What Is a Project Proposal?
A project proposal is a formal project management document used to present a proposed initiative in a clear, structured way before work begins. It defines what the project is, what it aims to achieve and the high-level requirements needed to move forward.
Rather than detailing execution, a project proposal establishes a shared planning framework that allows organizations and external stakeholders to review, discuss and refine an idea early. Because proposals are written for sponsors, clients or decision-makers, they must be tailored to their priorities and concerns. Understanding the audience is critical to presenting information at the right level of detail.
We’ve created a free project proposal template for Word to help structure documents, so you don’t have to remember the process each time.

Get your free
Project Proposal Template
Use this free Project Proposal Template to manage your projects better.
Get the template
What Is the Purpose of a Project Proposal?
A project proposal explains why a project should exist and provides the information decision-makers need to approve, fund or prioritize it. It justifies a business need or opportunity, communicates expected value and benefits, and helps secure executive or client buy-in.
By clearly defining scope, goals, deliverables, success criteria and assumptions, it aligns stakeholders around a shared understanding of what will be delivered. A proposal also estimates costs, resources and timelines, allowing organizations to compare alternatives, evaluate feasibility and reduce risk before committing resources.
In competitive contexts, it supports bids, funding requests and contract awards. Internally, it formalizes ideas into actionable plans, serves as a reference for decisions and governance, and enables prioritization by showing how the project fits strategic objectives.
Most project management teams use a project proposal for the following purposes:
- Justifying a business need or strategic opportunity
- Establishing stakeholder expectations and project success criteria early
- Serving as a reference for project-related decisions
- Supporting internal prioritization and portfolio decisions
- Communicating expected value and business benefits
ProjectManager is an award-winning project management software equipped with advanced project planning, scheduling and monitoring features to turn any project proposal into a successful project in any industry. Create a project timeline, estimate costs, track project budgets, allocate resources and much more with powerful Gantt charts, real-time project dashboards and reports. Get started for free today.
When to Use a Project Proposal
A project proposal is most useful at key decision points, before time, money or project resources are committed. It provides structure when an idea needs evaluation, approval or alignment, helping stakeholders understand what’s being proposed, why it matters and what’s required to move forward. Whether you’re introducing a new initiative, responding to a request or reassessing a change, a project proposal creates clarity and supports informed decision-making.
Most project management teams write a project proposal when:
- Requesting project approval
- Seeking project financing or budget allocation
- Responding to a client or stakeholder request
- Proposing a new initiative or idea
- Competing for a contract or bid
- Evaluating multiple project options
- Defining work before project initiation
- Clarifying scope, cost or risk
- Aligning cross-functional teams
- Committing significant resources
- Requiring formal re-approval after changes
- Documenting assumptions before execution
Types of Project Proposals
In terms of types of project proposals, you can have one that’s formally solicited, informally solicited or a combination. There can also be renewal and supplemental proposals. Here’s a brief description of each of them.
- Solicited project proposal: This is sent as a response to a request for proposal (RFP). Here, you’ll need to adhere to the RFP guidelines of the project owner.
- Unsolicited project proposal: You can send project proposals without having received a request for a proposal. This can happen in open bids for construction projects, where a project owner receives unsolicited project proposals from many contractors.
- Informal project proposal: This type of project proposal is created when a client asks for an informal proposal without an RFP.
- Renewal project proposal: You can use a renewal project proposal when you’re reaching out to past customers. The advantage is that you can highlight past positive results and future benefits.
- Continuation project proposal: A continuation project proposal is sent to investors and stakeholders to communicate project progress.
- Supplemental project proposal: This proposal is sent to investors to ask for additional resources during the project execution phase.
Related: 12 Free Proposal Templates
Project Proposal Template
All the elements in the above project proposal outline are present in our template. This free project proposal template for Word will provide you with everything you need to write an excellent project proposal. It will help you with the executive summary, project process, deliverables, costs—even terms and conditions. Download your free template today.
Project Proposal Outline
There are several key operational and strategic questions to consider, including:
- Executive summary: This is the elevator pitch that outlines the project being proposed and why it makes business sense. While it also touches on the information that’ll follow in the project proposal, the executive summary should be brief and to the point.
- Project background: This is another short part of the proposal, usually only one page, which explains the problem you’ll solve or the opportunity you’re taking advantage of with the proposed project. Also, the project background should provide a short history of the business to put the company in context to the project and why it’s a good fit.
- Project vision & success criteria: State the goal of the project and how it aligns with the goals of the company. Be specific. Also, note the metrics used to measure the success of the project.
- Potential risks and mitigation strategies: There are always risks. Detail them here and what strategies you’ll employ to mitigate any negative impact as well as take advantage of any positive risk.
- Project scope & deliverables: Define the project scope, which is all the work that has to be done and how it will be done. Also, detail the various deliverables that the project will have.
- Project approach: Define the approach you’ll use for the contract. There are several different types of contracts used in construction, for example, such as lump sum, cost plus, time and materials, etc. This is also a good place to describe the delivery method you’ll use.
- Expected benefits: Outline the benefits that will come from the successful completion of the project.
- Project resource requirements: List the resources, such as labor, materials, equipment, etc., that you’ll need to execute the project if approved.
- Project costs & budget: Detail all the costs, including resources, that’ll be required to complete the project and set up a budget to show how those costs will be spent over the course of the project.
- Project timeline: Lay out the project timeline, which shows the project from start to finish, including the duration of each phase and the tasks within it, milestones, etc.
- Stakeholders & roles: Identify key stakeholders, sponsors and decision-makers involved in the project, along with their roles, responsibilities and level of authority throughout the project lifecycle.
- Assumptions, exclusions & constraints: Document the assumptions the proposal is based on as well as any known constraints, such as budget limits, regulatory requirements, resource availability or fixed deadlines. It’s also important to define exclusions, activities or deliverables that will not be done.
- Project governance: Explain how the project will be governed, including review checkpoints, approval authorities and escalation paths for major decisions or changes.
- Change management approach: Describe how changes to the project scope, schedule or budget will be evaluated, approved and communicated once the project is underway.
- Communication plan: Define how project updates will be shared, how often reporting will occur and which stakeholders will receive which types of information.
- Quality management approach: Outline how quality will be planned, monitored and controlled to ensure deliverables meet defined standards and expectations.
- Legal, compliance & procurement considerations: Address contractual, regulatory or procurement requirements that must be met before and during project execution.
Turn your project proposal into a successful project with ProjectManager. It’s powerful project management features allow you to keep your projects on schedule and under budget while keeping stakeholders informed with real-time project dashboards and reports.

How to Write a Project Proposal
To make the best proposal possible, you’ll want to be thorough and hit on all the points we’ve listed above. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a persuasive priority proposal.
1. Write an Executive Summary
The executive summary provides a quick overview of the main elements of your project proposal, such as your project background, project objectives and project deliverables, among other things. The goal is to capture the attention of your audience and get them excited about the project you’re proposing. It’s essentially the “elevator pitch” for the project life cycle. It should be short and to the point.
The executive summary should be descriptive and paint a picture of what project success looks like for the client. Most importantly, it should motivate the project client; after all, the goal is getting them to sign on the dotted line to get the project moving!
2. Provide a Project Background
The project background is a one-page section of your project proposal that explains the problem that your project will solve. You should explain when this issue started, its current state and how your project will be the ideal solution.
- Historic data: The history section outlines previously successful projects and those that could have run more smoothly. By doing so, this section establishes precedents and how the next project can be more effective using information from previous projects.
- Solution: The solution section addresses how your project will solve the client’s problem. Accordingly, this section includes any project management techniques, skills and procedures your team will use to work efficiently.
3. Establish a Project Vision & Success Criteria
You’ll need to define your project vision. This is best done with a vision statement, which acts as the north star for your project. It’s not specific as much as it’s a way to describe the impact your company plans to make with the project.
It’s also important to set up success criteria to show that the project is in fact doing what it’s proposed to do. Three obvious project success criteria are the triple constraint of cost, scope and time. But you’ll need to set up a way to measure these metrics and respond to them if they’re not meeting your plan.
4. Identify Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
To reduce the impact of risk in your project, you need to identify what those risks might be and develop a plan to mitigate them. List all the risks, prioritize them, describe what you’ll do to mitigate or take advantage of them and who on the team is responsible for keeping an eye out for them and resolving them.
5. Define Your Project Scope and Project Deliverables
The project scope refers to all the work that’ll be executed. It defines the work items, work packages and deliverables that’ll be delivered during the execution phase of your project life cycle. It’s important to use a work breakdown structure (WBS) to define your tasks and subtasks and prioritize them.
6. Set SMART Goals for Your Project Proposal
The best mindset when developing goals and objectives for your project proposal is to use the SMART system:
- Specific – Make sure your goals and objectives are clear, concise and specific to the task at hand.
- Measurable – Ensure your goals and objectives are measurable so it’s obvious to see when things are on track and going well, and conversely, when things are off track and issues need to be addressed. Measurable goals make it easy to develop the milestones you’ll use to track the progress of the project and identify a reasonable date for completion and/or closure.
- Attainable – It’s important every project has a “reach” goal. Hitting this goal would mean an outstanding project that extends above and beyond expectations. However, it’s important that the project’s core goal is attainable, so morale stays high and the job gets done with time and resources to spare.
- Relevant – Make sure all of your goals are directly relevant to the project and address the scope within which you’re working.
- Time-Based – Timelines and specific dates should be at the core of all goals and objectives. This helps keep the project on track and ensures all project team members can manage the work plan that’s ahead of them.
7. Explain What’s Your Project Approach
Your project approach defines the project management methodology, tools and governance for your project. In simple terms, it allows project managers to explain to stakeholders how the project will be planned, executed and controlled successfully.
8. Outline The Expected Benefits of Your Project Proposal
If you want to convince internal stakeholders and external investors, you’ll need to show them the financial benefits that your project could bring to their organization. You can use cost-benefit analysis and projected financial statements to demonstrate why your project is profitable.
9. Identify Project Resource Requirements
Project resources are critical for the execution of your project. The project proposal briefly describes what resources are needed and how they’ll be used. Later, during the planning phase, you’ll need to create a resource management plan that’ll be an important element of your project plan. Project requirements are the items, materials and resources needed for the project. This section should cover both internal and external needs.
10. Estimate Project Costs and Project Budget
All the resources that you’ll need for your project have a price tag. That’s why you need to estimate those costs and create a project budget. The project budget needs to cover all your project expenses, and as a project manager, you’ll need to make sure that you adhere to the budget.
11. Define a Project Timeline
Once you’ve defined your project scope, you’ll need to estimate the duration of each task to create a project timeline. Later during the project planning phase, you’ll need to create a schedule baseline, which estimates the total length of your project. Once the project starts, you’ll compare your actual project schedule to the schedule baseline to monitor progress.
Project Proposal Example
The best way to understand what a project proposal should look like is to take a look at a project proposal example. Here’s a project proposal for a construction project that integrates some of the elements of the project proposal outline we’ve described above.
1. Executive Summary
This proposal outlines a small commercial tenant improvement to refresh a 1,200 square foot neighborhood café. The project upgrades finishes, counters, lighting and signage to improve customer experience and operational flow while minimizing downtime. The investment supports revenue growth, brand consistency and code compliance within a short construction window timeline.
2. Project Background
The café operates in a mixed-use retail corridor and has outgrown its current layout. Aging finishes, inefficient service flow and limited seating constrain sales during peak hours. This project modernizes the space, improves circulation and aligns the location with the company’s updated brand standards and local building requirements and permits.
3. Project Vision and Success Criteria
The vision is to deliver a refreshed café that enhances customer comfort, supports faster service and reflects the brand’s identity. Success is measured through schedule adherence, budget tracking, quality outcomes and operational readiness, ensuring the space opens on time, meets code requirements and achieves targeted performance metrics after completion launch.
| Goal | Objective | Target Outcome |
| Improve customer experience | Upgrade finishes and seating layout | Higher dwell time and satisfaction |
| Increase service efficiency | Optimize counter and queue flow | Reduced order wait times |
| Open on schedule | Complete construction in six weeks | On-time café reopening |
4. Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
| Project Risk | Mitigation Strategy | Risk Owner | Estimated Cost |
| Permit approval delays | Submit permits early and maintain follow-ups | Project Manager | €1,500 |
| Material delivery delays | Pre-order long-lead items and identify alternates | Procurement Lead | €2,000 |
| Unexpected site conditions | Include contingency and conduct early inspections | Site Supervisor | €3,000 |
5. Project Scope & Deliverables
| Scope Area | Description | Deliverable |
| Interior demolition | Remove existing flooring, fixtures and counters | Cleared and prepared interior space |
| Interior finishes | Install new flooring, paint and wall finishes | Completed finished interior |
| Service counter upgrade | Install new millwork and equipment layout | Operational service counter |
6. Project Resource Requirements
| Resource Type | Description | Estimated Quantity |
| Labor | Carpenters, electricians and painters | 6 workers |
| Materials | Flooring, paint, millwork materials | 1,200 sq ft |
| Equipment | Hand tools, lifts and safety equipment | As required |
7. Project Costs & Budget
| Cost Category | Description | Estimated Cost |
| Labor | Construction and installation work | €22,000 |
| Materials | Finishes, fixtures and millwork | €15,000 |
| Permits & fees | Municipal permits and inspections | €3,000 |
8. Project Timeline
| Project Phase | Duration | Milestone |
| Planning & permits | 2 weeks | Permits approved |
| Construction | 4 weeks | Physical work completed |
| Final inspection & handover | 1 week | Café ready for reopening |
9. Assumptions, Exclusions & Constraints
| Category | Description | Impact |
| Assumption | Existing utilities are in good condition | No major rework expected |
| Exclusion | Kitchen equipment replacement | Handled under separate project |
| Constraint | Fixed reopening deadline | Limited schedule flexibility |
Project Proposal vs. Project Charter
A project proposal is a detailed project document that’s used to convince the project sponsor that the project being proposed is worth the time, money and effort to deliver it. This is done by showing how the project will address a business problem or opportunity. It also outlines the work that will be done and how it will be done.
A project charter can seem like the same thing as a project proposal as it also defines the project in a document. It identifies the project objectives, scope, goals, stakeholders and team. But it’s done after the project has been agreed upon by all stakeholders and the project has been accepted. The project charter authorizes the project and documents its requirements to meet stakeholders’ needs.

Project Proposal vs. Business Case
A business case is used to explain why the proposed project is justified. It shows that the project is worth the investment of time and money. It’s more commonly used in larger companies in the decision-making process when prioritizing one project over another.
The business case answers the questions: what is the project, why should it be taken up, who will be involved and how much will it cost? It’s therefore related to a project proposal, but the project proposal comes before the business case and is usually part of the larger proposal.
Project Proposal vs. Project Plan
Again, the project proposal and the project plan in this case are very similar documents. It’s understandable that there would be some confusion between these two project terms. They both show how the project will be run and what the results will be. However, they’re not the same.
The project proposal is a document that aims to get a project approved and funded. It’s used to convince stakeholders of the viability of the project and their investment. The project plan, on the other hand, is made during the planning phase of the project, once it’s been approved. It’s a detailed outline of how the project will be implemented, including schedule, budget, resources and more.

In addition to these elements, it’s advisable to use a cover letter, which is a one-page document that helps you introduce your project proposal and grab the attention of potential clients and stakeholders.
Project Proposal Tips
Whatever project proposal you’re working on, there are a few tips that apply as best practices for all. While above we suggested a project proposal template that would have a table of contents, meaning it would be many pages long, the best-case scenario is keeping the proposal to one or two pages max. Remember, you’re trying to win over stakeholders, not bore them.
Speaking of project stakeholders, do the research. You want to address the right ones. There’s no point in doing all the work necessary to write a great proposal only to have it directed to the wrong target audience. Whoever is going to read it, though, should be able to comprehend the proposal. Keep the language simple and direct.
When it comes to writing, get a professional. Even a business document like a project proposal, business case or executive summary will suffer if it’s poorly constructed or has typos. If you don’t want to hire a professional business writer, make sure you get someone on your project team to copy, edit and proof the document. The more eyes on it, the less likely mistakes will make it to the final edition. You can also use an AI writing tool to help you proofread the project proposal and ensure the text is clear and concise.
While you want to keep the proposal short and sweet, it helps to sweeten the pot by adding customer testimonials to the attachments. Nothing sells a project plan better than a customer base looking for your product or service.
ProjectManager & Project Proposals
ProjectManager allows you to plan proposals within our software. You can update tasks for the project proposal to signify where things stand and what’s left to be done. The columns allow you to organize your proposal by section, creating a work breakdown structure (WBS) of sorts.
When building a project proposal, it’s vital to remember your target audience. Your audience includes those who are excited about the project, and see completion as a gain for their organization. Conversely, others in your audience will see the project as a pain and something to which they aren’t looking forward. To keep both parties satisfied, it’s essential to keep language factual and concise.
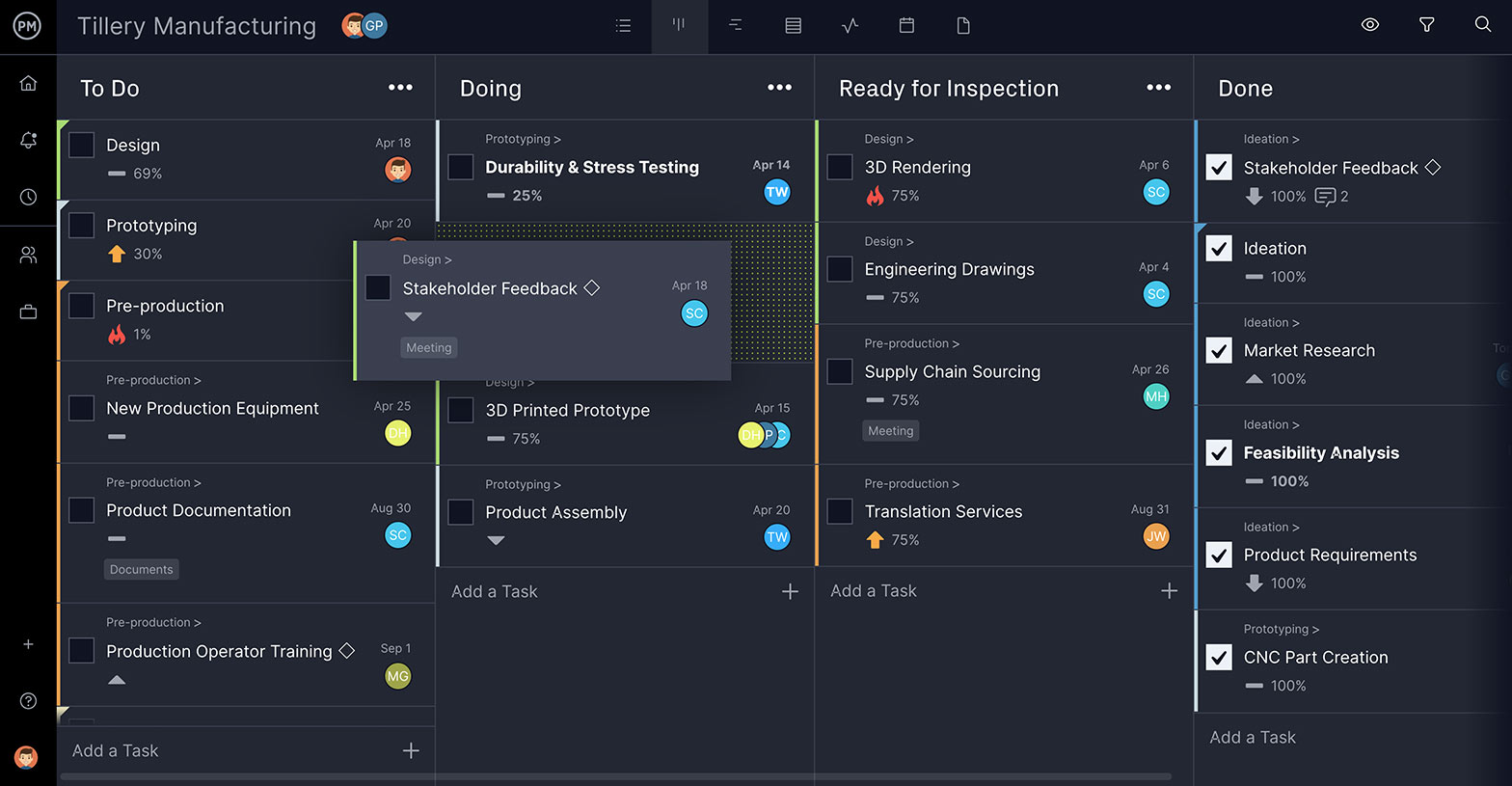
Our online kanban boards help you think through that language and collaborate on it effectively with other team members, if necessary. Each card shows the percentage completed so everyone in the project management team is aware of the work done and what’s left to be done.
As you can see from the kanban board above, work has begun on tasks such as product documentation and design. Tasks regarding stakeholder feedback, ideation, market research and more have been completed, and there’s a good start on the engineering drawings, 3D rendering, supply chain sourcing and translation services.
A PDF is then attached to the card, and everyone added to the task receives an email notifying them of the change. This same process can be used throughout the life-cycle of the project to keep the team updated, collaborating, and producing a first-class project proposal. In addition to kanban boards, you can also use other project management tools such as Gantt charts, project dashboards, task lists and project calendars to plan, schedule and track your projects.
Related Project Planning Content
- Project Documentation: 15 Essential Project Documents
- How to Create a Project Execution Plan (PEP)
- How to Write a Scope of Work
- Project Scope Statement: How to Write One With Examples
- ¿Qué es una Propuesta de Proyecto? (Con Ejemplo)
- Comment rédiger une proposition de projet
- Wie man einen Projektvorschlag schreibt
Project proposals are just the first step in the project planning process. Once your project is approved, you’ll have to solidify the plan, allocate and manage resources, monitor the project, and finally hand in your deliverables. This process requires a flexible, dynamic and robust project management software package. ProjectManager is online project management software that helps all your team members collaborate and manage this process in real-time. Try our award-winning software with this free 30-day trial.