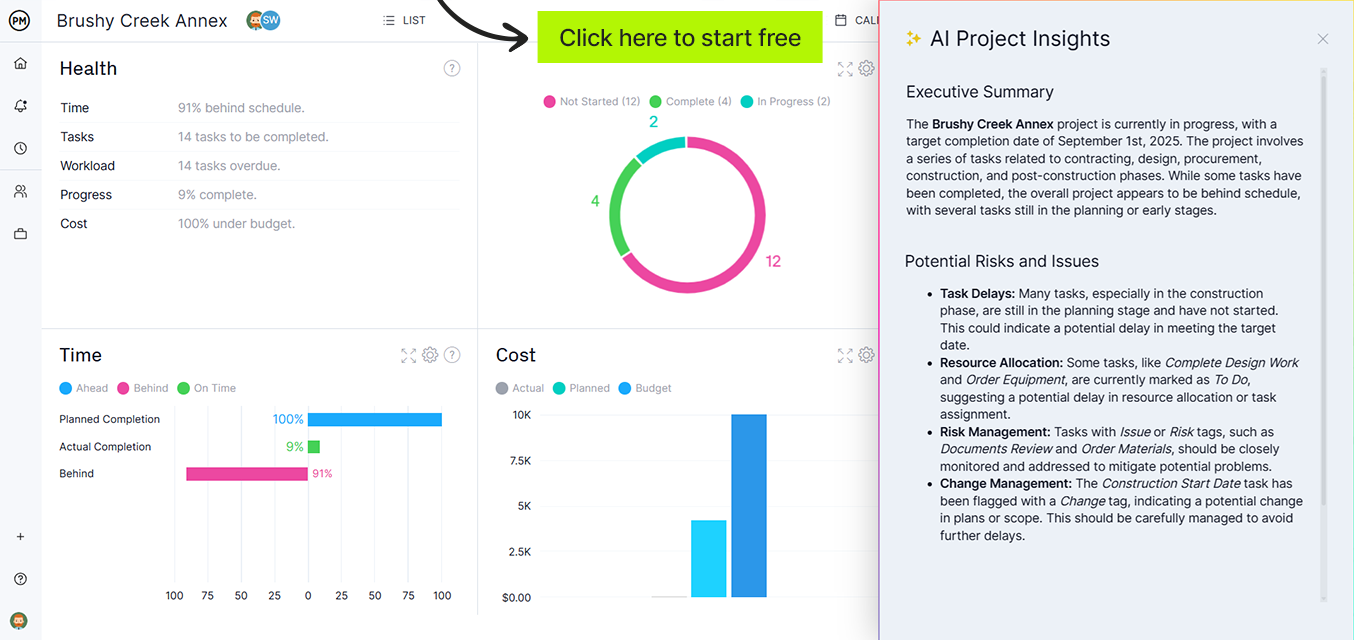
ProjectManager is the ideal tool for IT change management because it combines task management, workflow automation and reporting in a single platform. Managers can use dashboards to monitor change requests, allocate resources effectively, track approvals and generate compliance reports. Its integration capabilities allow seamless documentation and collaboration across IT teams, making it easier to implement and track every IT change efficiently. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
What Is ITIL Change Management?
ITIL change management is a framework within the IT Infrastructure Library that governs the lifecycle of all IT changes. It ensures that standardized processes are followed to reduce risk, minimize downtime and maintain service quality. ITIL change management helps organizations implement changes efficiently by providing structured procedures, approval workflows and consistent documentation, ensuring that IT systems remain stable and reliable while adapting to business needs.
Types of ITIL Changes
ITIL categorizes changes into types to streamline approval and implementation processes. Each type has specific procedures and risk levels, ensuring IT teams apply the appropriate level of oversight for every change.
- Standard IT Change: Pre-approved, low-risk changes that follow established procedures. These changes are routine, repeatable and do not require additional approval. Examples include software updates or password resets.
- Normal IT Change: Changes that require assessment and approval before implementation. They vary in risk and complexity and may include system upgrades or configuration modifications. A change advisory board typically reviews these.
- Emergency IT Change: Urgent changes that must be implemented immediately to prevent outages or resolve critical incidents. These bypass some standard procedures but still require post-implementation review and documentation.
ITIL Change Management Roles
ITIL change management defines specific roles to ensure changes are evaluated, approved and implemented efficiently. Each role carries clear responsibilities to maintain IT stability while supporting business objectives. Understanding these roles helps organizations assign accountability and streamline their change processes.
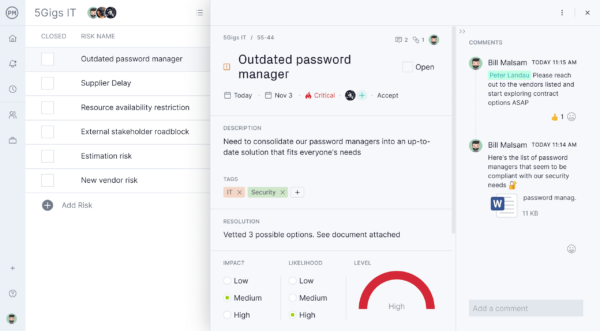
- Change Advisory Board (CAB): A group of stakeholders and experts who review and approve normal IT changes. The CAB evaluates the risks, impacts, and benefits of proposed changes to ensure they align with business priorities and minimize potential disruptions.
- Change Manager: Responsible for overseeing the change management process, coordinating approvals, scheduling changes and ensuring documentation. The Change Manager ensures policies are followed and that changes are implemented smoothly with minimal service interruption.
- Change Implementer / Owner: The individual or team responsible for executing the approved change. They carry out the technical tasks, follow implementation procedures,and report back on completion and any issues encountered during the process.
Related: 14 Free Change Management Templates for Excel and Word
IT Change Management Process Explained
The IT change management process outlines structured steps to handle changes in IT systems efficiently. It ensures minimal disruption, maintains compliance and improves service quality. Each phase from request to closure is documented to provide accountability, track performance and guide teams in implementing changes effectively.
1. Identify and Record the Change Request
All changes begin with a detailed change request, including the nature of the change, affected systems, requester information and desired timeline. Recording this ensures transparency, provides a reference for approvals and helps track the change throughout the lifecycle. Accurate documentation at this stage reduces errors and supports auditing processes.
2. Assess and Classify the Change
Once submitted, the change is assessed for type, priority and urgency. Classification determines whether the change is standard, normal or emergency. This step ensures proper review, assigns responsible personnel and sets timelines. Clear categorization helps allocate resources effectively and prevents unnecessary delays in handling critical updates.
3. Evaluate Risks and Impacts
Each change undergoes a risk and impact assessment to identify potential disruptions to services, security, or operations. The evaluation considers dependencies, resource requirements and compliance issues. By understanding risks and impacts beforehand, IT teams can develop mitigation plans, reducing downtime and avoiding costly mistakes.
4. Approve or Reject the Change
The change request is presented to the appropriate authority, often the Change Advisory Board or Change Manager. Approval is based on risk, benefit and alignment with business priorities. Rejected changes are documented with reasons, while approved changes move forward to implementation, ensuring accountability and traceability of decisions.
5. Implement the Approved Change
The approved change is executed according to the implementation plan. Change Implementers follow procedures, coordinate with stakeholders and document progress. Communication ensures users are aware of potential impacts. Successful implementation minimizes service disruption and adheres to IT policies, providing a controlled and repeatable process for all changes.
6. Review and Close the Change
After implementation, the change is reviewed to verify that objectives were met and no issues remain. Documentation is updated, lessons learned are recorded and the change is formally closed. This phase ensures accountability, allows performance evaluation and provides data for continuous improvement of the IT change management process.
Benefits of IT Change Management
Implementing IT change management provides organizations with structured processes to handle changes efficiently. It improves communication, ensures accountability, reduces errors and strengthens IT service reliability. Teams can manage risks better, minimize downtime and maintain business continuity while aligning changes with organizational goals.
Improved Service Stability
IT change management standardizes procedures for implementing updates, upgrades and modifications, ensuring that systems remain stable and reliable. By following defined workflows, teams reduce unplanned interruptions and conflicts. This structured approach allows IT departments to maintain consistent service quality, improve user satisfaction and prevent cascading failures across dependent systems.
Reduced Downtime
Changes implemented without proper management can result in outages and service disruptions. IT change management minimizes downtime by planning changes carefully, scheduling them during low-impact periods and testing updates before deployment. Teams can quickly address issues and recover from failures, keeping critical business operations running smoothly without major interruptions.
Better Risk Control
Through risk assessment and approval processes, IT change management allows teams to anticipate potential problems before changes are applied. By evaluating impacts and implementing mitigation strategies, organizations reduce operational, security and compliance risks. Proactive monitoring and documentation provide visibility and accountability, helping IT departments control risk and maintain system integrity.
Related: 9 Free Risk Management Templates for Excel
IT Change Management Tools & Documentation
Effective IT change management relies on structured tools and documentation to standardize processes, improve visibility and ensure accountability. These resources help teams track change requests, assess risks, obtain approvals and monitor implementation. Proper documentation provides a clear audit trail and supports continuous improvement across the IT environment.
Change Request Form
The change request form captures all essential details about a proposed IT change, including description, requester, date, priority and affected systems. It serves as the official submission for consideration, providing a standardized format that ensures no critical information is overlooked. Teams can review, track and assign changes efficiently.
Related: Change Request Form Template
Change Log
A change log records all submitted and approved changes in one centralized location. It tracks status, implementation dates, responsible personnel and outcomes. This log provides visibility to IT managers and stakeholders, ensures accountability and helps identify recurring issues or bottlenecks, supporting proactive risk management.
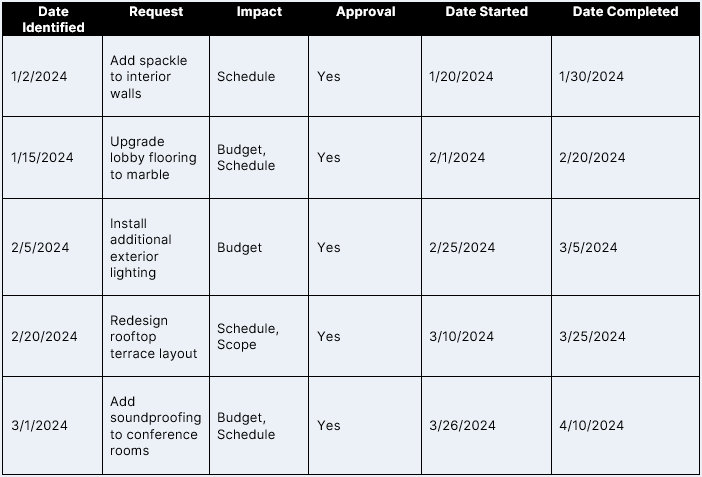
Change Impact Analysis
The change impact analysis evaluates the potential effects of a proposed change on systems, processes and users. By identifying dependencies and risks, teams can prioritize changes, mitigate negative consequences and develop contingency plans. This ensures smoother implementation and minimizes service disruptions.
Change Approval Matrix
The change approval matrix defines who must review and authorize each type of change. It clarifies roles and responsibilities, ensuring proper oversight for standard, normal and emergency changes. By formalizing approval hierarchies, organizations reduce risk, streamline decision-making and prevent unauthorized modifications.
Change Implementation Plan
The change implementation plan outlines step-by-step instructions for executing an approved change. It details tasks, timelines, resources and communication protocols. By providing a clear roadmap, teams can coordinate efforts, avoid errors and ensure that the change is implemented efficiently and effectively across all impacted systems.
Post-Implementation Review Report
The post-implementation review report evaluates the success of a change after deployment. It documents outcomes, issues encountered, lessons learned and opportunities for improvement. This report supports continuous process improvement, informs future change decisions and ensures accountability for both the planning and execution phases.

Best Practices for IT Change Management
Following best practices ensures IT change management is efficient, consistent and reduces risk. Structured processes, proper documentation and stakeholder engagement help organizations implement changes smoothly, minimize disruptions and maintain system stability. Applying these principles supports continuous improvement and better decision-making across IT projects and operations.
Maintain a Centralized Change Log
Keeping a centralized change log allows IT teams to track all submitted, approved and implemented changes in one location. It provides visibility into ongoing and completed changes, helps identify trends or recurring issues and supports auditing and compliance efforts. Centralization reduces errors and ensures accountability across the change management process.
Involve Stakeholders Early
Engaging stakeholders at the start of the change process ensures their requirements, concerns and priorities are considered. Early involvement improves communication, fosters collaboration and helps identify potential risks or dependencies before implementation. This proactive approach increases the likelihood of successful changes and reduces resistance from affected teams.
Related: 13 Free Stakeholder Management Templates for Excel & Word
Monitor Post-Implementation Results
After implementing a change, monitoring post-implementation results ensures it meets intended objectives and does not cause unexpected issues. Tracking system performance, user feedback and any incidents allows teams to correct problems quickly. This review supports continuous improvement, informs future changes and validates the effectiveness of the IT change management process.
Free IT Change Management Templates
These free IT change management templates help streamline your change processes and improve consistency across projects. Each template supports different stages of the IT change management process, from documenting changes to evaluating impacts and approvals. Using templates saves time, reduces errors and ensures all necessary information is captured for effective decision-making and compliance.
Change Log Template
Download this free template to help teams track all change requests in a centralized log. It records request details, status, priority, approvals and implementation outcomes. By maintaining a comprehensive change log, IT teams can monitor trends, ensure accountability and quickly identify any recurring issues across projects or systems.
Change Impact Assessment Template
Use this free change impact assessment template to allow IT teams to evaluate potential effects of a proposed change on systems, users and business processes. It captures risk levels, affected areas, required resources and mitigation strategies. Using this template ensures informed decision-making and minimizes negative consequences from unplanned impacts.
Change Request Form Template
This free form standardizes the submission of change requests, capturing essential details such as requester information, change description, priority and proposed timeline. It ensures requests are complete and consistent, enabling quicker assessment and approval. Teams can efficiently manage requests while maintaining documentation for audit and compliance purposes.
How ProjectManager Helps IT Teams
ProjectManager allows IT teams to track every change request and task in real time. Dashboards display task status, pending approvals and risk indicators, while reports provide insights into completion rates and delays. Teams receive alerts when issues arise, helping prevent downtime and maintain service stability. By tracking changes effectively, IT managers can ensure projects stay on schedule and IT change management processes are followed accurately, giving full visibility into ongoing work and outcomes.
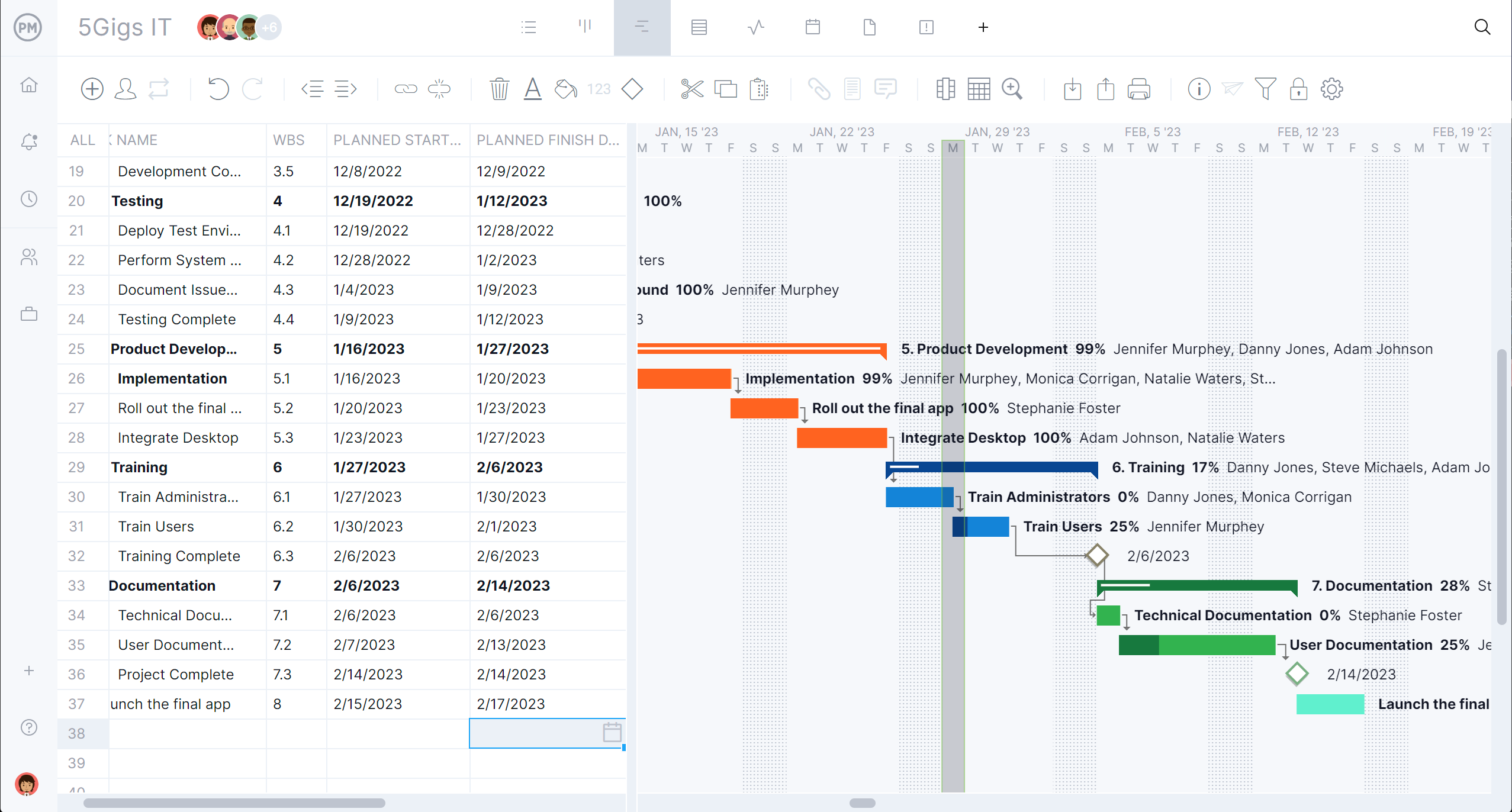
Visualize Project Timelines With Multiple Project Views
ProjectManager offers multiple project views, with Gantt charts as the central tool for IT teams. Tasks are linked with dependencies and timelines can be adjusted as priorities shift. Calendar, list and board views provide alternative perspectives to manage simultaneous changes. This flexibility helps IT managers see the full picture, coordinate tasks efficiently and identify potential scheduling conflicts before they impact deadlines, keeping IT change projects aligned with business objectives.
Manage Resources Effectively
Resource management tools in ProjectManager help IT teams assign work and monitor workloads. Team pages show who is working on what, while workload charts highlight over- or under-allocated staff. Managers can balance assignments, track time spent on tasks and forecast future needs. These features ensure IT staff are utilized efficiently, prevent burnout and optimize productivity, enabling teams to implement changes smoothly and meet IT and business goals.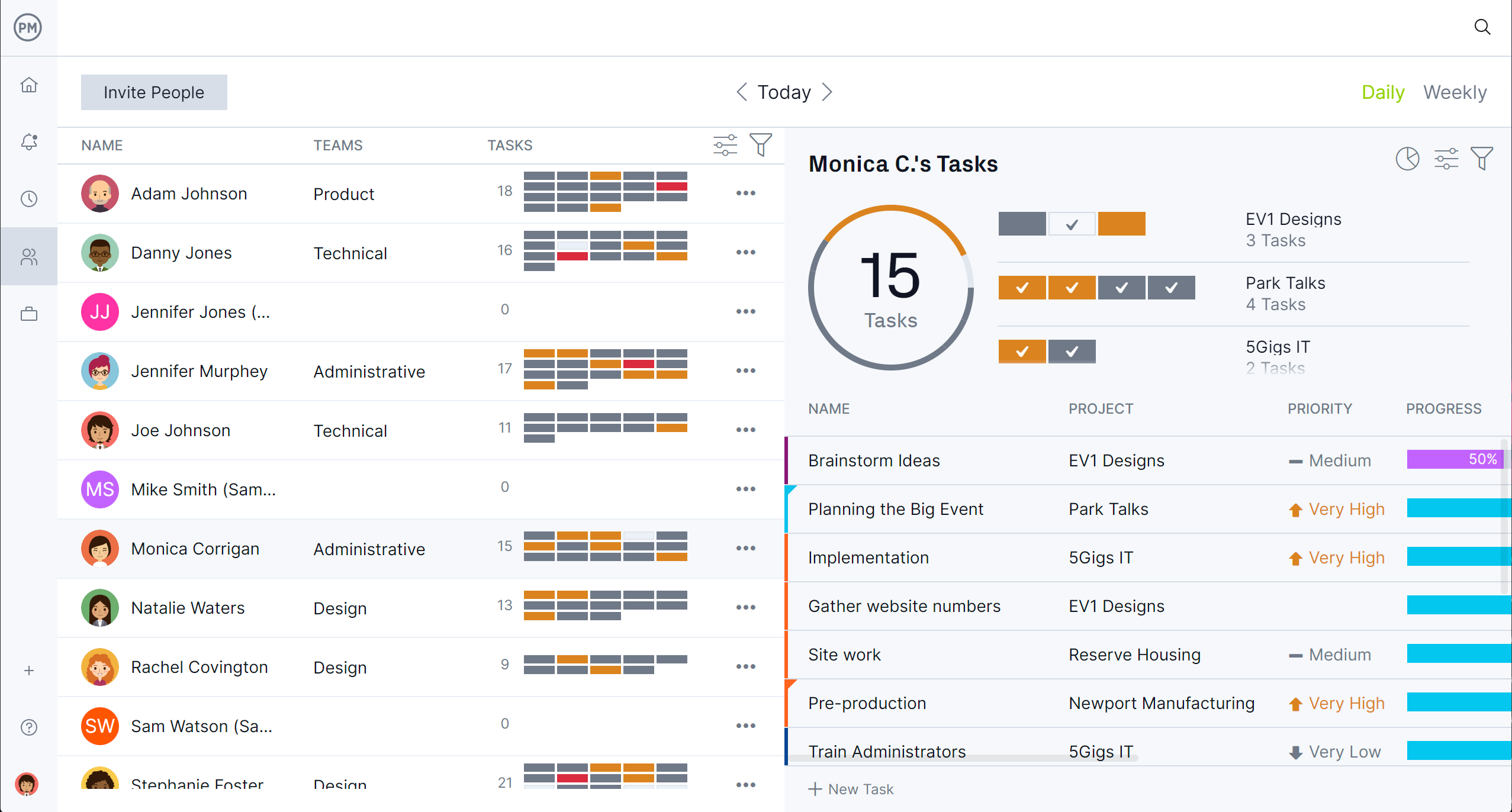
Related IT Change Management Content
For those who want to learn more about IT change management, check out the links below. There are articles that cover IT roadmaps, service management and much more.
- What Is an IT Roadmap? (Template Included)
- IT Service Management (ITSM): Frameworks, Processes & Phases
- How to Make an IT Disaster Recovery Plan
- IT Audit: Definition & Quick Guide (Checklist Included)
- IT Governance: Definitions, Frameworks and Planning
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams, whether they’re in the office or out in the field. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay up to date with email and in-app notifications. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

