Every phase of the project life cycle involves a set of essential activities that guide the work from start to finish. These project activities provide structure, helping teams move from idea to execution with purpose and control. Whether launching a new product or managing internal improvements, clearly defined actions at each stage support collaboration, accountability and alignment with goals.
Understanding how project activities unfold across the life cycle allows teams to plan better, respond to change and deliver consistent results. From initial planning to final delivery, each phase builds on the last, ensuring that decisions are informed, resources are used wisely and project objectives stay on track.
Project management software with Gantt charts helps manage project activities by organizing tasks along a timeline, showing start and end dates, dependencies and milestones. This visual structure makes it easier to plan, schedule and adjust activities as the project progresses, helping teams stay aligned and on time.
ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software with Gantt charts that go further by linking all four types of task dependencies, filtering for the critical path and allowing you to set baselines for tracking planned versus actual progress. These features give project managers precise control over activity sequencing and real-time visibility into potential delays or risks. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
Project Initiation Activities
The initiation phase lays the foundation for the entire project. It involves defining the project’s purpose, evaluating its feasibility, securing buy-in from key stakeholders and establishing the initial scope and goals. Strong initiation activities are critical for setting expectations and creating the structure for planning, execution and control. Without a well-managed initiation phase, projects risk starting without direction or alignment.
1. Make a Business Case
This outlines the rationale for the project, what problem it aims to solve, and the benefits it will bring to the organization. A compelling business case aligns the project with strategic goals, helps secure funding and ensures leadership support from the beginning.
2. Write a Project Charter
The charter formally authorizes the project and provides a clear summary of its objectives, scope, stakeholders, assumptions, constraints and the project manager’s authority. It acts as a reference document that guides all decisions throughout the life cycle.
3. Assemble a Project Team
Bringing together the right people ensures the project starts with the necessary skills, experience and internal support. Team selection should reflect the project’s scope and complexity and include input from stakeholders.
Related: 8 Free Scope Templates
4. Host a Project Kickoff Meeting
This is the first official meeting where the project team comes together to align on goals, expectations, roles, key dates and deliverables. A well-structured kickoff improves communication and sets a positive tone for execution.
5. Conduct a Feasibility Study
This study evaluates whether the project can be completed successfully within constraints like budget, time, resources and technology. Feasibility studies often assess operational, technical and financial factors.
6. Conduct a Cost-Benefit Analysis
By weighing expected benefits against estimated costs, this analysis helps stakeholders determine whether the project justifies its investment. It supports prioritization and decision-making at the program or portfolio level.
Project Planning and Scheduling Activities
The planning phase transforms broad goals into a detailed execution roadmap. It identifies tasks, assigns responsibilities, estimates resources and costs and outlines the timeline. Well-developed planning activities ensure clear direction, prevent scope creep and create a framework for monitoring and control.
7. Define the Project Scope with a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
The work breakdown structure divides the project into smaller, manageable components. This hierarchical structure ensures that all deliverables are accounted for and helps with estimating time, cost and resource needs.
8. Identify Project Resource Requirements
This activity specifies the human, material, financial and technical resources needed to execute the work. Resource planning must match the WBS to prevent shortages or bottlenecks during execution.
9. Estimate Project Costs and Make a Project Budget
Cost estimation includes both direct and indirect expenses. A detailed budget is essential for securing funding, managing spending and establishing the cost baseline used during project control.
10. Estimate the Duration of Tasks and Make a Project Schedule
Estimating task durations is critical for developing a realistic timeline. Tools like the critical path method (CPM) identify dependencies and determine the minimum project duration, while PERT accounts for uncertainty using probabilistic time estimates.
11. Write a Project Management Plan
This comprehensive plan includes details on scope, schedule, cost, quality, communication, risk, procurement and stakeholder management. It serves as the definitive guide for project execution, monitoring and closure.
Project Execution Activities
Execution is where planned tasks are carried out and deliverables are created. It involves assigning tasks, managing teams, ensuring quality and communicating with stakeholders. Effective execution relies on coordination, real-time adjustments and clear leadership.
12. Create Project Status Reports
Status reports track accomplishments, flag issues, highlight variances and provide transparency for stakeholders. These updates maintain momentum and ensure accountability across the team.

13. Communicate with Stakeholders
Open communication builds trust, manages expectations and reduces resistance to change. Regular updates and feedback loops ensure everyone remains aligned with project progress and goals.
14. Review the Quality of Project Deliverables
Each deliverable must meet predefined standards before moving forward. Quality reviews ensure that errors are caught early and prevent costly rework later in the life cycle.
Project Monitoring and Control Activities
This phase runs in parallel with execution and focuses on measuring progress, managing change and addressing issues proactively. Monitoring ensures the project remains within scope, on schedule and under budget.
15. Define Project Metrics and KPIs
These metrics help gauge how well the project meets its goals. Examples include schedule variance, cost performance index, milestone completion rate and customer satisfaction scores.
16. Establish Project Controls to Monitor Project Performance
Project controls such as earned value management, baseline comparisons and real-time dashboards help project managers identify risks and take corrective action before problems escalate.
17. Manage Project Changes
Change control systems ensure that scope, schedule and budget changes are evaluated for impact, documented and communicated. Structured change processes prevent scope creep and confusion.
18. Monitor Risks and Take Mitigation Actions
Risks are tracked throughout the project. Mitigation actions may include developing contingency plans, assigning risk owners or reallocating resources to avoid disruption.

19. Track Resource Utilization
Keeping tabs on how resources are used helps ensure tasks are completed efficiently. Monitoring utilization can reveal overallocation, underutilization or the need to reassign work to stay productive.
Project Closure Activities
The closure phase confirms that all deliverables have been accepted, documentation is complete and the project has met its objectives. It also ensures that knowledge is captured for future use and that resources are formally released.
20. Conduct a Post-Mortem Meeting
This reflective session helps the team analyze what went well, what didn’t and what can be improved for future projects. It encourages open feedback and continuous improvement.
21. Write a Lessons Learned Document
The lessons learned document captures key insights, challenges, decisions and successes. It becomes part of the organization’s knowledge base to guide future initiatives.
22. Archive Project Documentation for Future Review
Finalizing and storing all relevant materials—such as contracts, plans, reports and communication—ensures transparency and accessibility for audits, future projects or legal requirements.
How ProjectManager Helps Manage Project Activities
ProjectManager helps manage project activities by giving teams real-time tracking tools that ensure work stays on schedule and aligned with goals. Dashboards update automatically as tasks are completed, showing live status across timelines, budgets and progress.
Customizable reports provide deeper insights into project performance, while secure timesheets track hours worked to support accurate planning, billing and forecasting. These tools reduce guesswork and keep everyone accountable throughout each phase of the project.
Give Everyone The Right Tool to Execute Their Tasks
To keep project activities organized and easy to follow, our software offers multiple project views including Gantt charts, kanban boards, calendars, sheets and task lists. Teams can visualize dependencies and timelines in Gantt, move tasks through workflows in kanban, or break down work into actionable items with the list view. These flexible views make it simple to manage activities according to team preference or project complexity, ensuring that no detail is overlooked.
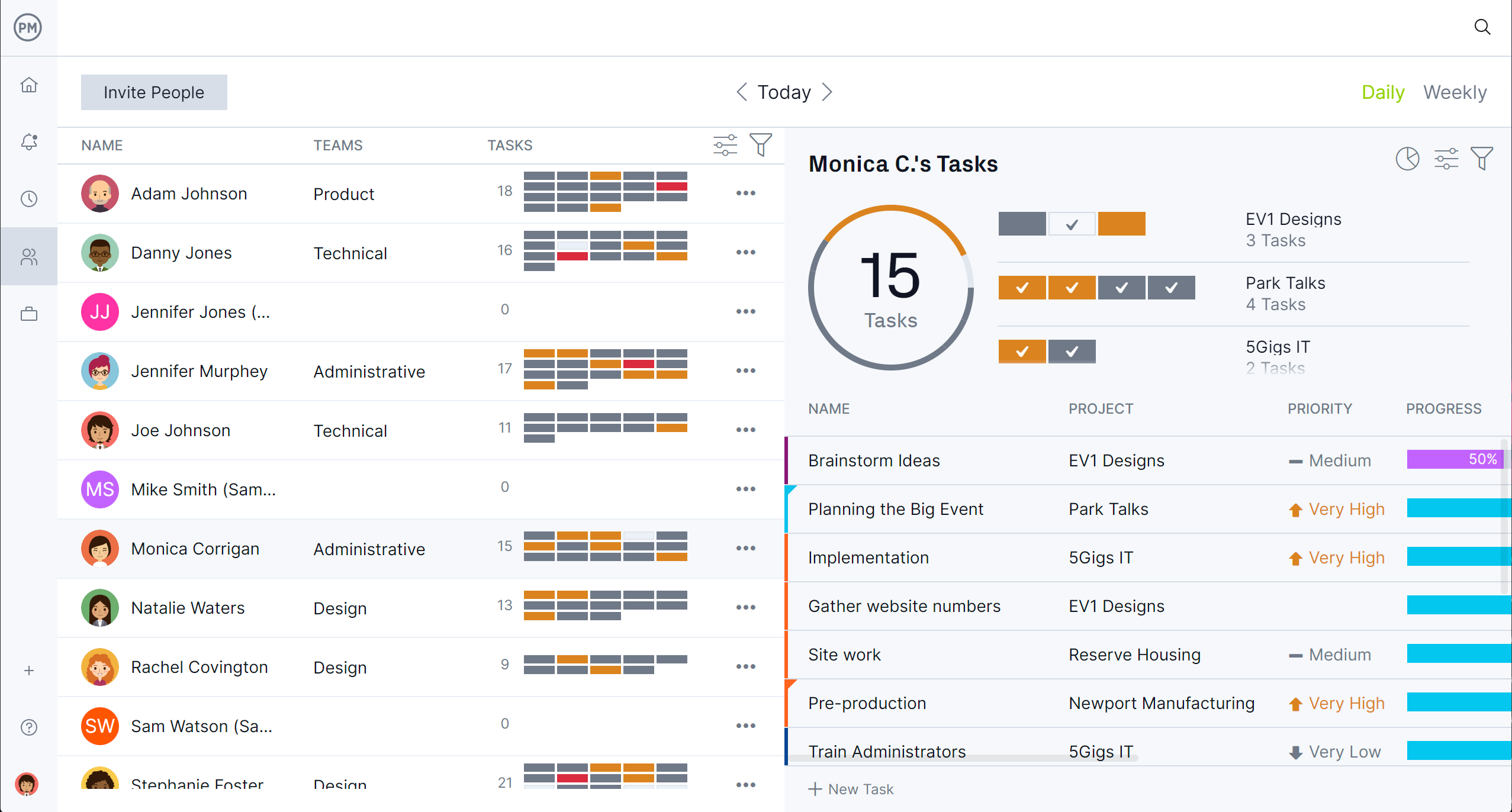
Use Built-In Tools to Manage Workload and Assign Tasks
Improve how project activities are resourced with built-in tools that help managers balance workloads and assign tasks effectively. The team page gives a clear overview of who’s available, the color-coded workload chart highlights overallocation, and availability settings ensure no one is overbooked. These features make it easier to plan, adjust and support activity execution across teams without delay or burnout.
Related Project Management Content
How to manage a project is answered by studying the basics of project management. For those who want to learn more, read the articles below. They cover hard and soft skills, certifications and the phases that make up every project.
- 22 Project Management Tools & Techniques for Project Managers
- 40 Project Management Skills: Soft, Hard & Technical Skills
- 21 Best Project Management Certifications (2025)
- The 5 Project Management Phases: A Quick Guide
- The 10 Project Management Knowledge Areas – (PMBOK)
- 100+ Project Management Terms: PM Terminology
- 14 Key Project Management Principles & How to Use Them
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams whether they’re in the office or out in the field. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who are using our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.


