Lean manufacturing addresses one of the worst things that can happen to any enterprise: waste. To not take full advantage of all of your resources is to lose efficiencies and, in so doing, stunt production and fail to offer value to your customers.
The manufacturing industry is, of course, rife with waste. Whether it’s idle workers, inefficient production lines or unused materials that can’t be recycled or repurposed, the results are the same: a drag on productivity. This insistence on eliminating waste and improving the manufacturing process to maximize the value offered to customers is where the idea of the lean manufacturing system developed.
What Is Lean Manufacturing?
Lean manufacturing is a production system that focuses on reducing waste, creating customer value and seeking continuous process improvement. This is achieved by applying lean principles, techniques and tools to eliminate waste from a manufacturing cycle.
This production philosophy emphasizes continuous improvement, efficiency and the elimination of non-value-added activities in the manufacturing process. Some key principles of lean production include defining value and analyzing and visualizing the flow of materials by value stream mapping. It seeks to eliminate overproduction, waiting, transport, extra processing and inventory.
Modernizing your project management tools can help your organization increase productivity and reduce waste. ProjectManager, an online project management software, has everything you need to streamline your processes and improve production quality. Build schedules with Gantt charts, execute tasks with task lists, track progress on dashboards and report on everything with built-in reporting features. Get started for free today.
When Was Lean Manufacturing Invented?
The lean manufacturing process, also referred to as lean production, was first implemented in the Toyota production system (TPS) in Japan, which revolutionized the company’s manufacturing process and then expanded all over the world. The principles of lean manufacturing were formalized during the 1950s and 1960s, as Toyota sought to improve efficiency and reduce waste in production. By the 1980s and 1990s, the concept had gone international and moved beyond the automotive industry.
What Is Waste In Lean Manufacturing?
We’ve referred to waste several times, but it’s important to understand what is meant by waste in this context. Waste in lean production refers to any activity or process that consumes resources but does not add value to the product or service from the customer’s point of view. The goal of lean is to identify and eliminate these wastes to improve efficiency, reduce costs and enhance overall quality. There are seven types of waste, or muda in Japanese, which we’ll explore later.
Lean Manufacturing Principles
Here are the eight lean management principles that are applied to optimize lean manufacturing systems:
Identify and Create Customer Value
One of the main principles of the lean manufacturing methodology is to create customer value through the efficient manufacturing of products and services. The first step in the lean production process is to identify what product features are important for customers and which aren’t so you can focus on what’s important. Once the customer defines what’s valuable, you can create a product that only has what’s necessary and remove the unnecessary work and components associated with it.
Value Stream Mapping
The value stream of a lean manufacturing system can be simply defined as the set of actions or steps that add value to customers during the manufacturing process from beginning to end. A value stream map allows managers to visualize each step in the production process to identify waste and opportunities for improvement to make the process more efficient and better serve customers.
Related: 10 Free Manufacturing Templates for Excel
Identify and Eliminate Waste (Muda)
The two previous steps are how one identifies and eliminates wastes. It’s a systematic approach that begins with conducting value stream mapping to represent the flow of materials and information in the process. This is followed by observing processes on the shop floor, such as workflows, and looking for delays, unnecessary movements and inefficiencies. Then collect data on cycle times, lead times and inventory levels, engage with employees and evaluate key performance indicators (KPIs).
Create Flow
One of the goals of lean manufacturing is process improvement. A manufacturing process can be improved by diagnosing wastes or inefficiencies such as a poorly planned manufacturing facility layout. By fixing functional barriers such as those, you can improve the flow of the value stream.
Pull System
The pull system consists of starting new work only when there’s customer demand for it. This eliminates unnecessary steps in the production process such as transporting materials, overproducing products and storing excess inventory, which are considered waste. This is what supports just-in-time production.
Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
Kaizen can be translated to continuous improvement. It’s a business practice that consists of making small, incremental changes over time to a process. In lean production, kaizen allows businesses to permanently identify problems and develop solutions to maximize customer value and eliminate waste.
It’s through these principles that the lean manufacturing system helps businesses improve their production process by eliminating waste. It simplifies operational structure to understand, perform and manage the work environment. To do all of this simultaneously, Toyota applies a mentoring methodology called Senpai and Kohai, which translates to senior and junior. This fosters lean thinking throughout an organizational structure from the ground up.
Automation with a Human Touch (Jidoka)
This principle emphasizes the integration of technology and human expertise to enhance productivity while maintaining a focus on quality and worker engagement. Automation shouldn’t replace workers but empower them. They should be able to leverage the technology to better their skills and decision-making capabilities. There should be flexibility in automated systems so they can adapt to changes in production volume and type. The goal is a collaboration between humans and machines.
Level Production (Heijunka)
Also known as production leveling, this lean manufacturing principle aims to smooth out production processes by maintaining a constant output rate. This reduces fluctuations in production, inventory levels and lead times. The goal is to improve efficiency and responsiveness to customer demand. Some key concepts include smoothing demand to produce a consistent rate that matches average customer demand, minimizing inventory, reducing lead times, improving resource utilization and balancing workload.
Get your free
Kanban Card Template
Use this free Kanban Card Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
Types of Waste in the Lean Manufacturing Process
Waste isn’t a simple concept in lean management. If approached simply, then the reduction will be limited. For lean project management to be most effective, all types of waste must be identified and eliminated.
First, let’s look at the seven lean manufacturing waste types developed by Taiichi Ohno, chief engineer at Toyota, for the Toyota production system (TPS).
- Unnecessary transportation: Unnecessary transportation of employees, tools, materials or equipment is a waste that must be eliminated by optimizing factory layouts.
- Excess inventory: Excess inventory can lead to several problems like not identifying defective products in time or increased lead time in the production process, among others.
- Unnecessary motion of people, equipment or machinery: This waste is eliminated by applying scientific management techniques to optimize the motion that people, equipment or machinery do during the production process.
- Waiting (Idle workers or idle equipment): This waste type occurs when employees can’t work because they’re waiting on materials or equipment, or in the opposite case, there can be idle equipment waiting on maintenance.
- Overproduction: Overproduction leads to excess inventory and other issues in the manufacturing process. That’s why lean manufacturing implements the just-in-time production method which consists of only producing what’s demanded by customers.
- Over-processing: This waste consists of adding components or features to a product that aren’t required by the customer, making them unnecessary.
- Defects: Having defective products it’s a waste that must be reduced as much as possible. They can affect customer satisfaction and increase costs.
In addition to these waste types, lean manufacturing experts have proposed an eighth waste type called “unused talent or ingenuity,” which occurs when workers’ opinions aren’t taken into account when identifying waste types and improving manufacturing processes. Their feedback is important because they get to experience issues every day and their thoughts can be helpful in the value stream mapping process.
To simplify things and make it easier to understand for your team members, these waste types can be grouped into three broader categories.
Mura: Unevenness, or waste due to fluctuations in demand. This can come from customer requests, but it can also be due to an organization adding new services and thus additional work.
Muri: Overburden, or waste due to trying to do too much at once. This has to do with resource allocation. When too few people try to do too much work, they often waste time switching from one task to another.
Muda: Non-value-adding work, or process waste. This waste comes as a byproduct of something else. Think about three things: value, work that adds immediate value for a customer; necessary waste, which is supporting activities that add value; and unnecessary waste, activities that don’t add value. Therefore, lean maximizes value, minimizes necessary waste and removes unnecessary waste altogether.
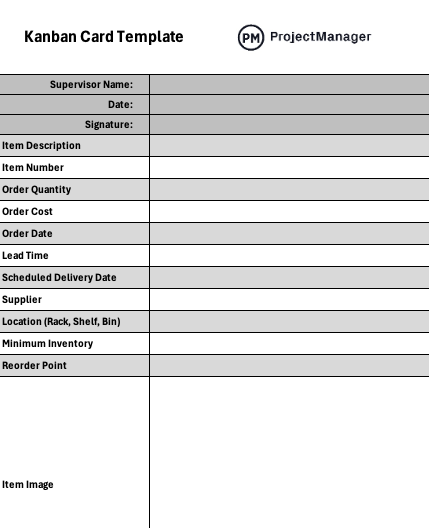
Free Kanban Card Template
Kanban cards are used by lean manufacturing companies to help them manage their inventories. This kanban card template will help you implement a kanban inventory system, which focuses on only ordering production inventory items when they’re needed, which helps minimize production costs, avoid production inventory shortage and optimize the use of warehouse space. Download this template, print it out and revolutionize your inventory management.
Lean Manufacturing Techniques
To apply lean principles to eliminate waste from your manufacturing process, you’ll need to use a set of lean manufacturing tools and techniques. Some of those lean management tools include:
Kanban Boards
Kanban is a project management method that’s used to visualize workflows. Kanban is helpful for lean production because kanban boards allow managers to assign tasks to their teams and track their progress. This helps prevent idle workers and prioritizes the work that creates the most value for customers. Learn more about kanban software.
Gemba
In lean manufacturing, the Japanese term “Gemba” refers to the act of walking down the production line to better identify waste as opposed to having managers theorize about these things from a conference room.
Andon
Andon is an alert system that’s implemented in manufacturing facilities to allow machine operators to alert everyone in the plant that there’s an issue with production that needs to be resolved. This could include a material shortage, machinery malfunction or a quality issue.
Poka-Yoke
Poka-yoke means error-proofing in Japanese. In lean manufacturing, poka-yoke consists of using a device or mechanism that helps avoid human mistakes in the production cycle. For example, some button-activated machines require the operator to turn a key before they press the button to turn them on. This can be considered a poka-yoke mechanism because it helps operators avoid the mistake of turning the machine on unknowingly.
Hoshin Kanri
Hoshin Kanri is a top-down strategic planning approach that starts when executives define long-term goals for an organization. This is then followed by a process of communicating this to all company layers so that all employees are aware of the objectives that must be achieved and how their efforts support the larger goals of the company.

Total Productive Maintenance
Total productive maintenance is an approach that consists of training all operators in a manufacturing facility to be able to diagnose when their machinery needs maintenance to help prevent breakdowns and malfunctions. This allows lean manufacturing organizations to keep their equipment running well and avoid waste.
5S
The 5 “S” is a workplace organization method that’s named after 5 Japanese words and their respective English translation: Sort (Seiri), Set in Order (Seiton), Shine (Seiso), Standardize (Seiketsu) and Sustain (Shitsuke). The goal of this method is to ensure the manufacturing workplace is uncluttered and clean which helps eliminate waste and keep employees safe and productive.
5 Whys
This technique consists of asking “why?” repeatedly to find the root cause of a problem. It helps lean production leaders find the cause of a problem by brainstorming with their teams to then develop potential solutions.
SMED
The single-minute exchange of die (SMED) is a method that’s used in lean manufacturing to limit manufacturing equipment changeover time to less than 10 minutes by doing as many changeover steps as possible while the equipment is running, as opposed to halting production to perform changeover procedures.
How to Implement a Lean Manufacturing System
Now that we’ve reviewed the principles, wastes, tools and techniques of lean manufacturing, let’s go through some of the steps you might take to apply this methodology.
- Map the value stream: As stated above, the main step when implementing a lean manufacturing system is to understand what the value stream of a manufacturing process looks like.
- Establish a pull system: When transitioning to lean production, you should stop producing products if that production isn’t directly tied to customer demand. This eliminates overproduction and excess inventory waste.
- Identify waste in your manufacturing facility: Walk through your manufacturing facility to identify unnecessary transportation of materials, people, equipment and machinery. Then, rearrange your production layout based on your findings.
- Apply the 5S: Now it’s time to establish procedures to keep the manufacturing facility clean and organized.
- Implement Andon and Poka-Yoke mechanisms: Make sure your manufacturing facility has mechanisms to help operators alert their supervisors when an issue occurs and also establish devices to help them avoid mistakes and spot quality issues. These two actions will help you reduce defective products.
- Provide total productive maintenance training: Train your employees to be aware of signs that machinery might need maintenance to prevent breakdown and idle time.
Lean Manufacturing Benefits
Reducing or eliminating waste is essential to lean project management, but the benefits of lean manufacturing can be different depending on who is asked. Some say it’s increasing company profit while others maintain its improvements are solely to create customer value and increase customer satisfaction. Some common goals follow.
- Improve quality: To stay competitive, companies can’t be complacent but must meet customers’ changing wants and needs. Therefore, processes must be designed to meet their expectations and requirements. Adopting total quality management can make quality improvement a priority.
- Inventory management: Thanks to the just-in-time production method, lean production reduces excess inventory, which reduces costs and prevents production issues.
- Process improvement: Lean production systems are always being improved, thanks to the “continuous improvement” lean principle. Value stream mapping it’s essential for this.
- Eliminate waste: Waste is bad for costs, deadlines and resources. It takes without adding any value to a product or service. By eliminating waste, a lean manufacturing system can produce better products, at lower costs.
- Reduce time: Time is money, as the adage goes, and wasting time is therefore wasting money. This is especially true for the manufacturing industry. Reducing the time it takes to start and finish a project will create value by adding efficiencies. Learn and apply some time management strategies.
- Reduce total costs: Money is saved when a company isn’t wasting time, materials and personnel on unnecessary activities. Overproduction also adds to storage and warehousing costs. Understanding the triple constraint is the first step to understanding cost management.
Lean Manufacturing vs. Six Sigma
While both methods are used to improve manufacturing processes, the main difference between lean manufacturing and Six Sigma is that lean production focuses on identifying and eliminating waste, while Six Sigma focuses on quality assurance and control.
Lean Manufacturing vs. Just-In-Time Manufacturing
While both methods are similar as they seek to improve the efficiency of manufacturing processes, the main difference between them is that lean manufacturing is customer-centered as it seeks to remove waste to maximize customer value, while the scope of just-in-time manufacturing is narrower. It focuses on optimizing inventory management, lowering costs and maximizing production profitability.
How ProjectManager Helps With Lean Manufacturing
Using project management software with features that assist in that ambition, such as ProjectManager, is the perfect way to pursue lean manufacturing. You can do this by visualizing the workflow to avoid bottlenecks and give teams only the work they have the capacity and resources to complete.
This is where our kanban project view comes in. The board-and-card system offers transparency into the different stages of production. Cards, which represent tasks, can be moved throughout the board to convey progress, giving teams a quick look at the most pressing tasks. Product backlogs can be managed in this fashion, and the production flow is controlled for greater productivity.
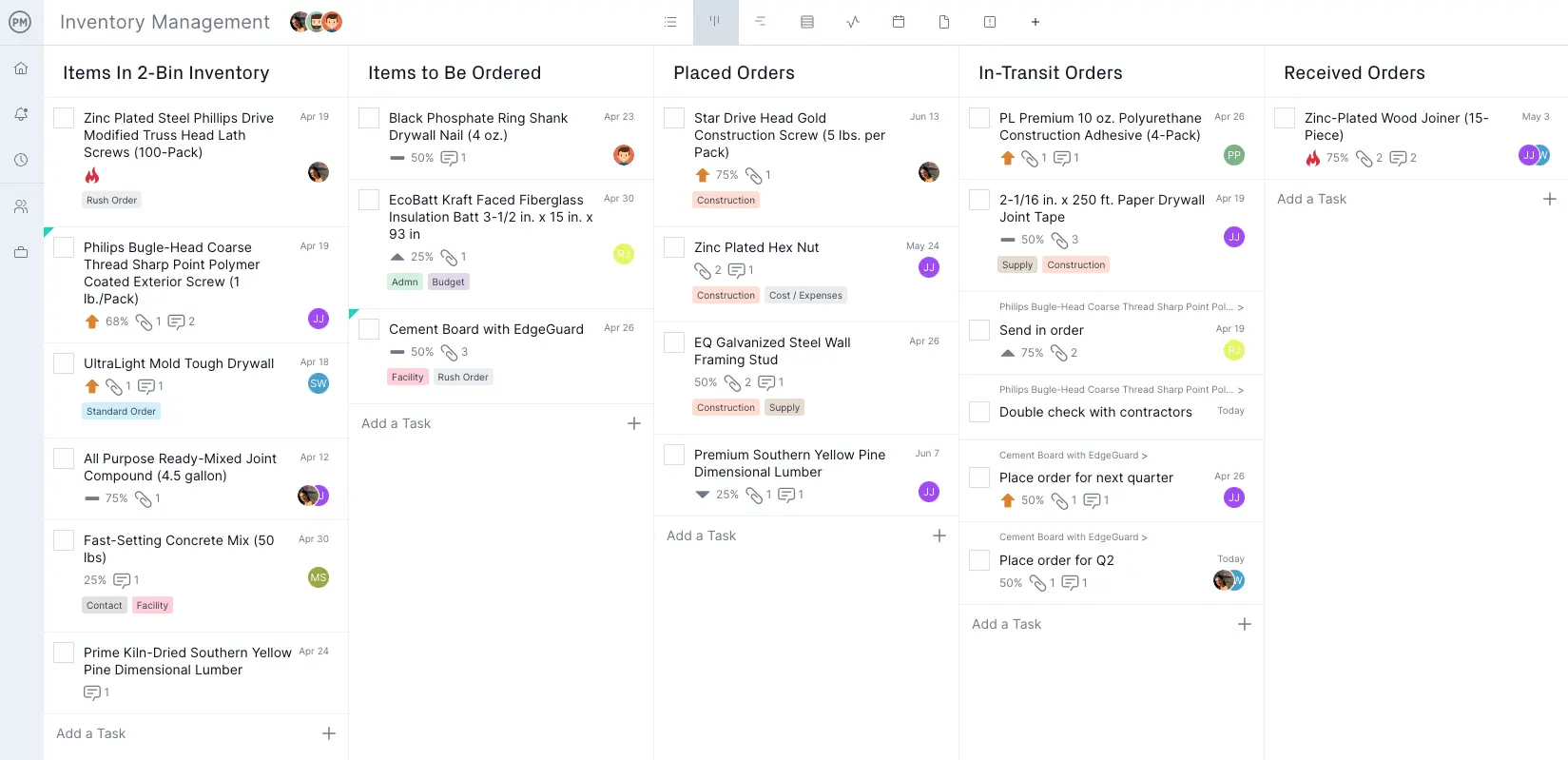
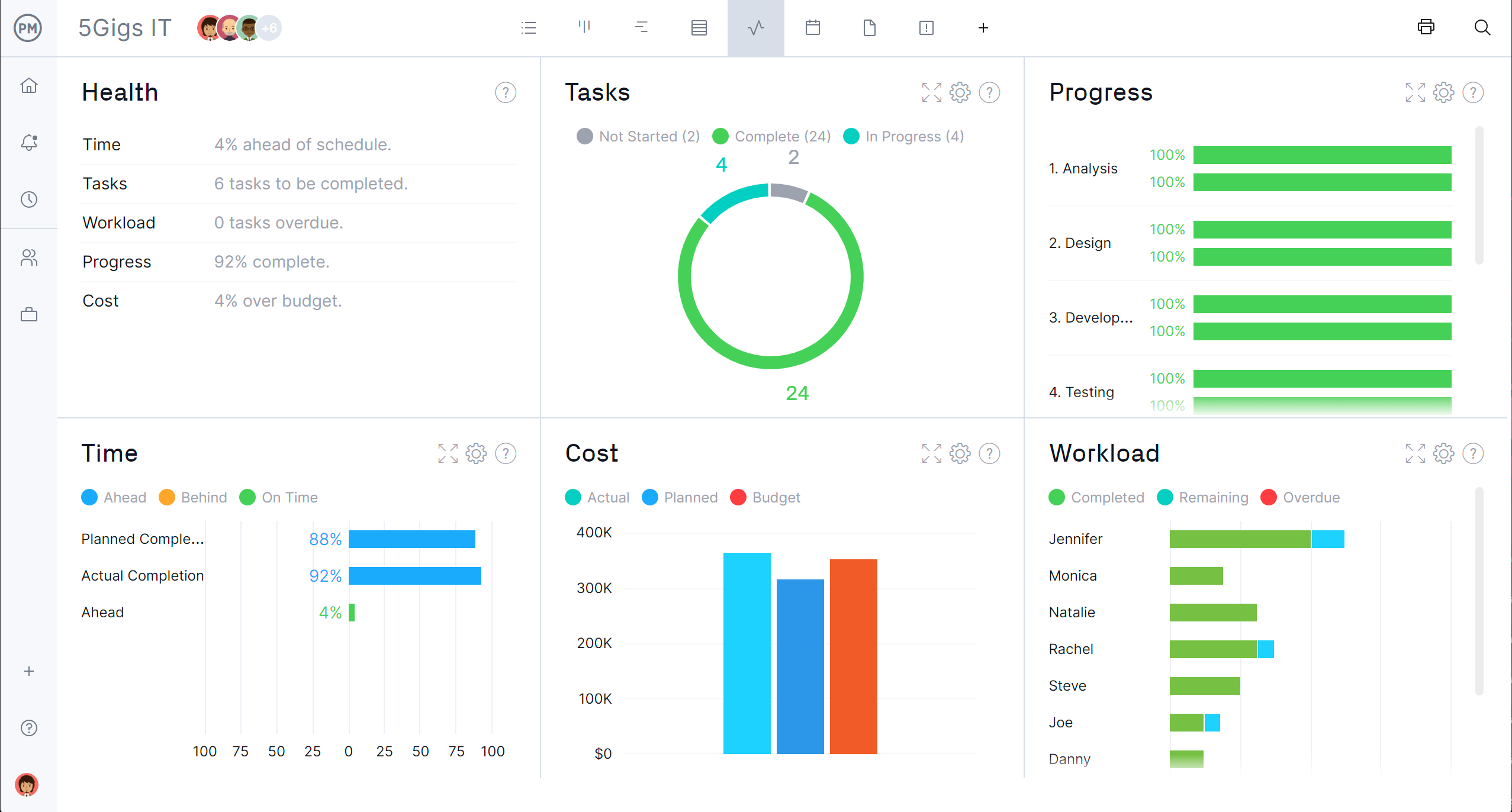
Easily Measure and Report Your Progress
To improve processes, another fundamental for lean, you need data. How are your processes doing? Are they meeting your planned expectations? To measure this, use our real-time dashboard that automatically monitors six key project metrics and displays them in colorful, intuitive graphs. See at a glance how you’re performing in real time—and with single-click reporting, share key data points to keep the team informed.
Related Content
- What Is Lean Project Management?
- What Is Lean Portfolio Management? A Quick Guide
- The 5 Lean Principles: Definitions & How to Use Them
- Ultimate Guide to Kanban
If you’re in the market for reducing waste, improving efficiencies and adding to your productivity through lean management, then you’ll want to use tools that can enhance your workflow, resource allocation and monitoring. ProjectManager is the perfect online project management software to assist you every step of the way. Cut waste today by trying ProjectManager with this free 30-day trial.

