Learning how to manage a project successfully is essential for meeting deadlines, staying within budget and delivering results.
How to Manage a Project Step by Step
This guide breaks down how to manage a project step by step, helping you move from project initiation to completion with confidence. Whether you’re leading your first project or refining your process, following a structured approach is key. Each step builds on the last to ensure your project stays on track and aligns with organizational goals and stakeholder expectations.
1. Prepare a Business Case to Justify the Project
A business case explains why a project is worth doing. It presents the problem or opportunity, outlines the proposed solution and shows the benefits of moving forward. This document helps decision-makers evaluate if the project aligns with strategic goals and delivers a strong return on investment. By identifying costs, benefits and risks, a business case ensures the project is based on sound reasoning. It’s the first step to gaining project approval and securing executive support.
A business case helps with the Gantt chart by providing the strategic foundation and justification for the project, which informs the planning and scheduling of tasks. It defines the project’s goals, scope, timeline and expected benefits, all of which guide how the Gantt chart is structured. With a clear business case, project managers can break down objectives into phases, assign tasks and set realistic deadlines in the Gantt chart. This alignment ensures that the visual timeline reflects both the high-level strategy and the practical steps needed to deliver results efficiently.
But not all Gantt charts are created equally. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software with robust Gantt charts that schedule tasks, resources and costs, but goes beyond the typical scope of basic Gantt charts found on less powerful project management software. Our Gantt chart can link all four types of task dependencies to avoid cost overruns, filter for the critical path to identify tasks with zero slack and set a baseline to track work in real time to help keep projects on schedule. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
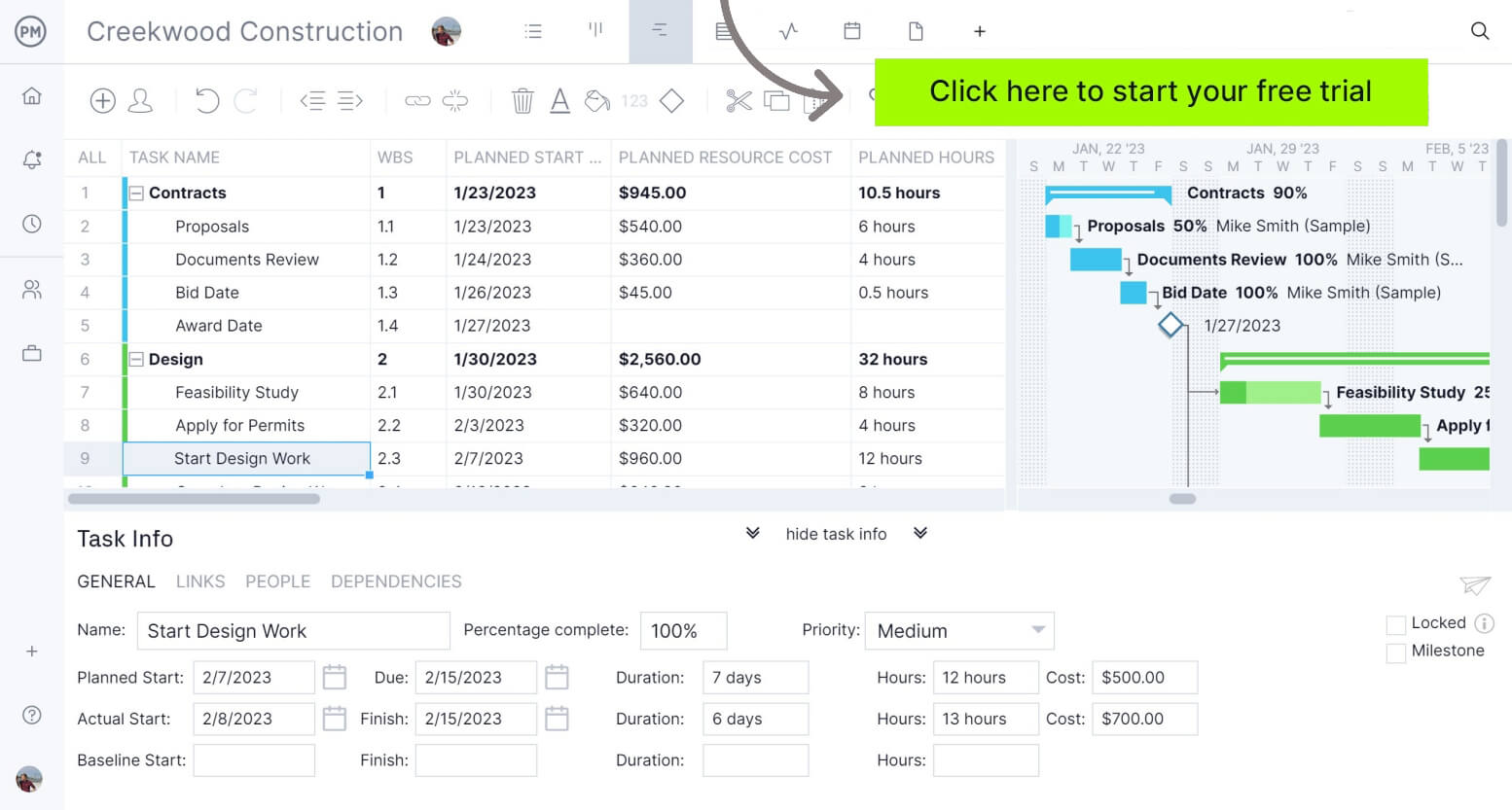
2. Write a Project Charter to Set the Stage for the Project
A project charter formally authorizes the project and outlines its essential details. It typically includes the project’s objectives, scope, stakeholders, timeline and assigned project manager. The charter also identifies key deliverables, constraints and high-level risks.

By defining these elements upfront, the charter creates a shared understanding among stakeholders and sets the foundation for the project plan. It gives the project manager the authority to allocate resources and lead the team. A well-crafted charter helps prevent misunderstandings, scope creep and delays by clearly establishing the project’s direction from the beginning.
3. Use a Work Breakdown Structure to Define the Project Scope
A work breakdown structure (WBS) is a visual tool that breaks down a project into smaller, manageable components. It organizes the total scope of work into deliverables and tasks, starting from the top-level objective down to individual work packages. This hierarchical structure helps clarify what needs to be done and serves as the foundation for project planning and control.
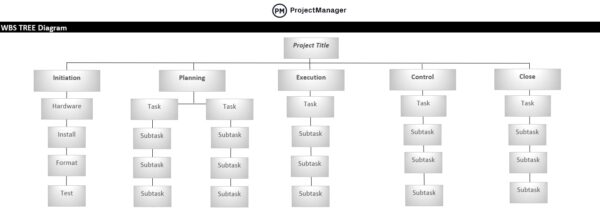
Identifying every task in a project is essential. It enables the project manager to estimate resources, costs and time more accurately. A complete task list supports the development of a realistic project schedule and budget. It also helps in assigning responsibilities clearly and avoiding overlooked work. With every activity accounted for, the project is less likely to encounter delays, cost overruns or confusion about team roles during execution.
4. Identify Resource Requirements for the Completion of Tasks
Once the WBS is complete, the next step is to determine the resources needed for each task. This includes people, equipment, software or materials. Estimating these requirements ensures the project has the right support at the right time. It also helps project managers allocate resources efficiently, avoid shortages and keep the project moving forward without unnecessary delays or overspending.
5. Estimate the Duration of Tasks and Make a Project Schedule
After defining project tasks with the WBS, the project manager must estimate how long each task will take to complete. This involves considering the complexity of the work, the availability of resources and any external constraints.
Once durations are estimated, the next step is to establish dependencies between tasks, determining which activities must be completed before others can start. Sequencing these tasks allows for the creation of a logical workflow. With all this information, the project manager can build a project schedule that shows the order of execution, start and finish dates and the project timeline as a whole.
This schedule serves as a roadmap, helping the team track progress and identify potential delays early. A well-structured schedule is critical for time management and successful delivery.
Related: 38 Project Management Excel Templates & Spreadsheets
6. Estimate Project Cost and Make a Project Budget
Once resource requirements are clear, the project manager can estimate the cost of completing each task. This includes labor, materials, equipment, software and any other needed items. By summing the estimated costs of all tasks, the total project cost can be projected. This becomes the basis for the project budget, which also includes contingency reserves for risks or uncertainties.
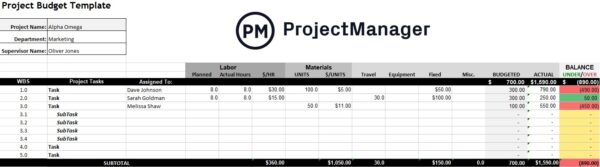
This step is critical, as a well-prepared budget ensures that the project remains financially feasible and provides a reference point to monitor expenses throughout the project. The project manager can then use the budget to request funding, allocate resources and manage costs effectively during execution. Accurate cost estimation and budgeting are essential for maintaining financial control, avoiding overspending and achieving project success within financial constraints.
7. Assemble a Project Team
Now that the project manager has a clearer picture of the project’s scope, tasks, resources and schedule, it’s time to assemble a project team. The team should include individuals with the right skills and experience to carry out the work outlined in the plan. Selecting the right people is essential to project success. Each member should understand their role and responsibilities to ensure collaboration, accountability and efficiency during execution. A strong team sets the foundation for productive project delivery.
8. Identify Project Stakeholders and Make a Communication Plan
Identifying project stakeholders is essential to understanding who will be affected by the project and who can influence its success. Stakeholders may include clients, executives, team members, vendors or end-users. Once identified, the project manager should assess their needs and expectations.

A communication plan outlines how and when stakeholders will be informed, consulted or involved. It ensures transparency, builds trust and reduces misunderstandings. Engaging stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle keeps them aligned and supportive, increasing the chances of successful outcomes.
9. Conduct a Project Kickoff Meeting
A project kickoff meeting is the first official meeting between the project team and stakeholders. It introduces the project, outlines objectives and reviews key elements such as scope, timeline and roles. The meeting sets expectations and provides an opportunity to align everyone involved. It typically marks the transition from planning to execution in the project management process.

The kickoff meeting is a critical step in the project management process because it sets the tone for collaboration and communication. It ensures everyone understands the project’s purpose and their responsibilities. It also helps build team cohesion and stakeholder buy-in from the start. By addressing questions early and creating alignment, the kickoff meeting reduces misunderstandings and prepares the project team for successful execution and delivery.
10. Create a Thorough Project Plan
A project plan is a formal document that outlines how a project will be executed, monitored and controlled. It serves as the master plan for project execution and includes a set of subsidiary plans covering key project management knowledge areas such as scope, schedule, cost, quality, risk, communications, resources and procurement.
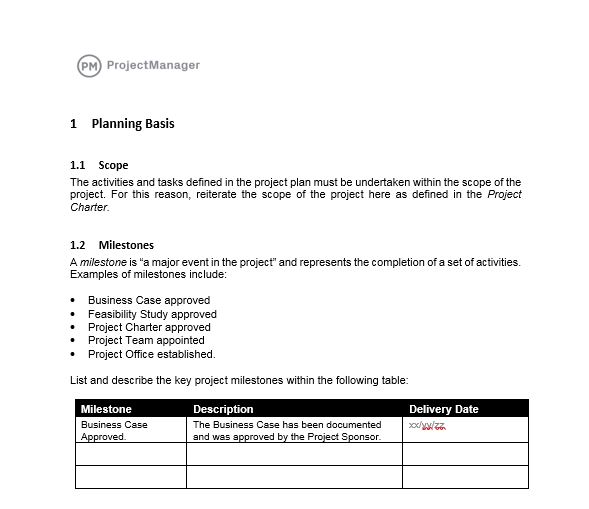
Each plan addresses a specific aspect of the project and provides guidance for managing that area. The project plan is developed during the planning phase and approved by stakeholders. It ensures all team members have a common understanding of how the project will be carried out and what is expected.
A thorough project plan provides direction and structure throughout the project lifecycle. It helps the team stay aligned, manage changes, avoid scope creep and deliver results on time and within budget. It is the cornerstone of effective project management.
Scope Management Plan
The scope management plan outlines how the project scope will be defined, validated and controlled. It ensures that all required work—and only the required work—is included in the project. This plan helps prevent scope creep by providing clear guidelines for managing changes and maintaining alignment with the project’s objectives, deliverables and stakeholder expectations throughout the project lifecycle.
Schedule Management Plan
The schedule management plan defines how the project schedule will be developed, monitored and controlled. It establishes guidelines for estimating task durations, setting milestones and managing changes to the timeline. This plan helps ensure that project activities are executed in the correct sequence and completed on time, providing a framework to keep the project on track and avoid delays.
Resource Management Plan
The resource management plan outlines how human, physical and material resources will be acquired, allocated and managed throughout the project. It identifies roles and responsibilities, skills required and resource availability. This plan helps ensure that the right people and assets are in place when needed, promoting efficiency, reducing bottlenecks and supporting successful project execution and delivery.
Related: 7 Free Resource Management Templates
Change Management Plan
The change management plan describes the process for managing changes to the project scope, schedule, budget or other critical elements. It includes procedures for submitting, evaluating and approving change requests. This plan ensures that all changes are properly assessed and documented, helping the project team maintain control, minimize disruptions and ensure that changes align with stakeholder expectations and project goals.
Budget Management Plan
The budget management plan outlines how project costs will be estimated, budgeted and controlled. It includes procedures for cost tracking, forecasting and managing cost variances. This plan ensures that the project remains within its financial limits by providing structure for financial decision-making and monitoring. It supports transparency, accountability and helps avoid cost overruns during the project lifecycle.
Stakeholder Management Plan
The stakeholder management plan identifies project stakeholders and outlines strategies for engaging them throughout the project. It includes communication preferences, levels of influence and methods for addressing stakeholder needs and concerns. This plan helps build positive relationships, manage expectations and ensure that all relevant parties are informed and involved appropriately, which contributes to project success and stakeholder satisfaction.
Risk Management Plan
The risk management plan defines how project risks will be identified, assessed and mitigated. It includes risk categories, probability and impact analysis and response strategies. This plan enables proactive risk management by preparing for uncertainties before they affect the project. It supports informed decision-making, reduces potential disruptions and increases the likelihood of achieving project objectives and timelines.
Quality Management Plan
The quality management plan outlines how the project will meet quality requirements and standards. It includes quality objectives, control measures, assurance processes and responsibilities. This plan ensures that project deliverables meet stakeholder expectations and comply with agreed-upon criteria. It promotes continuous improvement, reduces rework and supports the delivery of high-quality outcomes throughout the project lifecycle.
11. Establish a Project Baseline
Establishing a project baseline is essential for measuring and controlling project performance. A baseline captures the approved version of the project scope, schedule and budget at a specific point in time. It serves as a benchmark to compare actual progress against planned targets. Without a baseline, it’s difficult to identify deviations or assess performance accurately.
The project manager uses the baseline to monitor changes, evaluate impact and ensure that the project stays aligned with its original goals. Setting a baseline improves accountability, enhances forecasting and provides a solid foundation for managing scope, time and cost throughout the execution phase.
12. Establish Project Controls and Project KPIs
Establishing project controls and key performance indicators (KPIs) is arguably the most important step for monitoring the execution phase. Project controls include tools and processes for tracking schedule, budget, quality and scope. KPIs provide quantifiable metrics that help assess whether project goals are being met.
Examples include cost variance, schedule performance and milestone completion rates. Together, these controls and indicators help project managers detect issues early, take corrective action and maintain alignment with objectives. They also improve communication with stakeholders by offering measurable insights into project health. Effective project controls and KPIs support informed decision-making and drive successful project execution and delivery.
13. Monitor the Project Scope, Budget and Schedule
At this point, all project planning activities have been completed and the project moves into the execution phase. The team begins working on the project deliverables according to the plan. The project manager now shifts focus from planning to managing day-to-day operations. This phase involves coordinating tasks, leading the team and ensuring that all activities align with the project scope, timeline and budget established during the planning phase.
During execution, the project manager must constantly compare planned versus actual performance. Monitoring scope ensures the team is delivering what was promised. Tracking the schedule confirms that tasks are being completed on time. Managing the budget involves checking that spending aligns with cost estimates. Any deviations from the baseline must
14. Communicate with Project Stakeholders
Effective communication with stakeholders is vital throughout the project. The project manager should analyze each stakeholder’s communication preferences—such as frequency, format and level of detail—to ensure messages are well received. Regular project status meetings and written reports help keep stakeholders informed and aligned. Transparent updates on progress, risks and changes foster trust and support. Tailoring communication strategies to stakeholder needs improves engagement, prevents misunderstandings and ensures stakeholders remain invested in the project’s success from start to finish.
15. Conduct a Lessons Learned Session
A lessons learned session is a structured meeting held at the end of a project to evaluate what went well and what could have been improved. The project team and stakeholders reflect on the entire project lifecycle and document insights gained. This session promotes continuous improvement by identifying best practices and mistakes to avoid. It helps future project teams benefit from past experience. Lessons learned sessions contribute to organizational knowledge and support better project outcomes moving forward.
16. Create Project Closing Documentation
As the project concludes, it’s important to complete and organize closing documentation. Three of the most critical documents are the final project report, the formal acceptance document and the lessons learned report. The final project report summarizes performance, deliverables and overall outcomes.

The formal acceptance document confirms that stakeholders have reviewed and approved the project’s results. The lessons learned report captures successes, challenges and improvement opportunities. These documents provide closure, support accountability and serve as a historical record. Together, they validate that the project has met its objectives and is ready to be officially closed, ensuring a smooth transition to operations or the next project phase.
17. Archive Project Data for Future Project Planning
Archiving project data is an essential step for organizational learning and future planning. Past project records—including schedules, budgets, reports and risk logs—can serve as valuable references for estimating timelines, anticipating challenges and improving processes. Well-organized archives also support audits and compliance. By maintaining accessible records, organizations gain insights that help future project managers avoid mistakes, replicate successful practices and deliver more predictable outcomes.
How to Manage a Project Step by Step with ProjectManager
ProjectManager helps manage projects with multiple project views by letting teams work the way that suits them best while staying connected to the same real-time data. The Gantt chart maps out tasks, dependencies and timelines to support detailed planning and scheduling. The kanban board visualizes workflow in columns to help manage progress and identify bottlenecks.
The calendar view organizes tasks by due dates to give a time-based perspective. The sheet view resembles a spreadsheet for those who prefer a grid format. The list view breaks projects into actionable tasks with sortable details like priority and assignee. Together, these views make it easy to plan, execute and adjust work across different roles and preferences.
Manage Resources More Efficiently
Resource management tools—including availability settings, the workload chart and the team page—help ensure projects are properly staffed and running efficiently. Availability settings let managers schedule tasks based on each team member’s actual working hours and time off to avoid conflicts or unrealistic deadlines.
The workload chart shows how tasks are distributed across the team, so it’s easy to spot who is over or under-assigned and rebalance workloads quickly. The team page brings all this information together in one place, showing roles, assignments and capacity at a glance to support better planning and more effective use of resources.
Use Real-Time Dashboards, Reports and Timesheets
Our dashboards, reports and timesheets work together to give teams complete visibility and control over project performance. Dashboards provide live, visual summaries of key metrics like progress, workload and deadlines so managers can monitor activity in real time.
Reports offer deeper insights into areas such as resource use, task status and cost tracking to support data-driven decisions. Timesheets capture actual hours worked, making it easy to track labor costs, approve time entries and ensure accountability. Together, these tools help keep projects on schedule, on budget and aligned with goals.
Related Project Management Content
How to manage a project is answered by studying the basics of project management. For those who want to learn more, read the articles below. They cover hard and soft skills, certifications and the phases that make up every project.
- 22 Project Management Tools & Techniques for Project Managers
- 40 Project Management Skills: Soft, Hard & Technical Skills
- 21 Best Project Management Certifications (2025)
- The 5 Project Management Phases: A Quick Guide
- The 10 Project Management Knowledge Areas – (PMBOK)
- 100+ Project Management Terms: PM Terminology
- 14 Key Project Management Principles & How to Use Them
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams whether they’re in the office or out in the field. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay up to date with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who are using our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.


