For as long as there has been manufacturing, people have been working to increase efficiency. Faster and better production leads to greater profits and competitiveness. Using technology to achieve efficiency is called advanced manufacturing.
As technologies have become more innovative, advanced manufacturing technology also improves. This creates better products and processes that are used to create them. To better understand the term, we’ll define what advanced manufacturing is, its purpose and examples.
What Is Advanced Manufacturing?
Advanced manufacturing is the practice of using innovative technologies and methods to improve a company’s ability to be competitive in the manufacturing sector. Advanced manufacturing does this by optimizing all aspects of the value chain, from concept to end-of-life considerations.
This is accomplished through the use of advanced manufacturing technology, which integrates manufacturing and business activities to create a more efficient operation. Advanced manufacturing employs automation, computation, software, sensing and networking to create greater efficiencies.
One thing is constant, however, and that’s the need for workflow automation software to streamline processes and achieve greater efficiency. ProjectManager is project management software that automates workflows for removing busywork and has task approval settings for quality management. Plus you can build production schedules, manage execution and report on your projects in one tool. Get started with ProjectManager today for free!
Purpose of Advanced Manufacturing
The purpose of advanced manufacturing is to use technology to allow a company to produce goods or services of better quality, faster and at lower costs than their competitors, which will allow them to position themselves in the market.
What Is Advanced Manufacturing Technology?
The term advanced manufacturing technology refers to all the different technologies and techniques that can be used to improve an existing manufacturing process.
Related: 10 Free Manufacturing Excel Templates
Advanced manufacturing technology can take many shapes. From inventory management software that allows manufacturers to better understand what’s in their warehouse to using robots in the production line to cut down labor costs, to any other application of technologies in the manufacturing cycle. Let’s review the most common types of advanced manufacturing technologies.
Types of Advanced Manufacturing Technology
There are many types of advanced manufacturing technology. First, let’s divide advanced manufacturing into three main groups.
- Efficient production: The emphasis here is on simultaneous rather than sequential engineering and involves design, simulation, physical and computer modeling, advanced production technologies and control techniques. This is used in rapid prototyping and precision casting.
- Intelligent production: Uses ICT and related logistic systems to implement systems for the extended life and optimal use of production facilities. It does this through efficient monitoring, regular maintenance and repair.
- Effective organization: Coordinating and exploiting manufacturing resources, both physical and knowledge-based. This is used with virtual tendering, enterprise, shared facilities and resources, novel organization, incubation units, knowledge management and trading and electronic commerce.
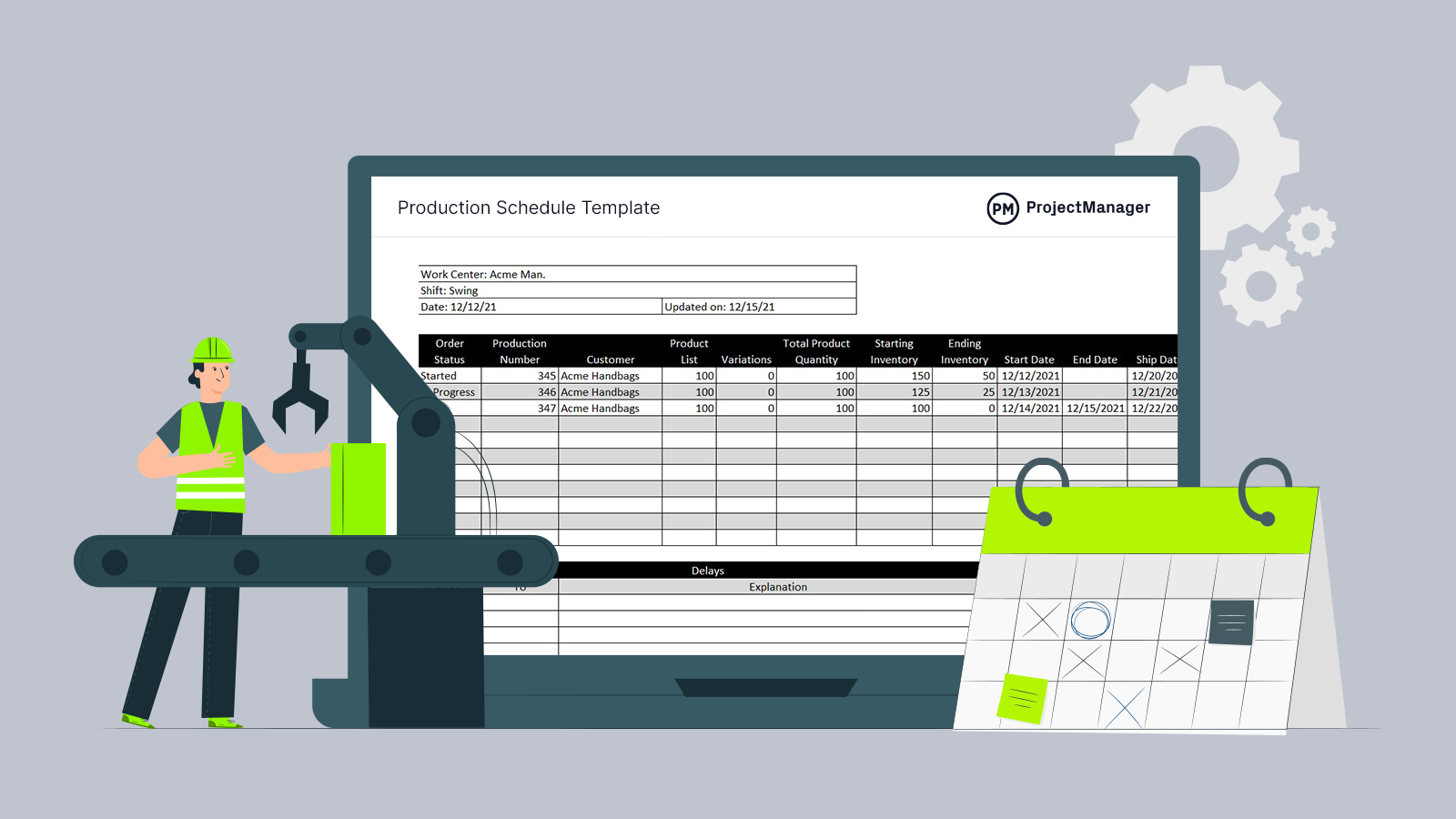
Get your free
Production Schedule Template
Use this free Production Schedule Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
10 Examples of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
The following are some of the ways that advanced technology is used to develop new markets, new technologies and new methods of manufacturing products:
1. Big Data Processing
Big data processing refers to the analysis of large data sets that are obtained through various business intelligence systems. Big data processing is an advanced manufacturing technology that helps businesses better understand what their customer demand is, track product quality, monitor workflows, and much more.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are used by manufacturers to automate aspects of quality control, maintenance logistics and inventory control. For example, AI and machine learning can be used to predict when machine failures and breakdowns are expected to occur so that effective maintenance can be performed.
3. Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented reality has multiple applications in the field of manufacturing such as employee training, product design and quality control and testing. For example, augmented reality helps manufacturers visualize what a product would look like in the real world, helping them correct any issues before creating a prototype.
4. Internet of Things (IoT)
The term Internet of Things refers to the devices, sensors, software and networks that are used to transfer data throughout a smart manufacturing process. For example, aerospace manufacturers use such devices to test the durability of the components of an aircraft.
5. Additive Manufacturing
This type of advanced manufacturing includes 3-D printing, powder-bed laser printing systems, fused deposition modeling and other processes that involve complex assemblies from continuous material. Benefits include reducing failure points in the system and reducing weight, complexity and thermal dissipation problems. This is used in aerospace, medical, prototyping, automotive, consumer goods and other sectors.
6. Advanced/Composite Materials
Here you create precise blends of metals, plastics, glass, ceramics, etc., for specific applications. They vary in terms of physical and chemical properties, creating performance breakthroughs and reducing material tradeoff decisions. Some of these composite materials include high-strength alloys, recyclable plastics and more.
7. Robotics/Automation
Uses automated systems for heavy lifting, precision movement and joining pieces on the factory line. It improves the consistency of the work and is ideal for tasks that are dangerous in that it limits human risk, overhead and waste while producing faster and cheaper. Robotics can be found in the automotive, aerospace, forging and consumer goods markets, and will likely grow with the advance of technology to include further industries.
8. Laser Machining/Welding
Laser machining and welding allow for greater precision and safety when welding and machining, including rapid and accurate processing of parts using laser technology. It reduces the amount of heat on the material and reduces cracking and poor joining. These processes are used in pressure vessels, proximity sensor welding, battery welding, sensitive electronics and more.
9. Nanotechnology
Being able to pack more into less space is one driver for nanotechnology. It’s used in chemical and biological applications to enhance material properties, control light spectroscopy and chemical reactivity. Using nanotechnology allows for advanced manufacturing systems to reduce their overall footprint and maximize functionality across the production line.
10. Network/IT Integration
The internet connects people and information. By using network communications on the factory floor, manufacturers can create closed-loop feedback and precision tuning electronically instead of manually. This reduces maintenance costs and improves the overall efficiency of production. The ability to have network access throughout the process allows manufacturers to instantly pinpoint issues and potential repairs to save time and time.
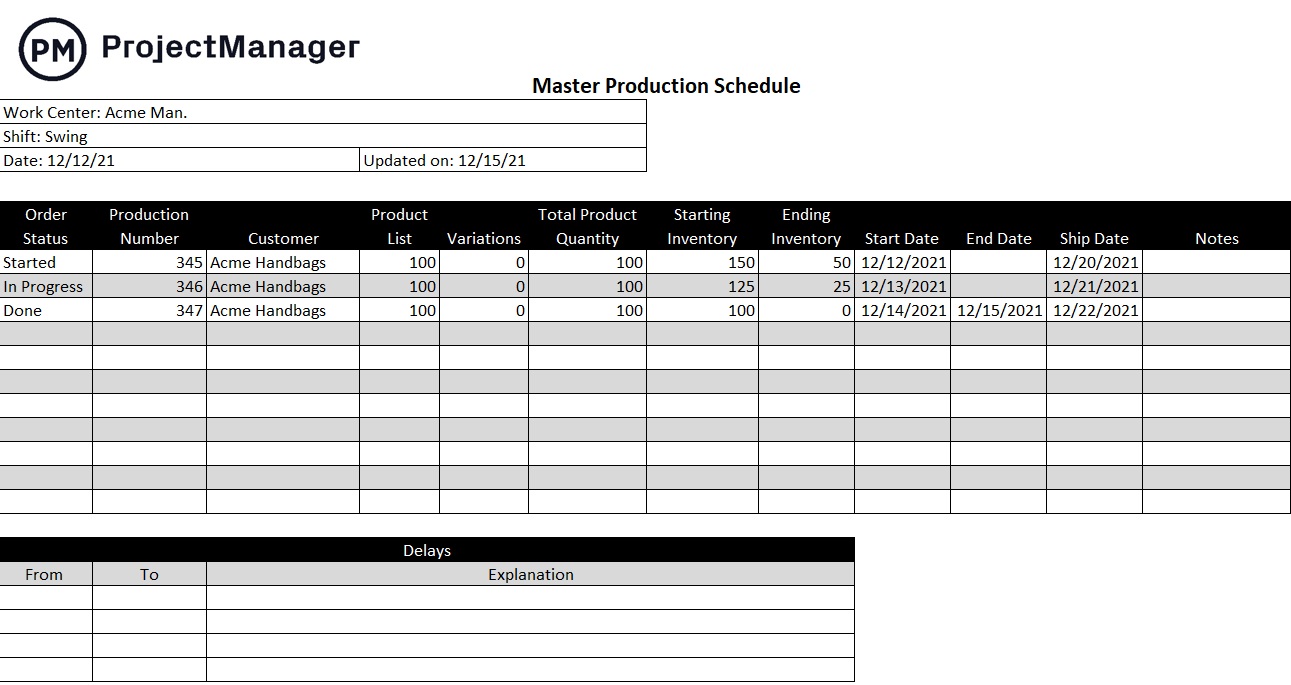
Free Production Schedule Template
Even with the aid of advanced manufacturing practices, you still have to stay on top of your production schedule to stay efficient and profitable. Download this free production schedule template for Excel to track orders, inventory, production dates and more.
Benefits of Advanced Manufacturing
Let’s take a closer look at the main benefits of advanced manufacturing.
- Innovation: The use of advanced manufacturing technology allows manufacturers to stand out from the competition by creating new, innovative products.
- Better product quality: By using innovative technologies in the manufacturing cycle, companies can improve the quality of their products. This is because advanced manufacturing technologies can be applied to the process of designing, producing and testing goods.
- Lower production costs: Advanced manufacturing can help businesses reduce their production costs in several ways. For example, advanced manufacturing technologies help companies reduce their labor costs, produce cheaper materials, cut steps in the production line, and lower inventory costs.
- Faster production of goods: Advanced manufacturing technology allows manufacturers to produce goods faster, which helps them outperform their competitors and pursue more business opportunities at a time.
What Industries Use Advanced Manufacturing Technology?
Advanced manufacturing can be found in just about every industry including:
- Automotive industry
- Aerospace industry
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Electronics industry
- Medical devices industry
- Robotic industry
- High-volume goods
- Rapid prototyping

Advanced Manufacturing vs. Traditional Manufacturing
Is advanced manufacturing much different from regular manufacturing? Traditional manufacturing, of course, is thought of as taking raw materials and creating a product that adds value.
Advanced manufacturing tends to be used in more cutting-edge industries, such as medical, aerospace and pharmaceutical. It’s based on scaling, labor skills, research and development and flexible production. However, the differences between the two are getting smaller, as traditional manufacturing begins to use more high-tech equipment and systems.
Production Strategy
That said, there are still differences between the two. For example, the production strategy is different. In traditional manufacturing, the strategy is mass production, while advanced manufacturing customizes and stays customer-focused. The organizational structure is also different. Traditional manufacturing is hierarchical and advanced follows a flat, open flow of information.
Labor
In traditional manufacturing, there’s usually an abundant supply of un- or semi-skilled labor; however, advanced manufacturing requires a skilled labor force with technical knowledge. Therefore, traditional manufacturing more often provides on-the-job training or just vocational school. Advanced manufacturing needs people who have a higher level of education and a technical degree.
The labor force in traditional manufacturing often needs about three semi-skilled workers for every skilled one. In advanced manufacturing, it’s almost the reverse; about four skilled workers for each semi-skilled one. This is because traditional manufacturing has a production technology that involves casting, welding, molding, brazing and machining, among other things. Advanced technology can include 3-D printing, powder bed, material deposition, etc.
Investment
Traditional manufacturing invests in production, and advanced manufacturing takes its revenues and puts them into research and development. Therefore, traditional manufacturing requires infrastructure space and advanced manufacturing is more focused on IT and digital infrastructure.
Logistics
Logistics is another area where the two types of manufacturing diverge. Traditional manufacturing delivers its product to the market through traditional channels, such as highways and rail. Advanced manufacturing uses global supply-chain management.
How ProjectManager Helps With Advanced Manufacturing
ProjectManager is online work and project management software that delivers real-time data for more insightful decision-making in advanced manufacturing. Real-time dashboards and one-click reports allow you to capture live data. Know what’s happening as it happens so you can reallocate resources as needed to avoid bottlenecks.
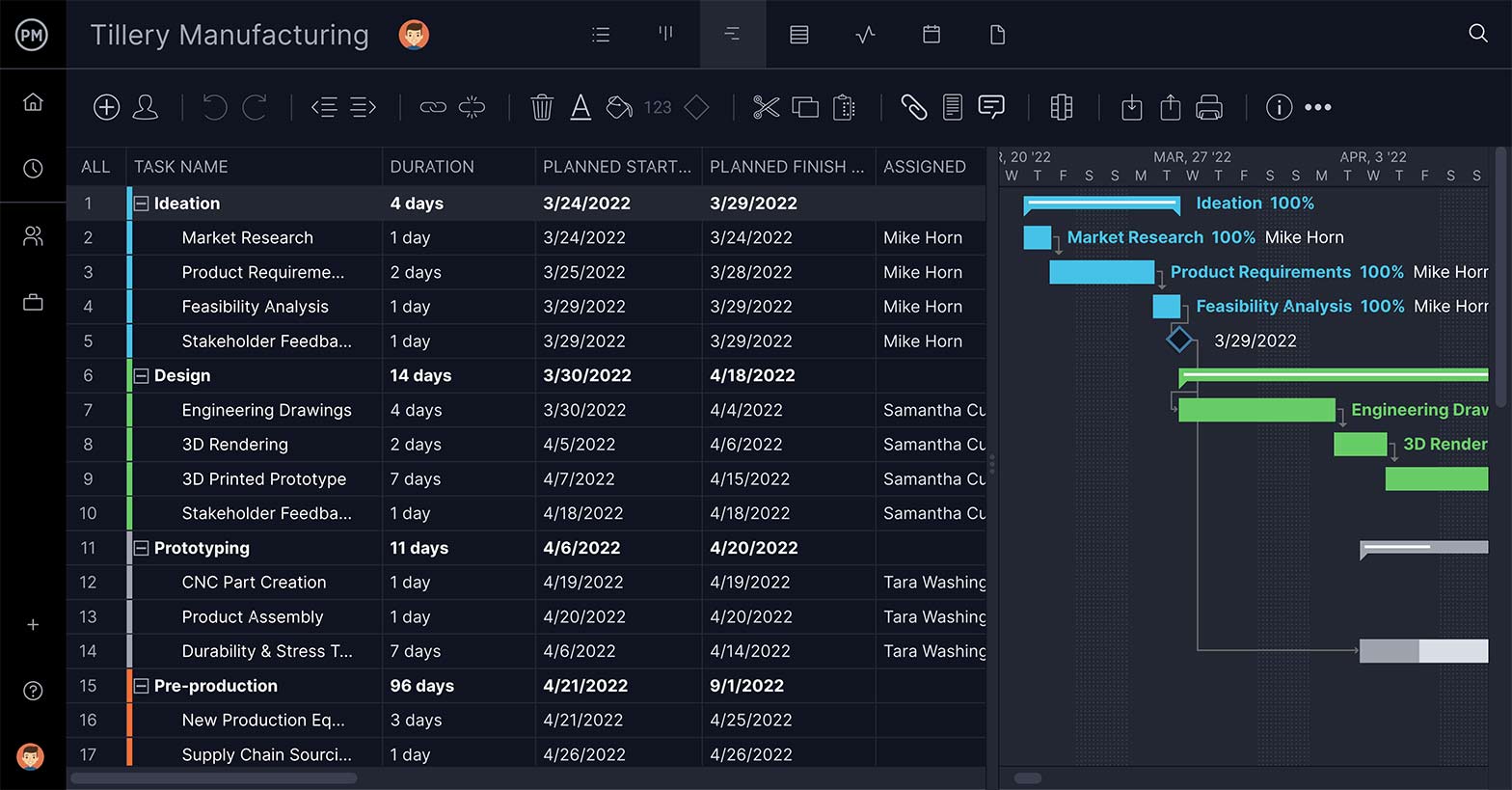
Schedule With Interactive Gantt Charts
Plan maintenance, schedule workers and more with online Gantt charts. You can see the entire production schedule on one timeline, link dependencies and even filter for the critical path. Once you’ve scheduled work, set a baseline to track the variance between the planned and actual effort in real time.
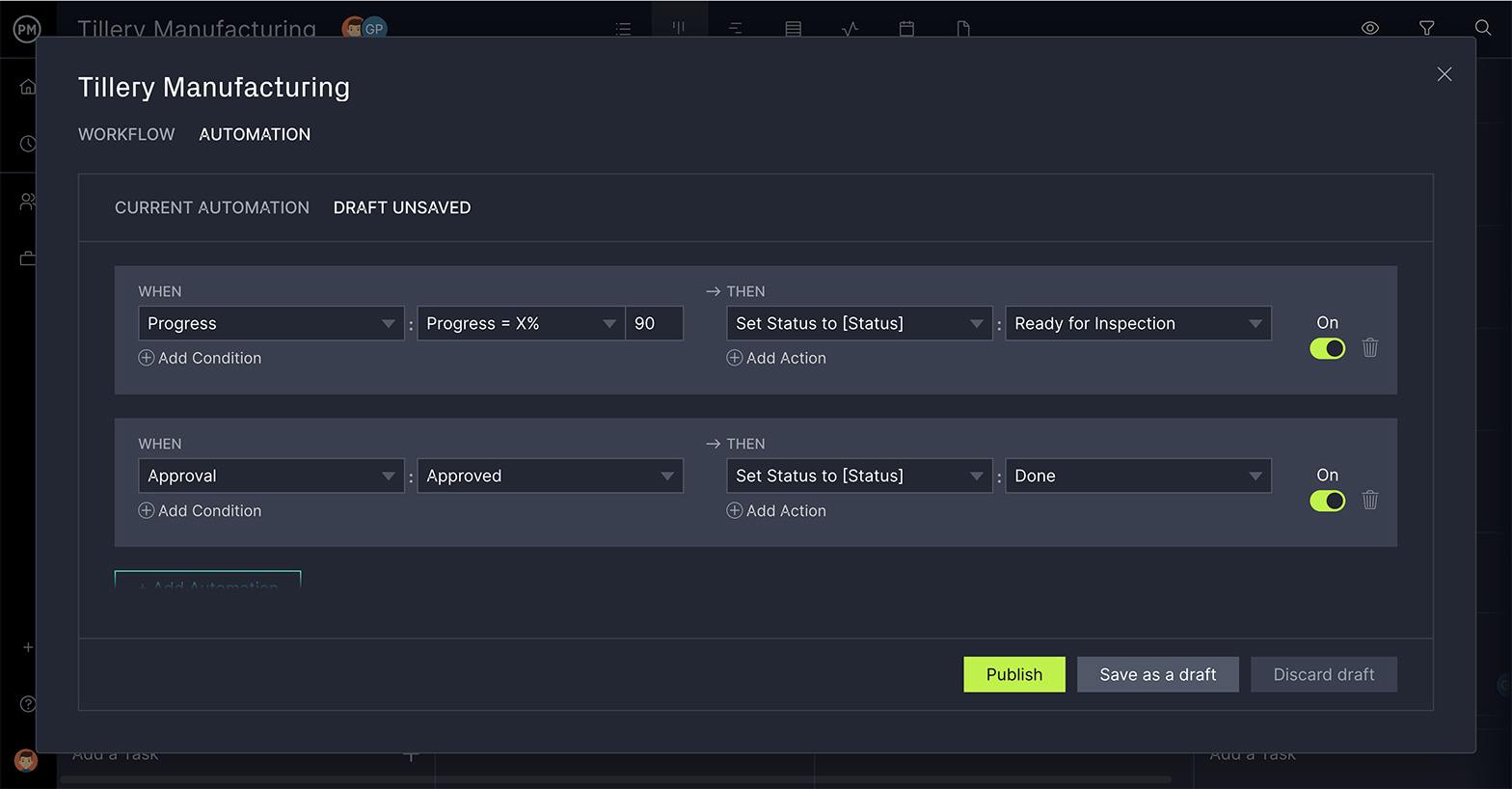
Streamline Processes With Workflow Automation
Keep your workers focused on what’s important by freeing them up from busywork. Set as many triggers as you need to automatically move work through production, change assignees and much more. Then, to ensure the quality of the work being done, created task approvals so only those authorized to change the status of work can do so.
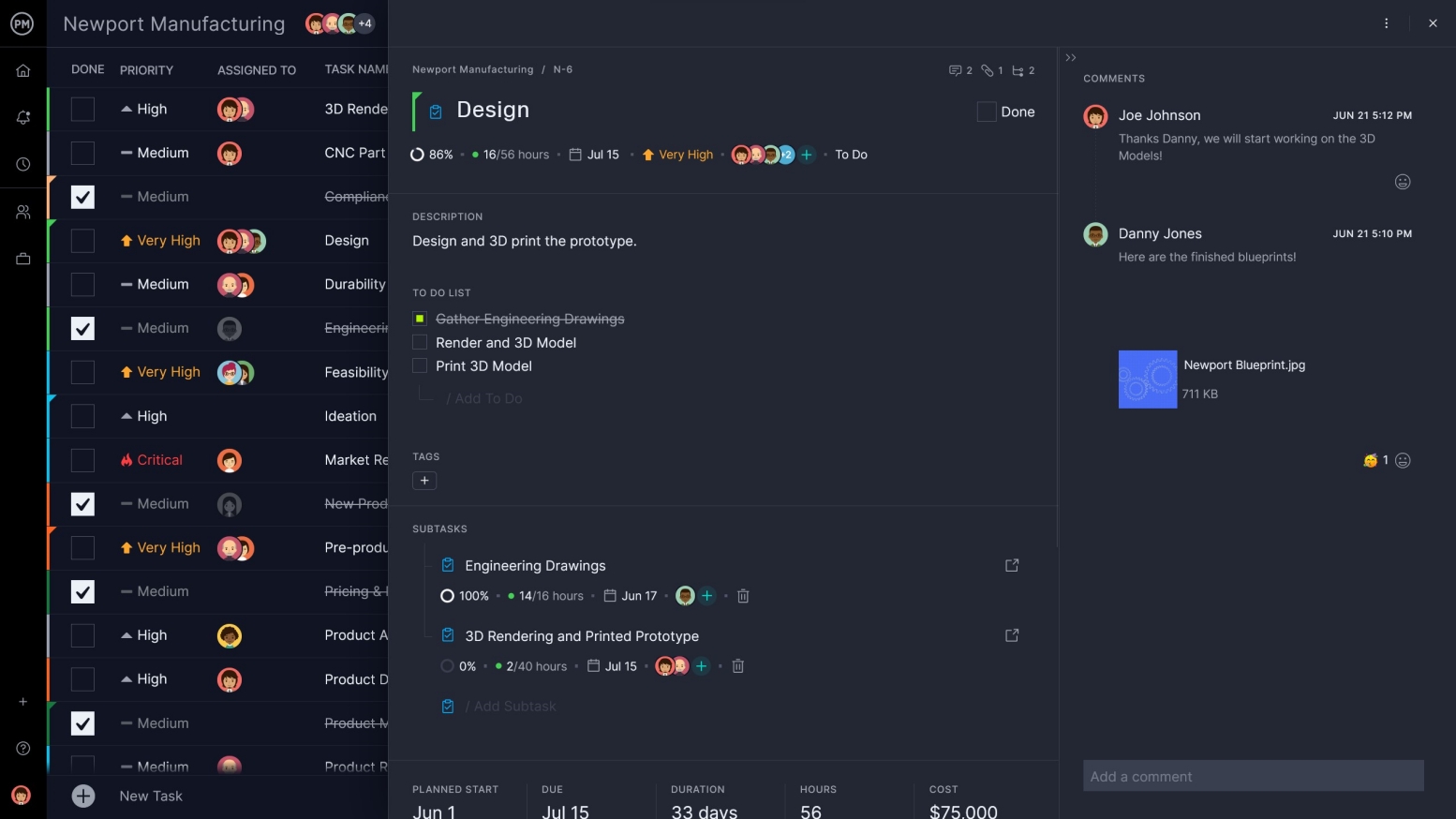
Flexible Features Serve the Entire Team
Advanced manufacturing requires flexible software that can work in the boardroom and on the factory floor. ProjectManager’s multiple project views mean you can schedule on Gantt charts or the sheet view while teams can manage their tasks on kanban boards, the list view or a robust calendar. All views can be automated and the data remains the same to establish one source of truth.
Our software lets you manage costs and resources and stay updated in real time with email notifications and in-app alerts so you know if someone comments or updates a task. Balance your team’s workload to keep them productive and use secure timesheets to streamline payroll and track your team’s work at the task level.
ProjectManager is award-winning software that helps manufacturers fabricate and deliver their products on time and within budget. Our flexible tool has a collaborative platform that allows every department to work better together and communicate in real time. Resources can be tracked and allocated as needed to keep the production cycle running smoothly. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.