Creating a project baseline is critical in effective project management, as it sets the original plan against which progress and performance are measured. It includes key components like scope, schedule and cost, forming a fixed reference point that guides decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
We’ll begin by defining a baseline in project management, its components and how to create one. This is important, as establishing a baseline helps teams stay aligned, manage expectations and quickly identify when things are veering off track, making it an essential tool for maintaining control and ensuring successful delivery.
What Is a Project Baseline?
A project baseline is a fixed reference point representing the original and approved plan for a project’s scope, schedule and cost. It’s established before execution begins and serves as the standard against which project performance is measured. The baseline helps project managers track whether the project is progressing as planned or deviating due to changes, delays or cost overruns.
There are typically three key components of a project baseline.
- Scope baseline, which defines the approved deliverables and work required
- Schedule baseline, which outlines the timeline for those deliverables
- Cost baseline, which sets the approved budget for completing the work
Together, these baselines allow for ongoing monitoring and control. If changes occur, they can be compared to the baseline to assess their impact and determine whether corrective actions or formal change control processes are needed. Without a clear baseline, it’s difficult to assess project performance objectively or justify changes to stakeholders. In short, a project baseline is essential for accountability, transparency and informed decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
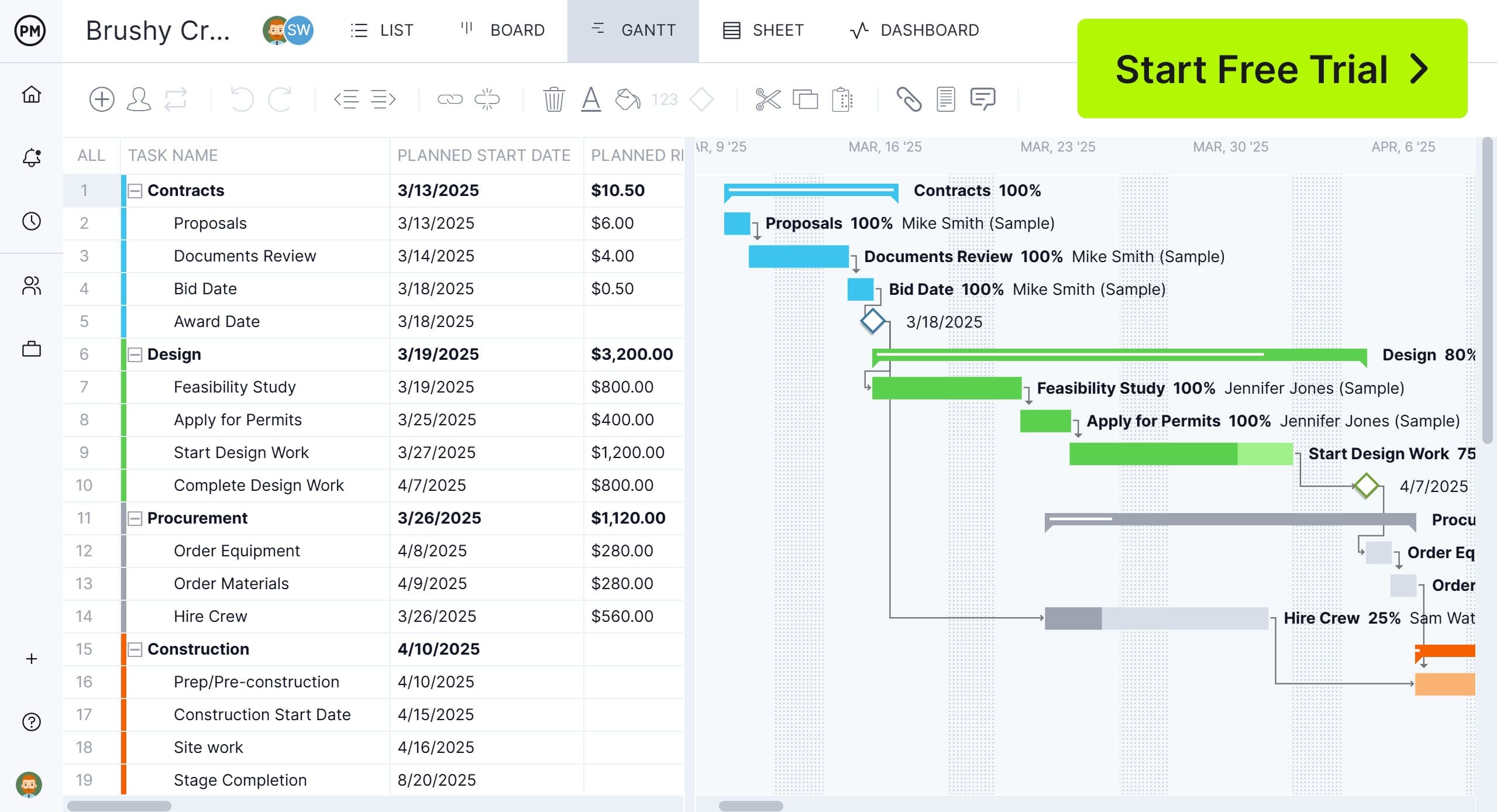
Monitoring a project’s baseline is essential to controlling it and delivering on time, on budget and meeting quality standards. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software with robust Gantt charts that can set a baseline capturing the scope, schedule and cost of the project plan and compare it to actual scope, schedule and cost in real time while executing the project. But that’s not all our Gantt charts do; they can also link all four types of task dependencies to avoid cost overruns and filter for the critical path to identify essential tasks and slack. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
What Makes Up a Project Baseline?
As noted above, the project baseline serves as the foundation for project planning and control, acting as a benchmark against which actual performance is measured. It combines three interrelated components: scope, cost and schedule.
Each of these baselines captures an essential aspect of the project plan and, when managed together, provides a comprehensive view of how the project is expected to unfold. Once approved, these baselines are “frozen” and used throughout the project’s lifecycle to monitor progress, assess changes and guide decision-making. Let’s take a closer look at each of these core elements.
Project Scope Baseline
The project scope baseline defines what the project will deliver—and just as importantly, what it won’t. It includes three key documents: the scope statement, the work breakdown structure (WBS) and the WBS dictionary. These elements outline all project deliverables, work packages and the project boundaries. By setting a scope baseline, project teams agree on what’s included in the project, helping to prevent scope creep, maintain focus and ensure all work aligns with stakeholder expectations.
Project Cost Baseline
The cost baseline is the approved version of the project budget, excluding any management reserves. It aggregates all the estimated costs for tasks, labor, equipment and materials, organized over time. Often presented as a time-phased budget, the cost baseline allows project managers to track spending and compare actual costs to planned expenditures at specific milestones or reporting intervals. Deviations from the cost baseline can trigger corrective action or reforecasting, making it a critical tool for financial control and accountability.
Project Schedule Baseline
The schedule baseline is the approved project timeline that outlines when each task or deliverable should be completed. It’s typically visualized using tools like Gantt charts and includes task durations, start and end dates, dependencies and key milestones. The schedule baseline serves as a reference for tracking progress and evaluating whether the project is on time. When delays or accelerations occur, comparing actual performance to the schedule baseline helps assess impact and make informed rescheduling decisions.
Who Defines the Project Baseline?
Defining the project baseline is a collaborative effort that involves several key roles, each contributing their expertise, priorities and approval to ensure the baseline reflects a realistic and agreed-upon plan. While the project manager typically leads the process, stakeholders, sponsors and the steering committee all play vital roles in shaping and finalizing the baseline.
Project Manager
The project manager is primarily responsible for developing the initial scope, schedule and cost baselines. They gather requirements, estimate resources and timelines and ensure the plan aligns with organizational goals and constraints. The project manager also coordinates inputs from the team and subject matter experts, integrating them into a cohesive and feasible baseline. Once drafted, they present the proposed baseline for review and approval, and ultimately use it as a benchmark for managing the project.
Project Stakeholder
Project stakeholders—including customers, end users and internal departments—play a crucial role in defining the project baseline by providing input on needs, expectations and constraints. Their feedback shapes the scope and determines acceptable timelines and budgets. Engaging stakeholders early ensures the baseline reflects actual business requirements and avoids misalignment later in the project lifecycle.
Project Sponsor
The project sponsor is a senior leader who champions the project and ensures it aligns with strategic objectives. They review and approve the baseline, especially in terms of funding (cost) and high-level deliverables (scope). Sponsors also help resolve conflicts and remove barriers during planning. Their approval is critical to “freeze” the baseline, giving the project the authority to proceed with full backing.
Project Steering Committee
The project steering committee—often composed of executive stakeholders and functional leaders—provides governance and oversight. They typically review and endorse the project baseline for large or high-impact initiatives, ensuring it aligns with organizational priorities and risk thresholds. The committee may challenge assumptions, request revisions or make decisions on trade-offs between scope, time and cost before granting final approval.
When Should the Project Baseline Be Defined?
The project baseline should be defined at the end of the project planning phase and before project execution begins. This timing ensures that all key planning activities—such as defining the scope, estimating costs, and developing the schedule—have been completed and reviewed. By this point, stakeholder requirements should be clearly understood, resources allocated, risks assessed and approvals secured.
Establishing the baseline before work starts is critical because it provides a clear, agreed-upon benchmark against which progress can be measured. Defining it too early risks setting unrealistic expectations due to incomplete information, while defining it too late can lead to uncontrolled work, misalignment and inefficiencies. A well-timed baseline ensures the project launches with clarity, control and a shared understanding of success.
How to Establish a Project Baseline
Establishing a project baseline is a structured process that transforms planning into a concrete, measurable framework. It involves defining clear goals, outlining the work involved, scheduling tasks, estimating resources and costs and setting up a system for monitoring and control. A well-developed baseline integrates the three core components—scope, schedule and cost—into a unified plan serving as a reference point throughout the project. Below are the key steps to creating a comprehensive project baseline.
1. Define the Project Goals and Objectives
The first step is to articulate what the project is intended to achieve. This involves aligning with stakeholders to define success criteria, outcomes and key deliverables. Establishing goals and objectives sets the direction for all subsequent planning and ensures that the baseline reflects the project’s true purpose.
2. Make a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
A work breakdown structure (WBS) breaks the project into manageable components, starting from the highest-level deliverables and decomposing them into smaller work packages. This step is crucial for defining the scope baseline, as it provides a detailed view of all the work that must be done. The WBS ensures no part of the project scope is overlooked and forms the foundation for accurate scheduling and costing.
Related: Free Work Breakdown Structure Template
3. Identify the Critical Path of the Project
After defining tasks, project managers use scheduling techniques to determine the critical path—the sequence of dependent tasks that determines the minimum project duration. This forms the schedule baseline, outlining when tasks should start and finish and identifying which delays will directly impact the project timeline.
4. Estimate the Resource Requirements of the Project
To develop a realistic plan, it’s essential to estimate the types and quantities of resources, such as labor, materials, equipment and time, needed to complete each task. This step feeds directly into defining the cost baseline, as resource needs drive cost estimates and budget planning.
5. Estimate Costs and Make a Budget
With resources identified, the next step is to estimate the costs associated with each task. This includes direct costs (e.g., salaries, materials), indirect costs and contingency reserves for identified risks. When combined with management reserves for unknowns, this forms a comprehensive budget, rounding out the cost baseline.
6. Combine the Scope, Schedule and Cost Baselines
Once the individual baselines are defined, they are integrated to form the complete project baseline. This unified baseline represents the approved plan and is used to monitor performance, manage changes and assess project health throughout the lifecycle.
7. Establish Project Monitoring and Control Measures
Finally, implement tools and processes to track project performance against the baseline. This includes setting up key performance indicators (KPIs), using dashboards or tracking systems and conducting regular status reviews. These measures ensure deviations from the baseline are quickly identified, allowing for corrective actions and informed decision-making during execution.
Benefits of Establishing a Project Baseline
Establishing a project baseline offers numerous advantages that help ensure a project stays on track and meets its objectives. As a formal reference point, the baseline provides clarity, structure and a solid foundation for performance measurement throughout the project lifecycle. Here are the key benefits.
- Provides a clear point of reference
- Enables effective performance tracking
- Improves decision-making
- Facilitates change control
- Increases accountability
- Enhances stakeholder communication
Related Project Management Templates
While a project baseline is best created and tracked in project management software, which can filter for the critical path and track it against actual effort in real time, for those who aren’t ready to upgrade, there are free templates that can help. We have over 100 free project management templates for Excel and Word available for immediate download on our site. They cover all aspects of managing projects across many industries. Here are a few.
Critical Path Template
Download this free critical path template for Excel to identify and visualize the sequence of dependent tasks that determine the minimum time needed to complete a project. This sequence, known as the critical path, includes tasks with zero slack, meaning any delay in one of these tasks will delay the overall project timeline.
Gantt Chart Template
Use this free Gantt chart template for Excel to visually map tasks along a timeline, showing their start and end dates and duration. Named after its inventor, Henry Gantt, the chart is typically structured with a vertical axis listing project tasks and a horizontal axis representing time. Horizontal bars plotted across the timeline indicate when each task begins and ends, allowing for a clear overview of the project schedule.
Project Budget Template
This free project budget template for Excel is used to estimate, track and manage the financial aspects of a project. It outlines all the projected costs associated with the project, including labor, materials, equipment, overhead and other costs. The template organizes these costs by tasks and project phases, allowing visibility into how funds are allocated and spent.
How ProjectManager Helps Establish and Maintain a Project Baseline
As we’ve mentioned above, creating and managing a project baseline with templates is not ideal. Templates, after all, are static documents that are not up to the job of dealing efficiently with dynamic projects. Think about it, do you want to constantly leave the project to manually update a template? Let’s not even get into the lack of collaboration baked into templates.
Project management software clears those hurdles, but not all software is equal. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software with multiple project views that are all updated in real time. Managers love our Gantt charts and sheet view, teams execute their tasks on task lists or kanban boards, while stakeholders stay updated on the calendar view.
Improve Allocation With Resource Planning
Our software goes further than multiple project views, with powerful resource management tools that allow users to assign specific resources to individual tasks. We provide visibility into hourly rates, availability workload with color-coded charts that show who is overallocated or underutilized.
Project managers can balance the team’s workload right from the chart. All this helps to align the scope of work with realistic resource capabilities. There’s also a team page for a daily or weekly summary of team activity, where tasks can be updated as needed.

See Real-Time Performance at a Glance
Some features play a critical role in maintaining and monitoring the project baseline. For a high-level overview, toggle over to the real-time project and portfolio dashboards that instantly compare actual progress against the baseline scope, schedule and cost, which helps to spot delays and cost overruns.
Data-driven reports are customizable to focus on the important data points or share progress reports with stakeholders. Even the secure timesheets help by tracking labor costs to stay on budget.

Related Project Management Content
A project baseline is one part of the larger project management process. For those who want to open the lens a bit and learn more about managing projects, check out the links below. There are blog posts on the basics, principles, tools and techniques.
- Project Management Basics: Definitions, Methods and Tools
- Key Project Management Principles & How to Use Them
- Project Management Tools & Techniques
- Top 15 Project Management Methodologies: An Overview
- PMBOK: The Project Management Body of Knowledge
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams whether they’re in the office or out in the field. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who use our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.