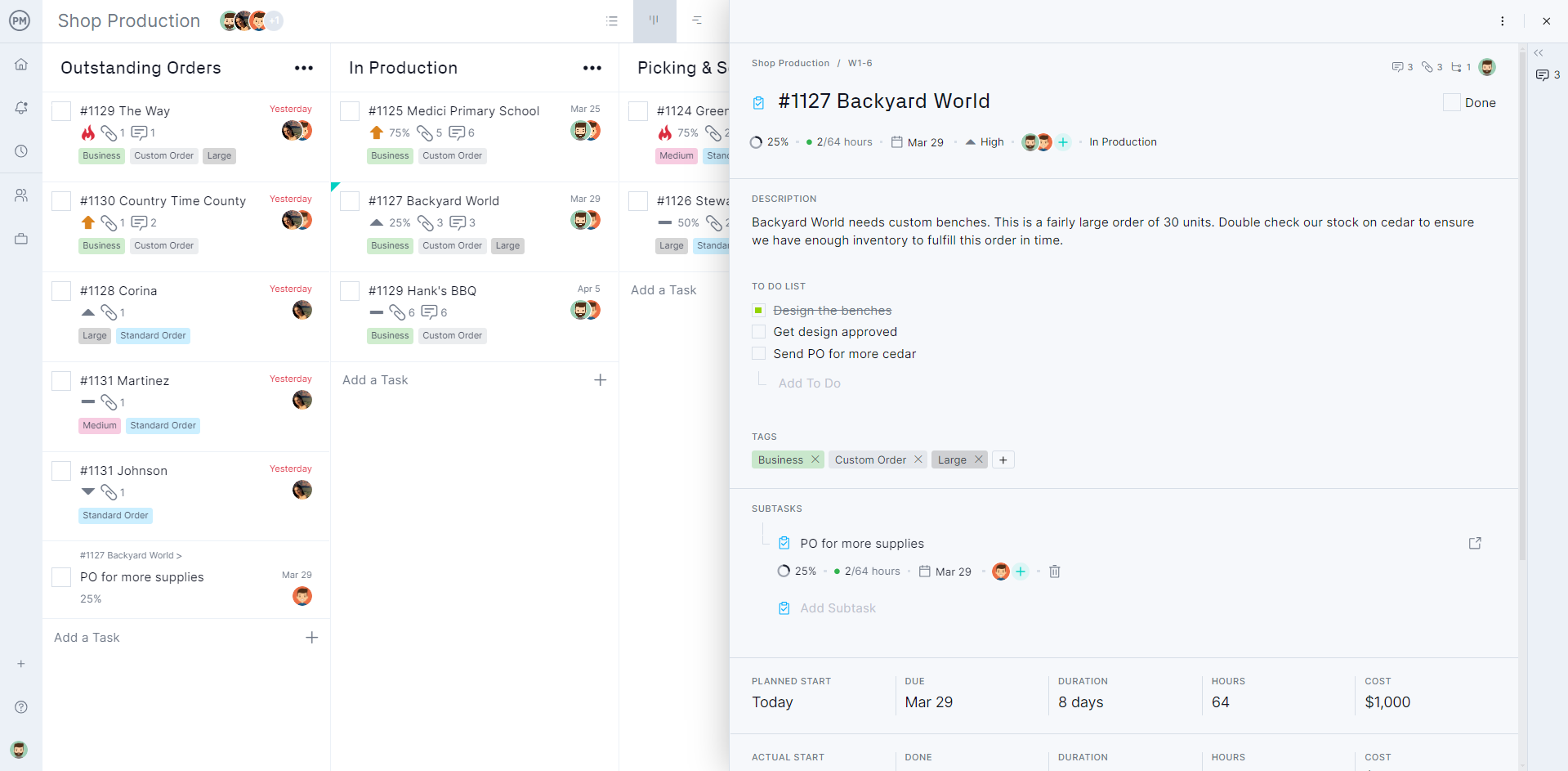
Products can be manufactured, but they don’t end up in a customer’s hands until they’ve been stored in a warehouse. It acts as a waystation, a part of the larger manufacturing and fulfillment processes. The better the warehouse management, the greater the company’s success.
After defining warehouse management and its importance, we’ll focus on its key areas and what the operation life cycle looks like. This is managed by a warehouse management system, which we’ll explain, and detail how project management software can help improve that process.
What Is Warehouse Management?
Warehouse management is the process by which the day-to-day operations of a warehouse are run. This includes high-level processes, such as receiving and organizing warehouse space, scheduling labor, managing inventory and fulfilling orders. At a more detailed level, that includes packing items, inventory management and order fulfillment.
To run all those processes efficiently requires optimizing and integrating them into the larger warehouse management to ensure they’re working together to increase productivity while keeping costs low. Some of those processes, such as managing inventory, tracking quantities, monitoring expiration dates and organizing products based on customer demand fall under inventory management.
Warehouse management can be done in-house, though many businesses choose to outsource warehouse logistics. Still, that work should be overseen by the business. They need a clear understanding of the planning, scheduling and monitoring of warehouse operations to ensure that they’re being done properly.
ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software that has multiple project views to help plan, schedule and monitor warehouse operations. For example, robust Gantt charts can organize tasks, delegate stock work to employees and track stock levels in real time. All four types of dependencies can be linked to improve workflows and avoid delays for faster shipping and delivery. Setting a baseline provides transparency into planned versus actual progress to monitor your warehouse operations to ensure they’re going smoothly. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
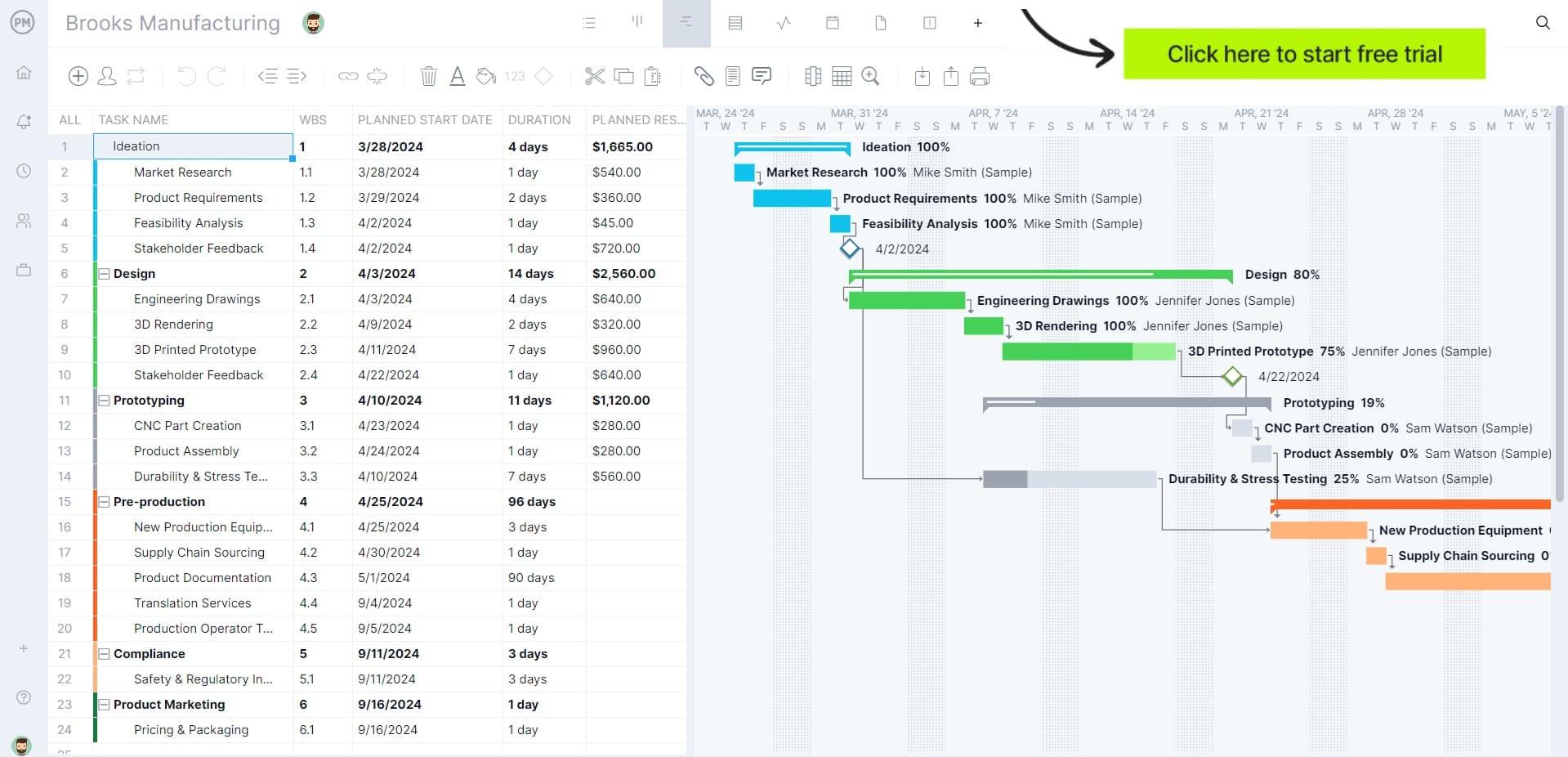
Why Is Warehouse Management Important?
While the customer doesn’t see how warehouse management impacts them at the purchase point, it’s an essential part of improving their satisfaction and loyalty to a brand. Warehouse management seeks to run its processes as efficiently and accurately as possible to support logistics management to ensure businesses deliver products efficiently to their customers, but that’s only one aspect of the benefits of warehouse management. Here are a few more.
- Supply Chain Management: The correct functioning of an organization’s warehouse has a direct impact on its supply chain management. Having fast, high-quality service at low cost can strengthen the entire supply chain, including relationships with suppliers as well as customers.
- Production Planning and Scheduling: Having an accurate forecast for the demand of a specific product and efficiently scheduling its production helps to avoid overproduction and minimizes inventory holding costs. It can eliminate bottlenecks and optimize resource use, all of which leads to saving money.
- Operational Efficiency: When operations are run smoothly, warehouses can quickly adapt to market fluctuations and demand, such as a spike in orders or a seasonal lull.
Key Areas of Warehouse Management
Warehouse management is composed of many different processes as a warehouse has other functions beyond storing stock. The following are some of the key functions, activities and processes that make up warehouse management.
Inventory Management
Most think of warehouses as a place to store things, which is one of its main functions. It deals with having access to what’s currently in stock, reviewing what has been in stock, analyzing sales to ensure that the available stock meets demand and identifying inventory levels to repurchase or retire stock demanding on business needs.
Order Processing and Fulfillment
Another key area of warehouse management is the ordering process, which is the workflow from order placement to deliveries or order fulfillment. Customer satisfaction depends on keeping this process reliable and accurate. Managing the process of receiving goods and then processing and delivering those orders to customers is a large part of warehouse management.
Warehouse Monitoring and Reporting
To be effective at inventory management and order processing and fulfillment required measuring and tracking key performance indicators (KPIs). Some of these KPIs include how efficient and productive the receiving process is, how accurate pricing is and what the ordering lead time, rate of return and inventory turnover are. Monitoring and reporting on these operational statistics provide insights into how well the warehouse is doing what it’s supposed to do.
Warehouse Optimization
This is the process that’s used to make sure that time, space and resources in the warehouse are being used as efficiently as possible. Warehouse optimization can be done through automation and careful planning, which lead to improvements in customer satisfaction and experience.
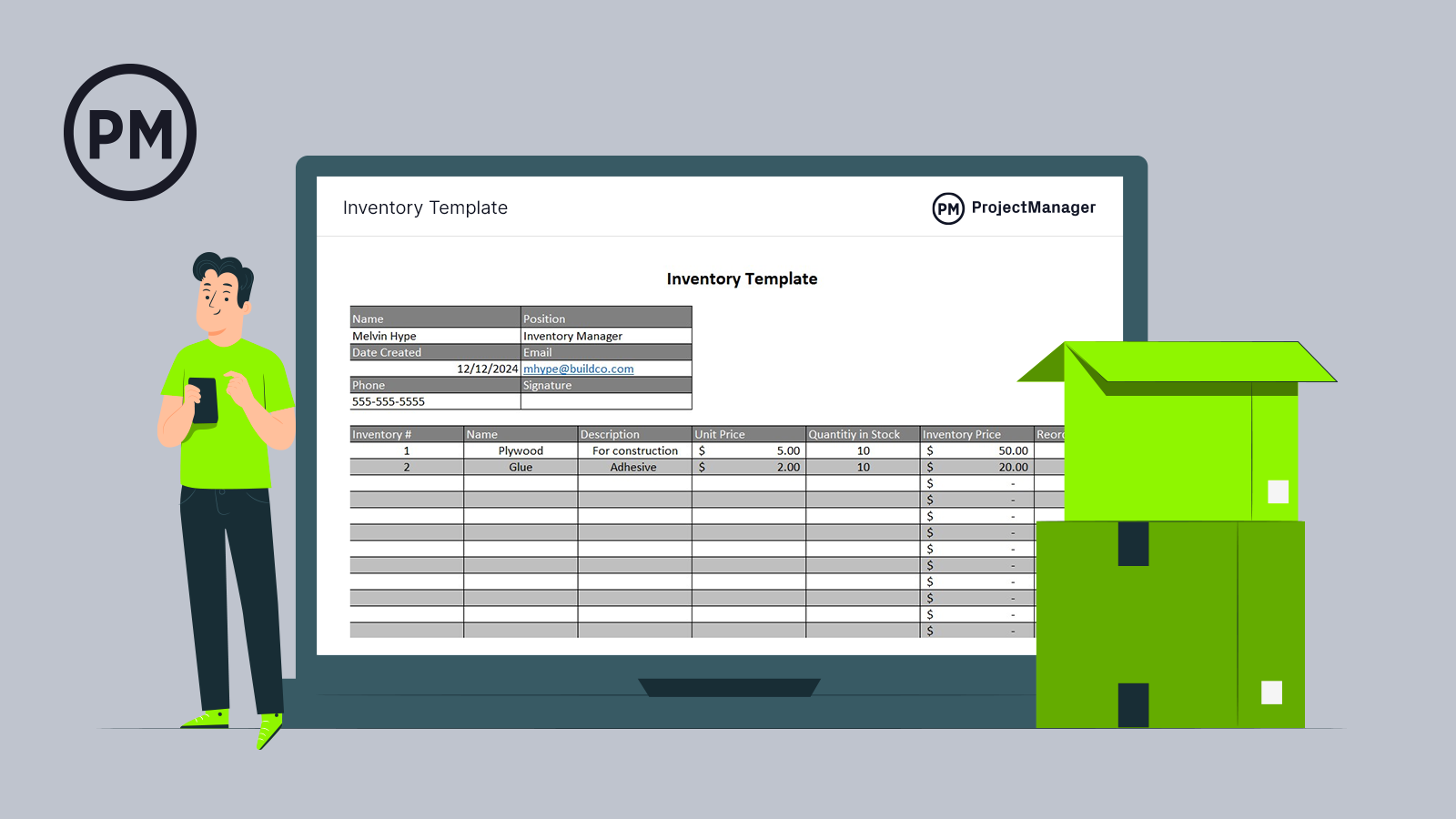
Get your free
Inventory Template
Use this free Inventory Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
Warehouse Operations
Warehouse operations are the activities associated with receiving, storing, packing and distributing goods in the warehouse. Warehouse management is responsible for controlling these warehousing operations to increase productivity and reduce costs. We’ve identified these processes and workflows below.
Receiving
This is when goods enter the warehouse. External suppliers often do this and it involves receiving checks, verifying orders against purchase orders, checking quality standards and making sure that everything is accounted for before they’re stored.
Storing
Once the receiving stage has been completed, the goods must be safely stored. Where items are stored depends on the item and can include cold storage units, room temperature racks, palletized racks, unit load devices, cage shelving systems or pallet racking systems.
Picking
When an order is being worked on, it needs to be picked up from the warehouse efficiently. There are several picking systems to do this, including batch, pick and pass, mobile scanning, wave, pallet, order consolidation cluster picking and more.
Packing
The process by which the picked items are placed in an appropriate shipping container. The packaging should be as cost-effective as possible without sacrificing the product’s safety. It must ensure that the product arrives undamaged and in working order.
Shipping
Shipping the package to the customer or a distribution center includes labeling the package, selecting the carrier and updating shipping information to all parties. This can be done in several ways, including dropshipping, self-fulfilling orders, or outsourcing fulfillment to a third-party logistics company.
Returning
If items are returned, the process follows these steps. They’re received and inspected for damage, completeness and accuracy. If there are issues, they’re reported to the appropriate department. The returned goods are then classified based on condition and intended disposition. They’re processed according to their classification and detailed records are kept, including the reason for the return, the condition, etc.
Benefits of Effective Warehouse Management
There are many advantages to employing warehouse management. Having a strategy and action plan in place always gives one more control over the process, which has its benefits. Below is a list of reasons why effective warehouse management is so important.
- Improved inventory control, tracking and demand forecasting
- Holding and labor cost reduction
- Enhanced customer service through faster order fulfillment and reduced errors
- Streamlined supply chain integration, supplier coordination and distribution channel integration
- Adaptability and scalability to market changes
Inventory Management Template
While project management software is a more effective tool to manage inventory, templates can be useful, too. This free inventory management template for Excel can record the level of stock and track turnover to document volume, price and more.
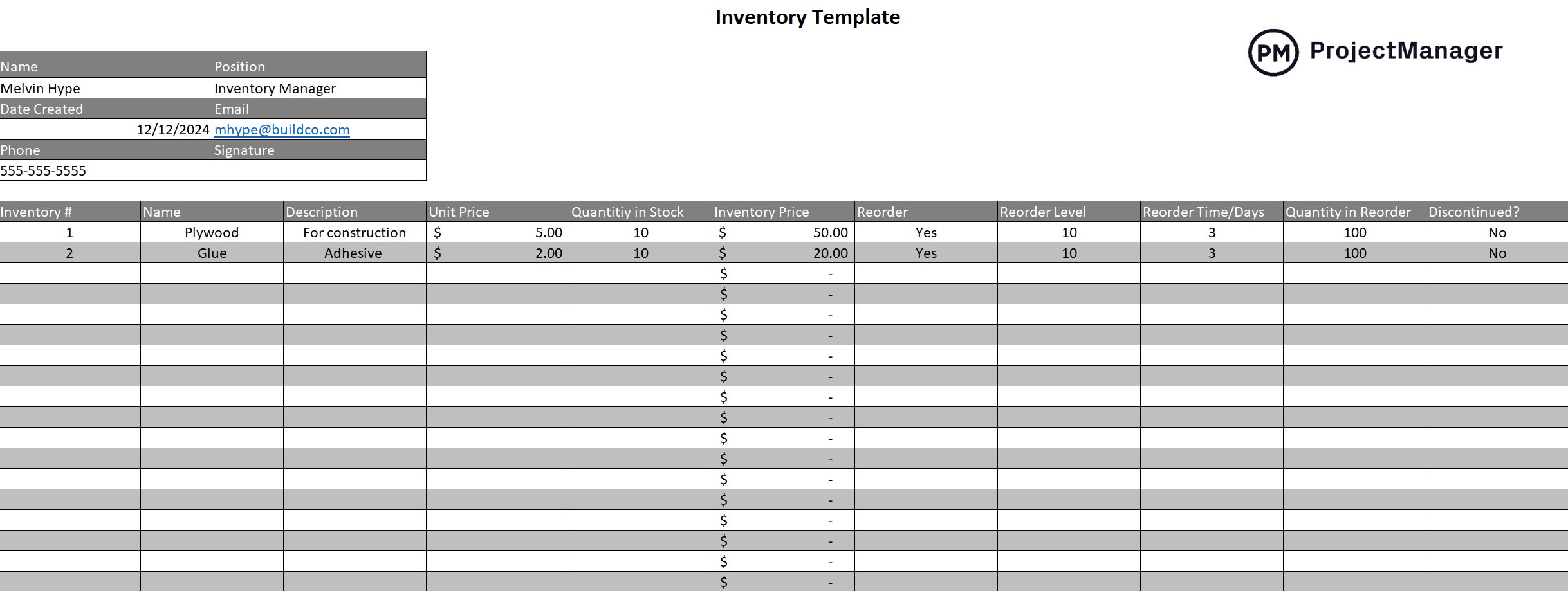
The free inventory management template for Excel lists products, items or components, describes them and adds the prices and quantity. There are also columns to note whether the item is being reordered and at what level that action should be taken.
What Is a Warehouse Management System?
A warehouse management system (WMS) is software that simplifies warehouse management. It can do an array of activities from leveraging data and automation to better analyze and forecast sales, provide real-time insights into inventory management and monitor productivity, among other things.
Using a warehouse management system provides data to better understand how to more efficiently operate a warehouse. Through these insights, improvements can be made to the warehouse geography to optimize space and more. Some can share data with other software, such as accounting and transportation management solutions, which further increase efficiency.
How ProjectManager Helps Manage Warehouse Operations
Using a warehouse management system is going to offer advantages to templates. Templates, after all, are static documents that require manual updates. They’re also standalone documents that hinder rather than facilitate efficient processes. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software that can plan, schedule and monitor warehouse operations in real time, as noted above. But it can also manage customer orders and track operational costs.
Manage Customer Orders With Kanban Boards
Tracking orders from customers and ensuring the fulfillment of their orders on time can be facilitated with the use of customizable kanban boards. It’s easy to create columns that reflect the order life cycle, attaching the order to a kanban card, which can include workflow automation to reduce time on minor activities and improve processing. Plus, task approval settings ensure quality control.

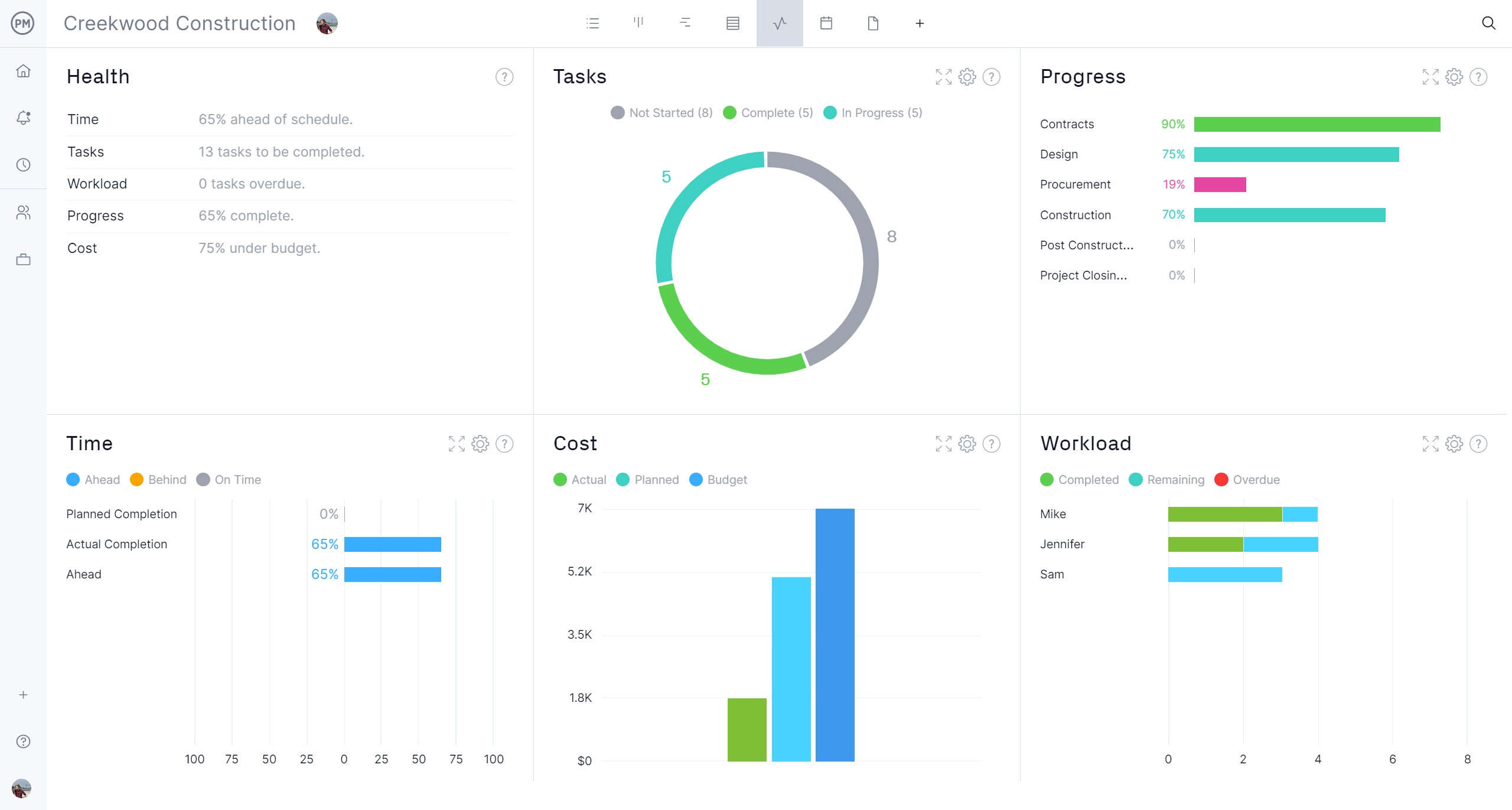
Track Warehouse Operations Costs With Timesheets and Real-Time Dashboards
Manage resources and keep employees working at capacity by visiting the team page that shows the allocation of all the employees. From there, balance their workload to keep everyone productive. Employees can auto-populate their timesheets weekly, which also gives managers insights into labor costs. For a high-level overview of operational costs, use the real-time dashboard that captures live data and displays it on easy-to-read graphs and charts that show costs, workload and more.

Related Manufacturing Content
Warehouse management is a small part of logistics management, manufacturing and production management. To read more on this topic, follow the links below. ProjectManager’s website is full of free resources, including weekly blogs, tutorial videos and free templates.
- Logistics Management 101: A Beginner’s Guide
- 10 Free Manufacturing Excel Templates (Download Now)
- Production Management: A Quick Guide
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams whether they’re in the office, the warehouse or anywhere in between. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay up to date with email and in-app notifications. Join teams from Avis, Nestle and Siemens who use our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.