Lean management originated in Japan where it grew out of the Toyota Production System. Today, lean manufacturing is widely used in industries such as project management, software development, construction and more.
Lean principles stem from the Lean Enterprise Institute (LEI), where founders James P. Womack and Daniel T. Jones declared the five key lean principles. Let’s take a look at what those five lean management principles are and the templates and tools that can help you employ them.
Get your free
Inventory Template
Use this free Inventory Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
What Is Lean Manufacturing?
Before we explain the five lean principles, let’s put them in context. In general, lean is a set of management practices designed to remove waste and improve efficiency and productivity. Lean defines waste as anything that does not add value for the customer.
There are eight lean types of waste. The acronym DOWNTIME can help you remember them:
- Defects
- Overproduction
- Waiting
- Non-utilized talent
- Transportation
- Inventory
- Motion and extra-processing
There is also the concept of lean enterprise, which expands the ideology to the entire value stream or supply chain. Lean manufacturing and enterprise ideally work together to reach the fullest expression of the lean philosophy. Any supplier or subcontractor that doesn’t employ lean practices will put a drag on eliminating waste and boosting productivity.
What Are the 5 Lean Principles?
The five lean principles are:
- Defining value
- Value stream mapping
- Creating flow
- Establishing pull
- Continuous improvement
Following these lean management principles proves to be an effective way to manage teams across industries.
Before we explore each one in detail, it’s important to note that without a software tool, it’s nearly impossible to act on them. ProjectManager is work and project management software that lets you eliminate waste by streamlining processes and automating workflows. Continuous improvement is achieved by task approvals that maintain quality deliverables. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
1. Defining Value
Identifying value in a lean project is always defined by what the customer needs for the product. This might mean the time to market, pricing or other expectations that must be met. This is the core principle and must be shared with everyone involved in the project so they always work with the customer’s needs in mind. This is one of the most important lean thinking principles, as helps identify waste.
2. Value Stream Mapping
After you’ve defined the value for your end-user, next you need to map the value stream. This means defining all of the steps and related processes that take your product from raw material to final deliverable. You can also identify the actions to produce your product in design, procurement, HR, administration, delivery and customer service. The map should be on only one page and you should remove any steps that offer no value to the customer.
3. Create Flow
Once you’ve removed the waste from your value stream, it’s time to ensure those steps flow smoothly from one to another. You don’t want any interruptions, delays or bottlenecks that can slow down production and threaten your schedule and budget. To do this, you want the value stream steps to be in a tight sequence. This leads to cross-functional teams that work together across departments to create greater productivity.
4. Establish Pull
“Pull” means that the customer can pull the product with a shorter production cycle, often turning what could have been months into weeks. This lets you avoid having to build in advance or stockpile materials, which saves on inventory costs that can be passed on to your customers. This is all dependent on the flow you created in the previous step.
5. Strive for Perfection
If the first step is the most important of the five lean principles, this step is a close second. It means approaching perfection in all aspects of your corporate culture. Specifically, you want to use this step to loop you back to the first step. Yes, you should never stop following these steps. This continuous improvement, also referred to by the Japanese word kaizen, is essential to lean project management.
Lean Techniques
Lean management principles take concepts and guide them through action. By using these lean thinking principles work can become more efficient, less wasteful and add value to processes and operations. While originating from lean manufacturing, these lean techniques can be applied across various industries. Here are some examples of lean practices.
5S
This lean technique is about organizing and managing the workspace for efficiency and effectiveness. It’s done by following these five words, all of which begin with S. First, sort, which means eliminating unnecessary items. Next, set it in order by organizing tools and materials for easy access. Shine is about keeping the workplace clean. Then standardize to establish procedures for consistency and, finally, sustain to maintain the improvements over time.
Kaizen
Kaizen. or continuous improvement as we mentioned above, is a philosophy that focuses on continuous, incremental improvements in processes and operations. The approach for this is to engage the employees at all levels of the organization. Everyone should be trying to identify and implement improvements.
Kanban
Kanban refers to the visualizing scheduling system that uses cards to signify tasks or activities on a board that is divided into columns, which represent the stages of production. This helps to manage workflow and inventory levels. Using kanban can improve efficiency by controlling work-in-progress and ensuring that resources are utilized effectively.
Poka-Yoke
Poka-yoke is error-proofing. This technique is designed to prevent errors or defects in processes. Ways to error-proof are by creating simple mechanisms or a checklist to ensure that tasks are performed correctly the first time.
Just In Time (JIT)
We’ve mentioned just-in-time when defining kanban. JIT is a philosophy that focuses on continuous, incremental improvements in processes and operations. In an organization, JIT is used to engage employees throughout the business and have them identify and implement improvements.
Heijunka
Heijunka is also referred to as production leveling or workload leveling. It aims to smooth out production processes and reduce waste to improve efficiency. This is done by balancing production over time, rather than producing in large batches that lead to peaks and valleys in the workload.
Value Stream Mapping
Value stream mapping is a visual tool that maps out all the steps in a process to identify value-added and non-value-added activities. The purpose of this lean technique is to find areas of the process that are wasteful, as well as opportunities, that can be addressed and improved.
Employ Lean Principles with These Templates
Templates are a good shortcut to managing a lean project. They can provide you with the tools to produce your products, track progress and more:
Project Brief Template
This free project brief template for Word is a document that starts off any project by defining in broad terms its goals, objectives, constraints, assumptions, scope, target audience, success criteria, budget and more. It’s a good place to capture the value when you’re defining your customer needs.
Gantt Chart Template
Once you have your value defined, you need to map your value stream. ProjectManager’s free Gantt chart Excel template helps you visualize the entire project on a timeline. You can organize raw materials, color-code tasks to make the Gantt chart easier to read and make updates as the project moves forward. It also lets you see the flow and eliminate waste to make the flow as smooth as possible.
Project Dashboard Template
Part of continuous improvement is having the data to see how your project is performing. In order to get a high-level view of your project’s performance and progress, you need ProjectManager’s free project dashboard template for Excel. Once you manually input the data, this free dashboard template creates colorful graphs and charts to show you where you are in terms of completing your tasks, your team’s workload, costs and more.
ProjectManager’s Lean Project Management Tools
ProjectManager is work and project management software that offers more than templates to eliminate waste and help you work more efficiently. Unlike templates, ProjectManager automatically updates in real time and facilitates collaboration across the team. Here are some features that can help you run a lean project.
Kanban Boards
ProjectManager’s kanban boards provide managers with transparency into the production cycle and help give teams the right amount of work they need to meet their capacity. Because you can see the entire production cycle, if there are any bottlenecks ahead, it is fast and easy to reallocate resources and keep everyone working. Teams can manage their backlog and collaborate on sprints for greater productivity.
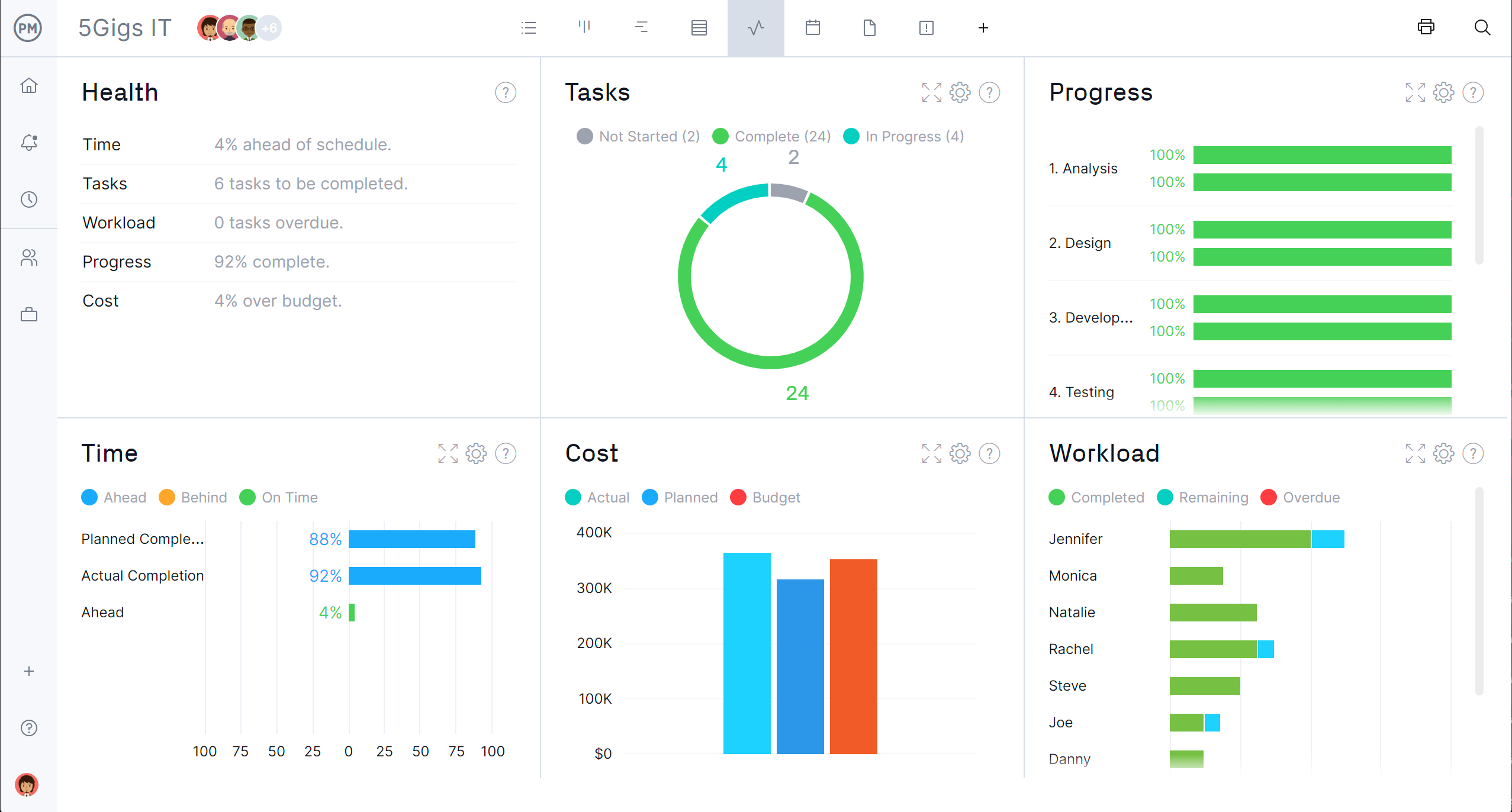
Real-Time Dashboards
For even more visibility into the progress and performance of your project, use our real-time dashboards. There’s no setup required and our live dashboard automatically collects and calculates real-time data, which is then displayed in easy-to-read graphs and charts that pinpoint six project metrics.
Task Automation Software
As mentioned above, you can automate workflows to eliminate waste and boost productivity. Create as many triggers as needed to automatically set up actions that change the assignee, tags and more on any given task. You can even control the task status so it’s not done until the approver says so. This allows you to keep the pace and quality of projects high.

Related Content
- What Is Lean Project Management?
- What Is Lean Construction?
- What Is Lean Manufacturing?
- What Is Lean Portfolio Management? A Quick Guide
ProjectManager is award-winning software that connects hybrid teams on our collaborative to the core platform so they all share one source of truth for more productivity. Join teams from NASA, Siemens and Nestle who have used our tool to deliver success. Get started with ProjectManager today for free!

