Earned value analysis is one of the most reliable ways to measure performance across cost and schedule in any project. Teams use it to track planned work, actual progress and budget usage in real time so they can stay ahead of problems before they cause delays or cost overruns. Whether you are in construction, manufacturing or software development, earned value analysis helps project managers gain insight into project health and make confident decisions about scope, schedule and resources.
Modern teams are under pressure to deliver faster with fewer resources, and earned value analysis in project management gives them the data they need to succeed. By combining planned value, earned value and actual cost, project leaders can see if they are ahead or behind schedule and over or under budget. This approach is used everywhere from earned value analysis in construction projects to earned value analysis in software project management, providing a single view of performance that aligns the entire team.
What Is Earned Value Analysis?
Earned value analysis is a project management technique that integrates cost, schedule and scope to measure performance. It compares planned work against completed work and the actual cost to determine if the project is progressing as expected. By calculating metrics such as cost variance, schedule variance and cost performance index, teams can see exactly where they stand at any point during the project.
When teams use earned value analysis, they get a single, objective measure of progress that highlights whether they are ahead, on or behind schedule and whether costs are within budget. This is why earned value analysis in project management is a preferred method for complex projects such as construction, manufacturing or earned value analysis in software engineering, where tracking performance is critical.
Using software streamlines earned value analysis by automating calculations and consolidating project data in one place. Instead of manually pulling information from spreadsheets, teams can see earned value analysis metrics like planned value, earned value and actual cost updated in real time. This helps project managers identify issues early and take corrective action quickly.
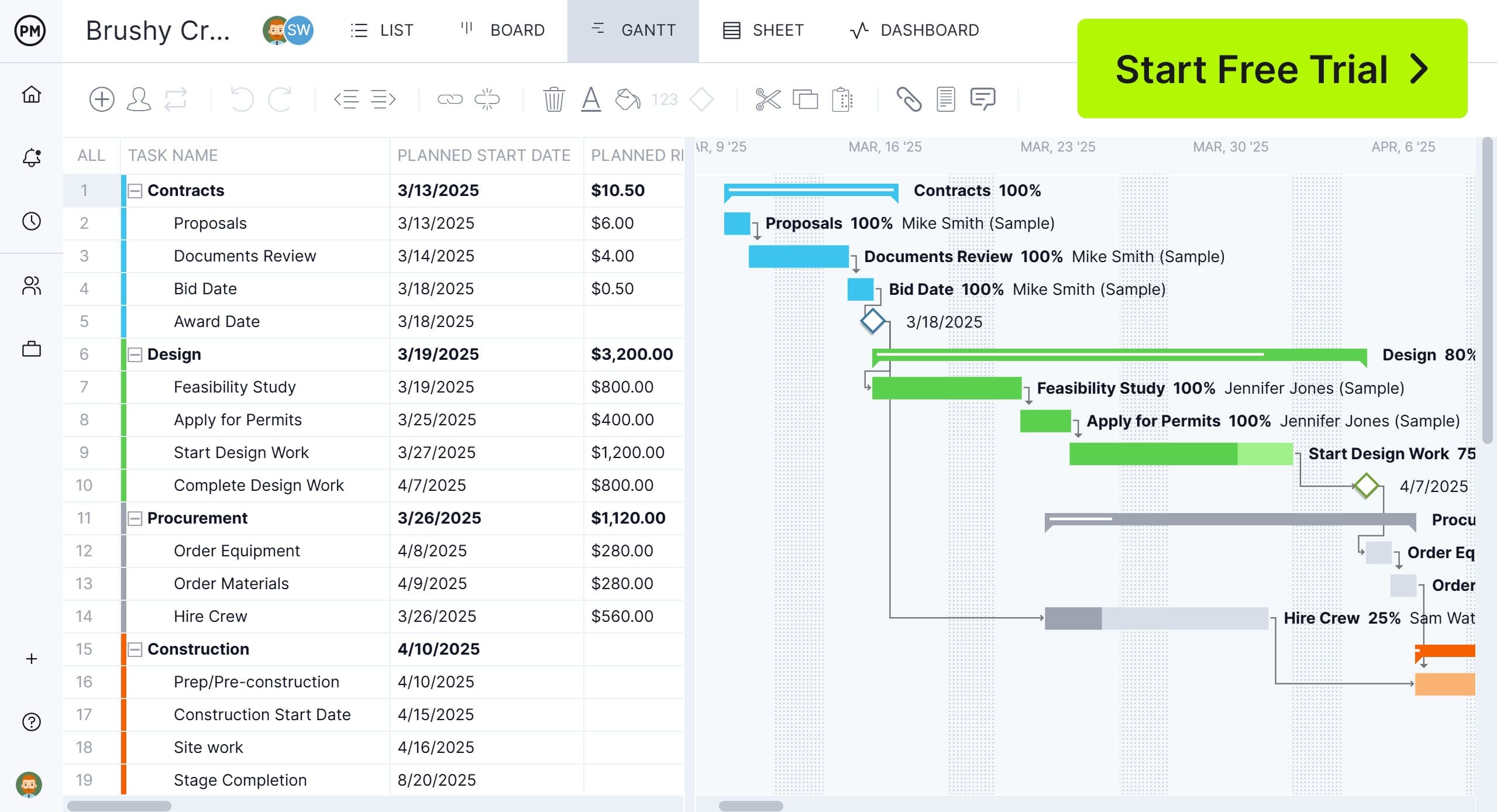
ProjectManager makes earned value analysis simple and powerful with Gantt charts that link all tasks and dependencies, real-time dashboards that track cost and schedule performance, and reporting tools that instantly generate earned value analysis reports. You can set a project baseline to measure variance, use workload management to balance resources and track actual costs directly in the software. This combination of planning, tracking and reporting makes our software the perfect tool for earned value analysis project management across industries. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
Why Is Earned Value Analysis Important in Project Management?
Earned value analysis is important in project management because it provides a single, objective way to measure project health. Instead of looking at cost and schedule separately, earned value analysis combines them to show whether the work being completed matches the plan. This helps project managers see potential issues earlier, avoid budget overruns and keep the project on schedule.
Without earned value analysis, teams might not notice problems until deadlines are missed or costs have already exceeded the budget. By using earned value analysis, project management teams can monitor performance in real time, compare planned versus actual progress and make informed decisions quickly. This level of insight is essential for industries such as construction, manufacturing and software development, where delays or cost overruns can be expensive.
When Should Earned Value Analysis Be Implemented in a Project?
Earned value analysis should be implemented as early as possible in the project life cycle, ideally during the planning phase. Setting a baseline for scope, cost and schedule before work begins allows earned value analysis to provide accurate insights throughout the project. Without a baseline, it is impossible to measure performance or variance effectively.

Get your free
Project Plan Template
Use this free Project Plan Template to manage your projects better.
Get the Template
Once work is underway, earned value analysis in project management should be used consistently at regular intervals, such as weekly or monthly status meetings. This ensures that variances are detected quickly and corrective action can be taken before problems escalate. By making earned value analysis a recurring activity, teams can maintain control over budget, schedule and deliverables.
Benefits of Earned Value Analysis in Project Management
Earned value analysis offers project managers clear, data-driven insights that go beyond basic progress tracking. By combining cost, schedule and scope, this approach gives teams a complete picture of project performance and enables better decision-making. Here are some of the key benefits of earned value analysis in project management.
- Objective Performance Measurement: Provides a single metric to assess cost and schedule performance without guesswork.
- Early Problem Detection: Highlights variances quickly so managers can act before they affect deadlines or budgets.
- Better Forecasting: Uses data trends to predict future performance and completion dates with greater accuracy.
- Improved Cost Control: Tracks planned value, earned value and actual costs to manage budgets more effectively.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Gives teams real-time information to support corrective actions and resource adjustments.
- Supports Stakeholder Communication: Presents clear, quantifiable project status updates for stakeholders and executives.
- Integrates Schedule and Budget: Aligns financial data with the project timeline for a comprehensive view of health.
- Boosts Accountability: Makes team performance visible, encouraging ownership and timely task completion.
Related: 20 Best Resource Management Software of 2025 (Free & Paid)
12 Key Earned Value Analysis Metrics and Formulas
To get the most value from earned value analysis, project managers need to understand the key metrics and how to calculate them. These earned value analysis formulas transform raw project data into actionable insights that reveal cost and schedule performance. Mastering these calculations allows teams to spot trends early, take corrective action and improve overall project outcomes.
1. Planned Value (PV)
Planned Value (PV) is the authorized budget for the work scheduled to be completed by a certain point in time. It’s one of the core earned value analysis metrics that allows project managers to measure whether their project is on track against the original plan. By comparing PV to actual progress, teams can determine if they are ahead, behind or right on schedule, which helps drive better resource allocation and timely decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
Planned Value Formula
Planned Value (PV) = Planned % Complete × Budget at Completion (BAC)
2. Earned Value (EV)
Earned Value (EV) represents the value of work actually completed as of a certain date, expressed in monetary terms. This earned value analysis metric provides insight into how much of the budgeted work has been finished, regardless of how much was spent. Comparing EV to planned and actual costs allows project managers to spot cost overruns early, validate schedule performance and adjust workloads before delays or overspending grow into major project risks.
Earned Value Formula
Earned Value (EV) = Actual % Complete × Budget at Completion (BAC)
3. Actual Cost (AC)
Actual Cost (AC) is the total amount spent to accomplish the work completed so far. This earned value analysis metric includes all direct and indirect costs, such as labor, materials, equipment and overhead. Tracking AC is essential to understanding whether your project is within budget and where money is being consumed most rapidly. When compared with EV, it provides a clear picture of cost efficiency and highlights potential overspending before it becomes critical.
Actual Cost Formula
Actual Cost (AC) = Sum of all costs incurred so far
4. Schedule Variance (SV)
Schedule Variance (SV) shows the difference between earned value and planned value, telling you if the project is ahead or behind schedule. This earned value analysis metric is measured in currency or work hours, giving teams a tangible figure they can use to communicate progress. A positive SV means the project is ahead of schedule, while a negative SV indicates a delay, prompting corrective actions like reassigning tasks or adjusting timelines.
Schedule Variance Formula
Schedule Variance (SV) = EV – PV
5. Cost Variance (CV)
Cost Variance (CV) compares the earned value to the actual cost, revealing whether the project is under or over budget. As one of the most widely used earned value analysis metrics, CV enables teams to control spending by monitoring financial performance in real time. A positive CV shows that the project is costing less than planned, while a negative CV warns of cost overruns that need immediate management attention.
Cost Variance Formula
Cost Variance (CV) = EV – AC
6. Schedule Performance Index (SPI)
The Schedule Performance Index (SPI) is a ratio that shows how efficiently time is being used compared to the original schedule. This earned value analysis metric is especially useful for forecasting whether the project can be completed on time. An SPI greater than 1.0 means work is progressing faster than planned, while a value below 1.0 signals schedule inefficiency, allowing managers to take proactive measures to recover lost time.
Schedule Performance Index Formula
Schedule Performance Index (SPI) = EV ÷ PV
Related: 7 Free Resource Management Templates
7. Cost Performance Index (CPI)
The Cost Performance Index (CPI) is a powerful earned value analysis metric that measures cost efficiency for the work performed. It tells project managers how much value is being delivered per dollar spent. A CPI above 1.0 indicates the project is under budget and using resources effectively, while a CPI below 1.0 reveals that costs are higher than planned, signaling the need to control spending or adjust resource usage.
Cost Performance Index Formula
Cost Performance Index (CPI) = EV ÷ AC
8. Budget at Completion (BAC)
Budget at Completion (BAC) is the total approved budget allocated for the entire project. This earned value analysis metric is a baseline that all other cost-related metrics reference, allowing teams to gauge financial health throughout the project. Knowing the BAC ensures that managers can measure progress against the full budget, assess whether spending patterns are sustainable and accurately forecast final project costs using other earned value formulas.
Budget at Completion Formula
Budget at Completion (BAC) = Total planned budget
9. Estimate at Completion (EAC)
Estimate at Completion (EAC) forecasts the total cost of the project based on current performance trends. This earned value analysis metric is vital for predicting budget outcomes and deciding whether corrective actions are needed. By comparing EAC to BAC, project managers can see if the project is expected to come in under or over budget and make informed choices about resource reallocation or scope adjustments.
Estimate at Completion Formula
Estimate at Completion (EAC) = AC + (BAC – EV) ÷ CPI
10. Estimate to Complete (ETC)
Estimate to Complete (ETC) calculates how much more money will be required to finish the remaining project work. This earned value analysis metric helps managers plan for future expenditures, ensuring there are enough resources available to complete the job. ETC also allows for better cash flow management and helps teams avoid last-minute budget surprises by providing a clear picture of upcoming financial needs.
Estimate to Complete Formula
Estimate to Complete (ETC) = EAC – AC
11. Variance at Completion (VAC)
Variance at Completion (VAC) predicts the difference between the original budget and the forecasted final cost of the project. This earned value analysis metric lets managers know whether the project will finish under or over budget. A positive VAC means savings are expected, while a negative VAC signals potential overspending, giving teams time to take preventive actions and mitigate financial risks before the project concludes.
Variance at Completion Formula
Variance at Completion (VAC) = BAC – EAC
12. Time Estimate at Completion (Time EAC)
Time Estimate at Completion calculates how long it will take to finish the project based on current schedule performance. This earned value analysis metric gives project managers a data-driven way to forecast completion dates and assess schedule risk. If the time EAC shows a delay, teams can implement schedule compression techniques like fast-tracking or crashing to bring the project back on track and meet critical deadlines.
Time Estimate at Completion Formula
Time Estimate at Completion (Time EAC) = Planned Duration ÷ SPI
Free Project Management Templates
Free project management templates make it easier to plan, track and deliver projects efficiently without starting from scratch. They save time and bring consistency to how teams manage tasks, budgets and timelines. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced manager, these templates give you a structured way to organize information and collaborate with your team so nothing falls through the cracks during a project’s life cycle.
Gantt Chart Template
Download this free Gantt chart template to schedule tasks, set dependencies and visualize project timelines in one easy-to-read view. It helps project managers see how work overlaps, spot potential delays early and make real-time adjustments to keep the project moving. This template is great for keeping teams aligned and communicating deadlines clearly across multiple stakeholders.
Project Budget Template
Use this free project budget template to plan costs, allocate resources and track spending as the project progresses. It shows where money is being spent and compares it against the planned budget so you can quickly catch overruns. This template ensures better financial control and supports more accurate forecasting for future projects.
Project Review Template
This free project review template captures key lessons learned, successes and areas for improvement once the project is complete. It creates a consistent format for evaluating performance, analyzing metrics and documenting feedback. This template helps teams refine processes and apply best practices to future projects for continuous improvement and greater efficiency.
How to Manage Projects With ProjectManager
Managing projects with ProjectManager gives teams a central hub where planning, collaboration and execution come together. Its cloud-based platform allows managers to build schedules, assign tasks and set deadlines while giving teams a real-time view of project progress. With everything stored in one place, communication improves and projects stay organized from start to finish.
Visualize and Organize Work
Use ProjectManager’s multiple project views to see work in the way that makes the most sense for your team. Switch between kanban boards for workflow management, task lists for detailed breakdowns, sheet view for spreadsheet-style planning and calendar view for scheduling. These views help teams stay aligned, spot bottlenecks quickly and keep every task moving toward completion.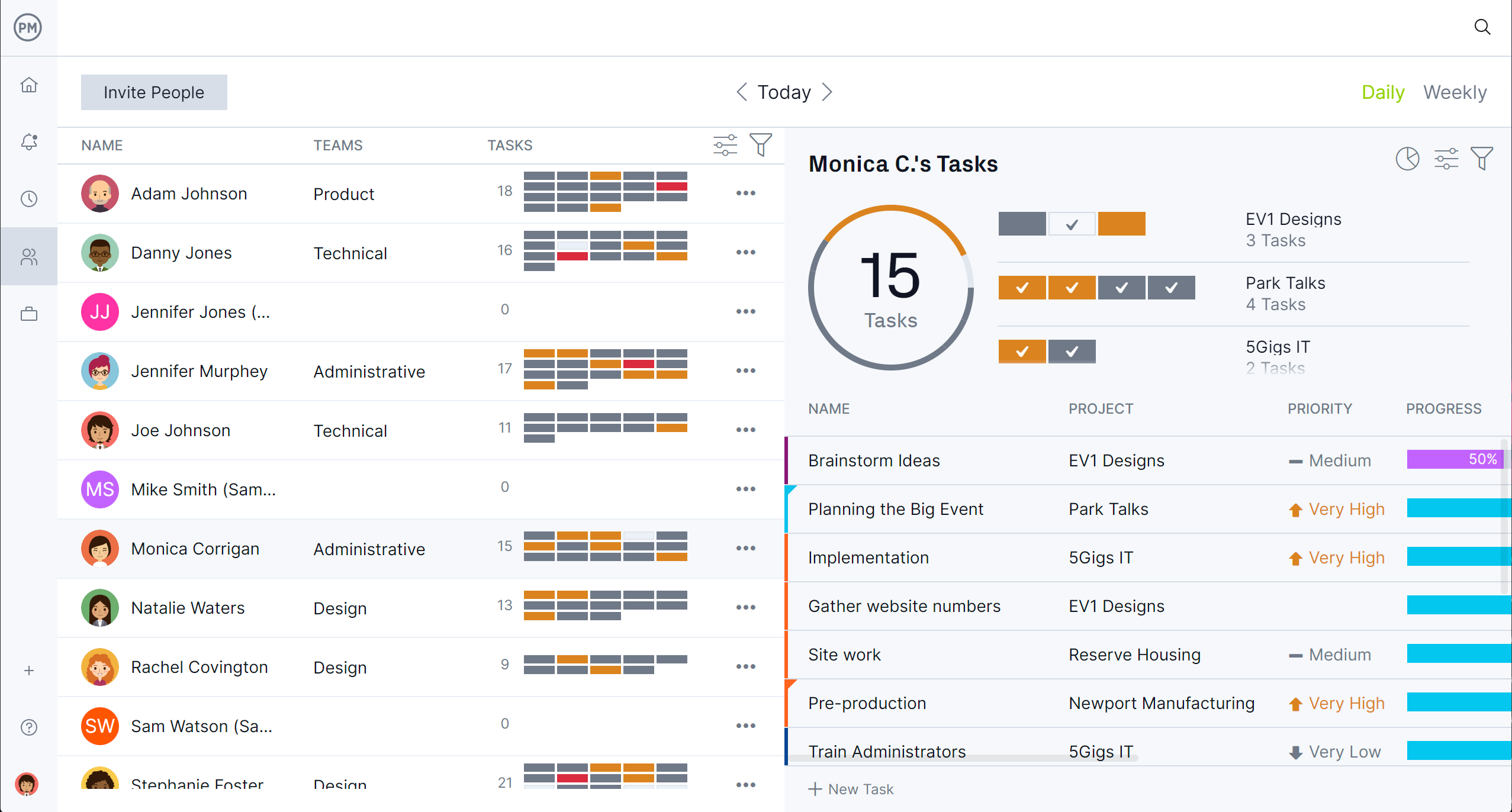
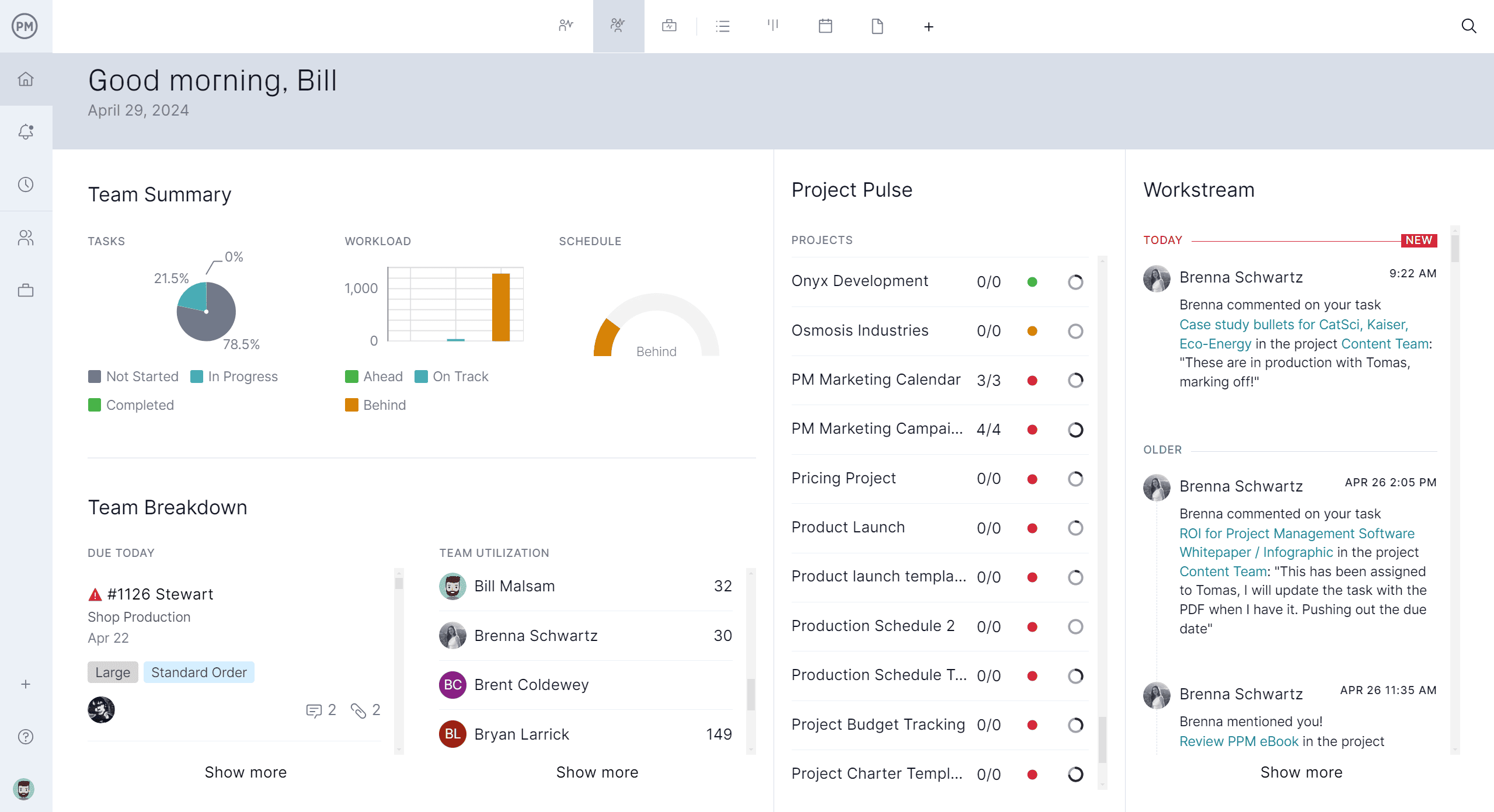
Track and Optimize Performance
Monitor project health with real-time dashboards and customizable reports that track progress, cost and workload. Set baselines to measure variance, filter data to focus on critical tasks and share reports instantly with stakeholders. This makes it easier to identify risks, adjust resources and optimize performance to keep projects on time and within budget.
Related Earned Value Analysis Content
For readers who want more on earned value analysis, check out the links below. They go into using it to measure project performance, as well as related categories, such as cost and schedule variance.
- How to Calculate Cost Variance for a Project
- Using Earned Value Management to Measure Project Performance
- Schedule Performance Index (SPI): An Introduction
- Schedule Variance: What Is It & How Do I Calculate It?
- Cost Performance Index (CPI) In Project Management
- Calculating Estimate at Completion (EAC)
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams, whether they’re in the office or out in the field. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

