To ensure that your project is meeting scheduling and budget milestones, you need to have project metrics to measure your progress and performance. Project metrics are essential to delivering a project on time and within its budget.
But what are project metrics? Why are they so important to a project? We’ll answer those questions and show you some examples of common project metrics. Then we’ll explain what a project metrics dashboard is and why it’s one of the essential project management software features.
What Are Project Metrics?
Project metrics are data pulled from the performance of the project. They are data sets, formulas and calculations that provide measurements to chart progress, success and much more. Project managers use project metrics to compare their actual effort against their plan so they know if they’re on schedule and keeping to their budget.
They can also be used to keep project stakeholders informed, though they’re usually only interested in two project metrics: time and cost. Project metrics are also tools that help organizations find, reduce and alleviate risks as well as inform effective strategic development, continuous improvement and even employee and customer sentiment.
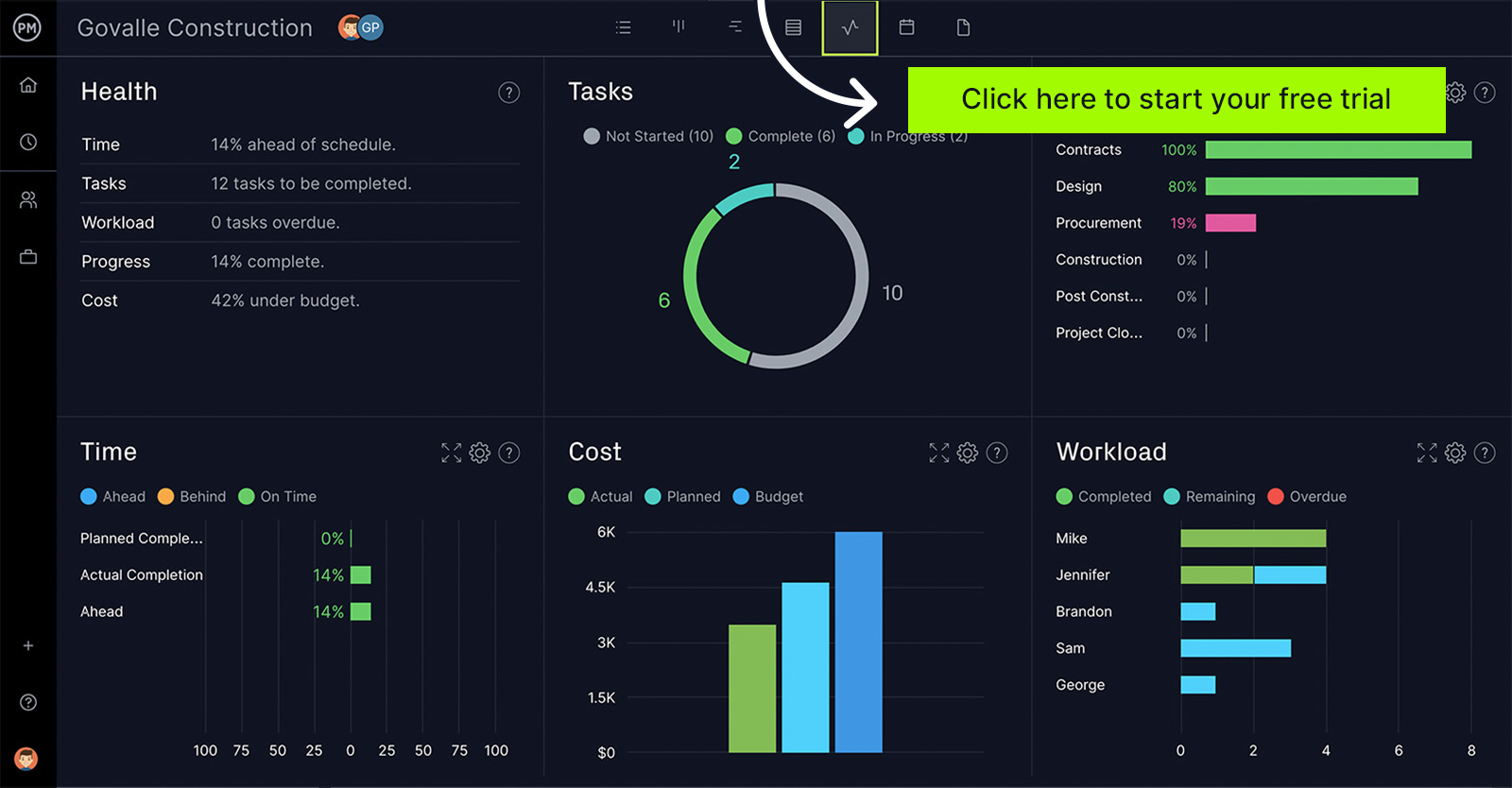
Project management software makes gathering and calculating project metrics easier. ProjectManager is award-winning project management software that has real-time dashboards that automatically gather six types of project metrics and display them in easy-to-read graphs and charts. Unlike other project management software, our live dashboard doesn’t take forever to set up. All you have to do is toggle over for a high-level overview of the project. It’s ready with real-time data for more insightful decisions whenever you are. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
Why Are Project Metrics Important?
Project metrics are important for project management. Without them, you’re driving blind, with no way to accurately measure if you’re keeping to your schedule and budget. They’re used to define a project’s health, progress and performance.
All projects hit bumps in the road, but project metrics help you get back on track faster. That’s because you know you’ve gone off the road quicker and can reallocate resources as needed to get back on track faster.
There would be no way to know if you’re meeting project goals without project metrics until the very end of the project. At that point, it’s too late. Metrics improve performance which will positively impact an organization’s bottom line.
Organizations can see the return on investment (ROI) of their projects. They can use project metrics as the data that drives their decision-making process. That leads to better prediction of future outcomes and allows organizations to adjust their business strategies to stay competitive.
Project Management Metrics Examples
So what are some examples of project metrics? There are many, but we’ll define some of the more common ones that are tracked when managing a project. Use these project metrics to keep track of your project and make sure you deliver it successfully, on time and within budget.
1. Net Profit Margin
The net profit margin is the measurement of an organization’s net earnings after the expenses have been accounted for, including its interest and tax payments. In terms of measuring a project’s profitability, the net profit margin is a useful project metric for keeping track of the budget against the actual spending at that point in the project.
2. Gross Profit Margin
The term gross profit margin is a financial project metric that project managers use to assess the project’s financial health. To get the gross profit margin, subtract the direct expenses or cost of goods sold (COGS) from net sales, which is the gross revenues minus returns, allowances and discounts. That number is divided by net revenues, then multiplied by 100 percent. The project with the higher gross margin is more profitable because it generates more profits and incurs fewer costs.
3. Return on Investment (ROI)
The return on investment is used to determine if the project is going to be worth the time and effort necessary to deliver it. It basically calculates the amount of money that has to be spent and the amount of money or benefits that will result from a successful delivery of the project. ROI is expressed as a percentage and is calculated by dividing an investment’s net profit (or loss) by its initial cost or outlay.
3. Cost Variance (CV)
The project metric cost variance is used to evaluate the financial performance of your project. It does this by determining the difference between the budgeted cost of work performed (BCWP) and the actual cost of work performed (ACWP). In other words, by comparing the current costs of the project to where the budget says you should be at this point in the project. If the two figures are the same, then you’re on the right track. However, if you’re spending more than you’ve budgeted for at that point in the project, then you have to adjust either the project scope or schedule to get back on track.
4. Schedule Variance (SV)
Just as cost variance tracks the financial performance of the project, schedule variance is used to figure out how much a project is ahead of schedule or behind schedule. It does this by measuring the actual progress of the project and comparing that to the expected progress, according to the project schedule. As with cost variance, if the project is behind schedule, then the scope or budget of the project has to be adjusted.
Get your free
Budget Proposal Template
Use this free Budget Proposal Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
5. Cost Performance Index (CPI)
To measure the cost efficiency and financial effectiveness of a project, project managers use the cost performance index. To calculate this, the formula is earned value (EV) / actual cost (AC) = cost performance index (CPI). The cost performance index ratio with a value higher than 1 indicated that the project is performing well in terms of its budget.
6. Earned Value (EV)
Earned value is used to measure and monitor how much work has been done on a project in comparison to the project plan. You can use it to see if you’re on, behind or ahead of your project schedule. To calculate the earned value, multiply the percentage complete by the total project budget. To get more from your earned value project metric, use it with the cost and schedule variance project metrics.
7. Planned Value (PV)
According to the Project Management Institute (PMI), planned value in project metrics is “the authorized, time-phased budget assigned to accomplish the scheduled work.” That means, it’s putting the project cost over the time baseline at any point in the schedule. Project managers can use this project metric to identify deviations from the project plan and mitigate issues faster. To calculate this, find the percent of the project completed (planned) multiplied by the budget at completion (BAC).
8. Actual Cost (AC)
When you’re talking about actual cost in a project, you mean the true total and final costs accrued in the project. It’s made up of such costs as direct labor hours, direct costs and indirect costs. Actual costs should be itemized throughout the project, not just at completion.
What Is a Project Metrics Dashboard?
There are many project metrics, each with its own equation to calculate. That takes time that most project managers don’t have. Project management software often comes with a project metrics dashboard, which is a high-level view of the project, offering a glance at valuable data.
Many project metric dashboards deliver real-time data, which helps project managers by giving them the current status of their project as opposed to a snapshot from the past. This leads to responding quickly to issues as they arise and helps project managers make more informed decisions.
Some project metric dashboards require a user to set them up before they can get an overview of the project, while others automatically gather project metrics and share that data instantly. Either way, the project metrics dashboard is an essential project management tool for project managers to effectively measure the triple constraint of scope, costs and time.
How ProjectManager Helps Track Project Management Metrics
ProjectManager is award-winning project management software with real-time dashboards that track project metrics. Our live dashboard doesn’t require any time-consuming setup as with lightweight project management tools. It features six project metrics: health, tasks, progress, time, cost and workload. There are many more features that help you plan, manage and track your projects in real time, but for now, let’s look at how to plan a project to track project metrics and what tools can give you more detail than the dashboard when you need that deep dive.
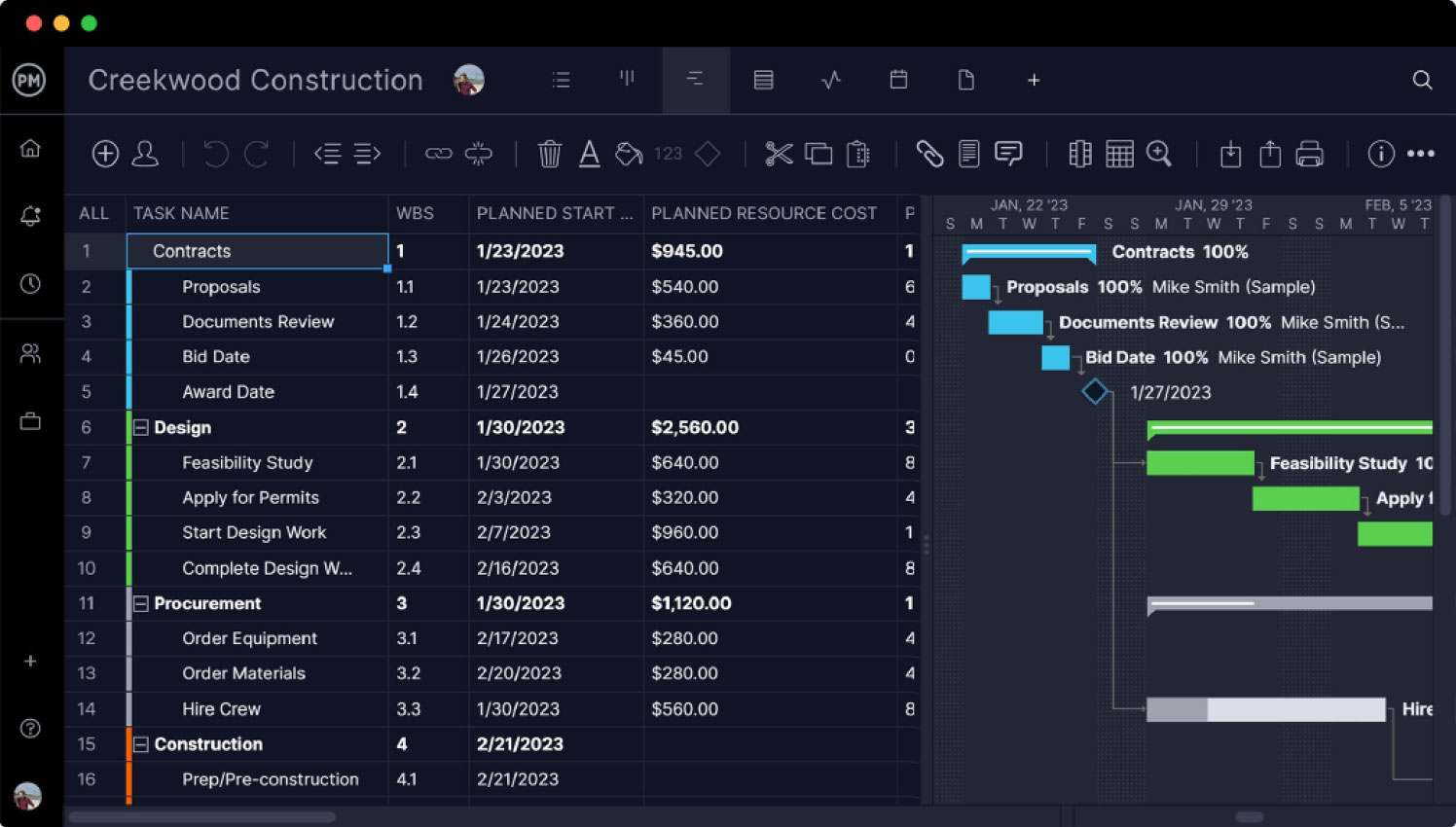
Plan on Robust Gantt Charts
Before you can track project metrics, you have to have a plan. Our powerful Gantt charts help you organize your tasks, link all four types of dependencies and even filter for the critical path. But most importantly, once the schedule has been created you can set a baseline. This captures your project plan and allows our software to automatically calculate project metrics such as cost and schedule variance. Now you can make sure you’re meeting milestones and not overspending.
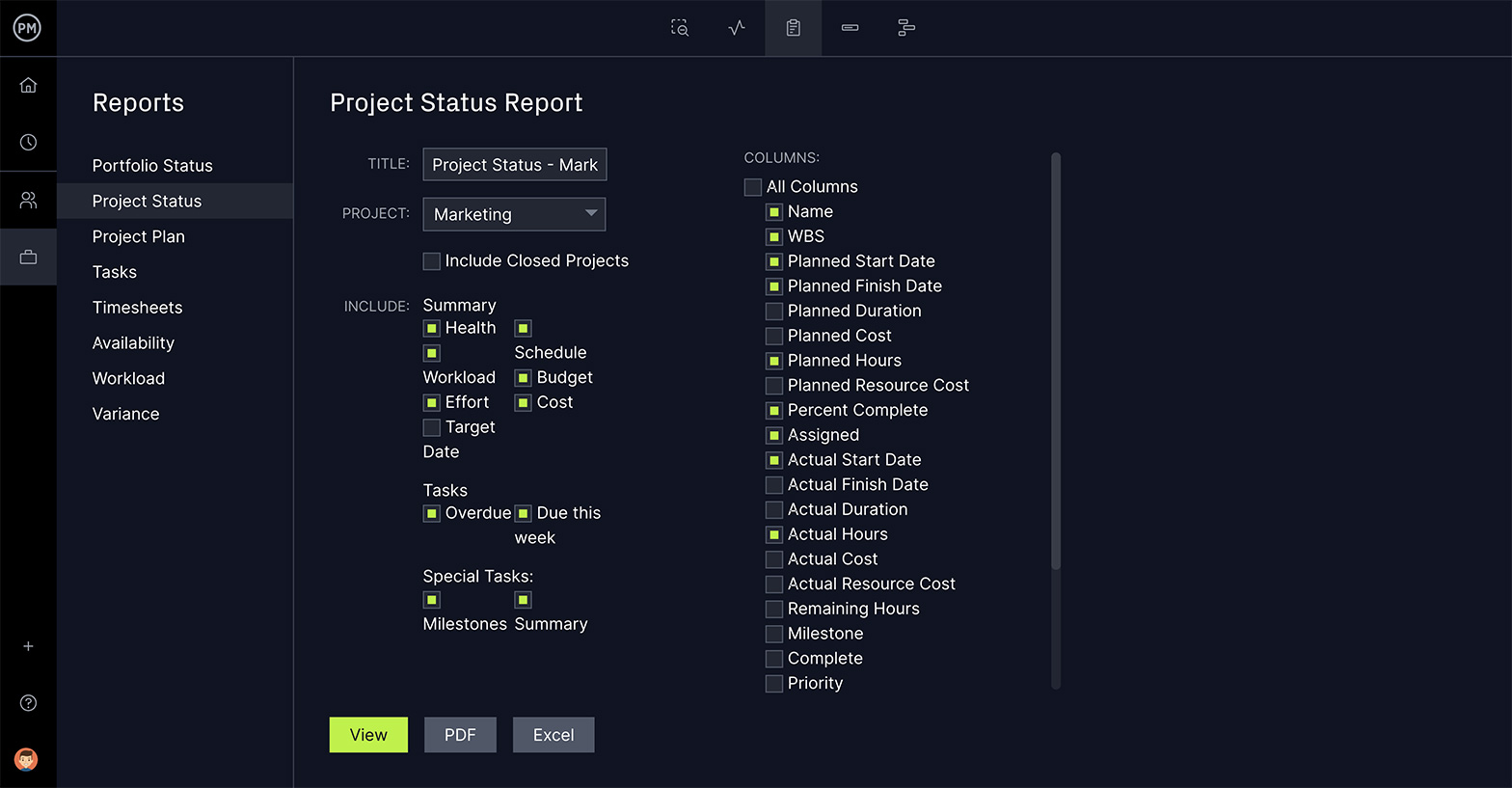
Get Deeper Into the Data With Customized Reports
When you need more information than you can get from the high-level dashboard, toggle over to the report section of our tool. Then you can quickly generate reports on project status, or portfolio status if you’re managing multiple projects, as well as reports on variance, tasks and more. All reports can be filtered to show only the data you’re interested in. Then they can be shared in a variety of formats to keep stakeholders informed.
Beyond tracking projects, our tool has multiple project views that allow you to work how you want. From the visual workflow of kanban boards to task lists, calendars and more, cross-functional teams can collaborate because all project views are updated together in real time. We also have task management, risk management and resource management features to help control your project and deliver it on time and within its budget.
ProjectManager is online project management software that connects teams whether they’re working in the office, at the job site or anywhere in between. They can share files, comment at the task level and more. Join teams at companies such as Avis, Nestle and Siemens who use our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

