The project design phase is the first step when planning a project. It sets the stage for the project initiation and project planning phase and important documents like the project charter and project plan.
What Is Project Design?
Project design is a brainstorming process where the project management team starts thinking about the project from a high-level perspective, outlining goals, methodologies, resources and success criteria to establish a project approach that’ll be presented to stakeholders to then begin with the project initiation and project planning phases. In this project stage, the decisions about how to manage and govern are made.
After the project design phase, a project proposal, project charter and a project plan can be created. These project documents will then be used to manage the execution phase of the project life cycle.
The thinking that goes on during the project design, however, doesn’t focus on details as much as it works on a higher level in terms of managing the project. Project planning software can help organize both the high-level strategy and the specific details of a project design.
ProjectManager, for instance, has Gantt charts for making detailed schedules, but also kanban boards for easy collaboration for the strategic aspect of project design. Manage your strategy, plan, schedule, execution and reporting in one easy-to-use project management software. Try it for free today.

What Is the Purpose of the Project Design Process?
The project design defines the overall project methodology that’ll be used and an overview of the project. It describes the major deliverables, products or features that will be completed. The project design also roughly estimates the budget and outlines how to monitor and evaluate progress. There can be more than one design presented to stakeholders, who can then choose which they think best suits their needs.
When Does the Project Design Process Take Place?
The project design process typically occurs after the initial project concept and feasibility studies are completed, but before actual construction begins. It takes place during the project initiation phase and can extend into the planning phase.
During the initiation phase, a high-level aspect of project design is started. Details will come later. This includes broad project requirements that set the stage for actual design as the project moves into the planning phase.
It is now that most of the design work is done. The high-level ideas developed in the initial phase and are now refined in the planning phase into an actionable plan. Designers, engineers and architects flesh out the ideas into technical specifications and blueprints.

Get your free
Project Plan Template
Use this free Project Plan Template to manage your projects better.
Get the Template
Who Participates in the Project Design Process?
Several people in and around the project team are involved with the project design process. Here are some details about them.
Project Sponsor
They define the project goals, budget and requirements, as well as overall direction for the project. In addition, the project sponsor provides feedback and approvals throughout the design phase to ensure that it aligns with objectives, budget, scope and priorities.
Project Manager
The project manager is responsible for overseeing the entire project. That includes coordinating with stakeholders, managing timelines and ensuring that the project stays on schedule and within budget, but also the design process. They are a bridge between the stakeholders and the technical experts.
Project Stakeholders
A stakeholder is anyone who is invested in the project’s success. Therefore, stakeholders can include end-users, clients, employees, community members and investors. They’ll provide input on needs, preferences and any concerns that arise during the design process. Stakeholders are committed to the project meeting their expectations.
Project Team Members and Subject Matter Experts
The project team includes the project manager, architects, engineers and designers, who work together to ensure that all aspects of the project align with its overall vision. They collaborate on scope, budgeting and scheduling as well as design development, reviewing drafts, providing feedback and ensuring the design aligns with project goals. Subject matter experts (SMEs) provide specialized knowledge, consultation and input, problem-solving, validation and review as well as training and guidance throughout the process.
Why Is the Project Design Phase Important?
Project design is a major first step toward a successful project. A project design is a strategic organization of ideas, materials and processes for the purpose of achieving a goal. Project managers rely on a good design to avoid pitfalls and provide parameters to maintain crucial aspects of the project, like the schedule and the budget.
Project Design Process: How to Design a Project Step-By-Step
There are steps to take for defining project designs and developing an implementation strategy, and they’re the most important steps in a project. Therefore, you want to involve your team and stakeholders in the process to ensure you’re covering all the bases. Take the time to complete this stage thoroughly.
1. Define Your Project Vision
What’s your vision for the project? This isn’t some far-fetched hope, but a vision statement, which envisions a problem that needs resolution. That means clarifying the reason for the project. The vision statement is a formal document that states the project’s potential. It’s presented to stakeholders to show the viability of the project and its benefits.
It isn’t a long, detailed document. You can have a short, idealistic vision in terms of the outcome of the project; after all, this is how you sell the project. So, paint a picture of the project’s success, and place it in a larger context.
2. State the Problem Your Project Will Solve
To support that vision document, you need to identify a problem that needs solving. A needs assessment is often required, so you can see the obstacles the business is encountering. This aligns the problem you’re addressing with the organization and its strategy. It’ll also provide you with the necessary data to design an optimal solution for the problem.
To begin, what information are you gathering? What sources are there for that information, and how will you then gather the information? Next, analyze and determine the problems that your project is being created to resolve. Collect those results in a document.
3. Conduct a Feasibility Study
Often the design process occurs after the feasibility study, but sometimes it’s a part of the larger process. In those cases, the feasibility study provides market analysis, site analysis, technical and financial feasibility and legal and regulatory review. Its impact on the design process informs decision-making, refinement of scope, design direction and stakeholder buy-in. Again, typically this is done before the design phase but informing the design phase.
4. Estimate the Project Resources That’ll Be Needed
Next, you need to recognize the necessary resources to get the project done. Resources are anything from people to equipment to the facilities necessary to complete the project successfully.
A good way to determine the resources is the same way journalists approach a news story, with the five W’s: who, what, where, when and why. Who do you need to execute the project, what resource management tools are required, where will the work be done, when will the project start and end and why are these resources needed?
5. Outline Your Project Goals
You can’t achieve your goals if you haven’t identified them first. A goal is something at the end of the project that’s both observable and measurable and it coincides with the resolution of a problem.
Create a goal statement that explains how the goals are addressed in the project. To do this well, apply the SMART method, which stands for specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time-relevant. Each goal should be defined by these terms.
6. Structure Your Project Strategy
To achieve the project goals, there must be a strategy in place. A strategy is a process to reach the goals of the project within the project constraints, such as its resources, schedule, budget, etc. How can a strategy be created to achieve the project goals?
Consider precedent and look back on similar projects from the past and what they might have shown in terms of the pros and cons of their applied strategies. Best practices for project management are always a good foundation and building a strategy incrementally, creating a pathway to success.
7. Prepare a Contingency Plan
Any project manager knows that very few things proceed as planned. There needs to be a backup plan to respond quickly and rightly to issues as they arise in a project. Therefore, this must be included in your project design.
Look for the negative risks inherent in the project. They’re embedded in various places, such as teams, which might lack skills, have unavoidable absences, turnover, etc. Schedules can be plagued with delays. The scope might have been poorly defined. Costs are underestimated or funds dry up. Have a plan to address these risks.
8. Establish an Evaluation Plan
A project must always be under evaluation. An evaluation plan will help you monitor the project, and maybe even alert you when it starts to veer off track. Use this plan to analyze the components of the project, the outcomes and the impacts.
Outcomes are measurable changes, while impacts are how well the project goals are being achieved. Therefore, the evaluation plan is a detailed document that defines criteria to determine the project’s effectiveness and efficiency by tracking progress on all aspects of the project.
9. Estimate Costs and Create a Project Budget
The budget outlines the financial resources that drive the project. A budget will assign a cost to each of the project’s requirements. Creating a project budget means formalizing financial resources that’ll be allocated to the project. This begins with choosing a way to estimate costs, identify impacts and report on the evaluation.
10. Create a Project Proposal
All of this leads to a project proposal to explain why the project should be executed and what its benefits are. The previous steps are summarized, writing out the vision of the project and a brief description of the problem that it speaks to. Then state the goals of the project and outline the strategy that will be used to achieve those goals.
11. Write a Project Charter
The project charter formally authorizes the project, providing the project teams with the authority to proceed with the design. It summarizes the project’s purpose, goals and constraints. Therefore, its impact on the design process is that it guides the design team and provides stakeholder engagement, scope and risk management.
Project Design Example
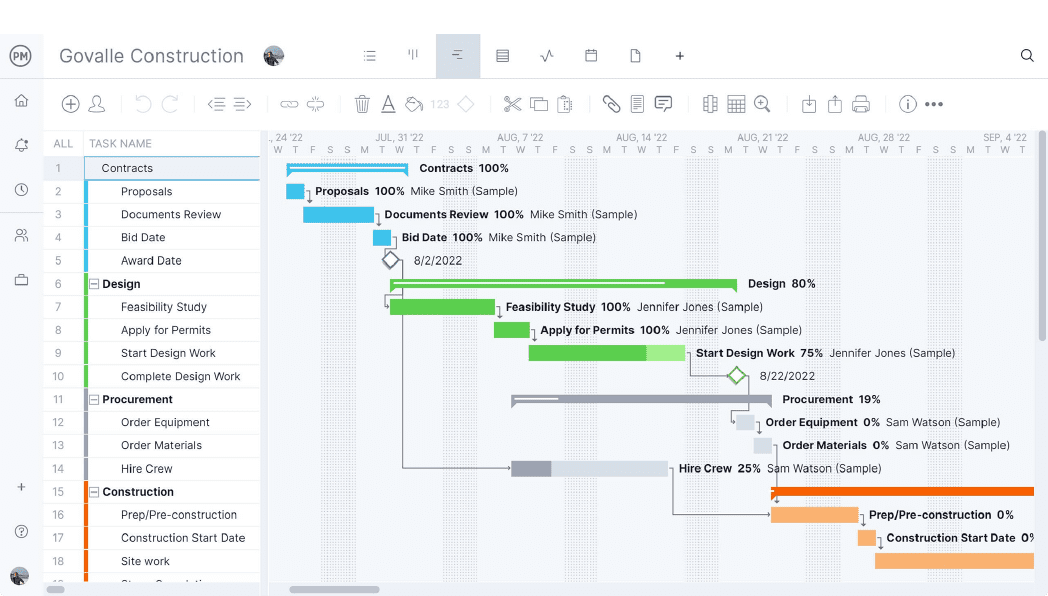
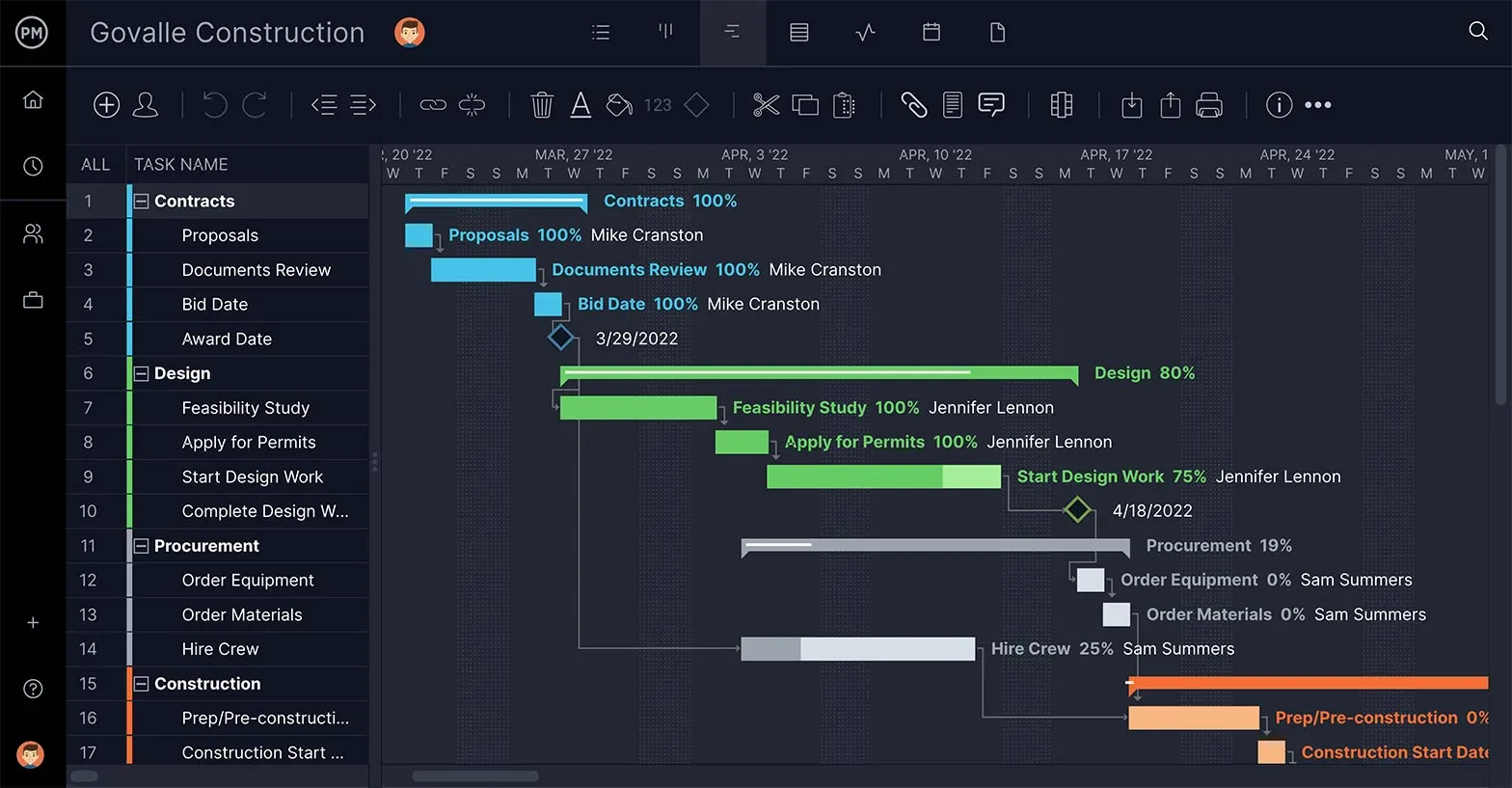
Project managers use project management tools such as Gantt charts to structure their project designs. Here’s a simple project design example that shows how the project design ideas are added to this project planning tool.
For this project design example, let’s take a look at a construction project. As you can see in the image below, during the project design phase, project managers can use Gantt charts to add the major tasks and deliverables as well as build the work breakdown structure of a project to outline the phases of the project execution.
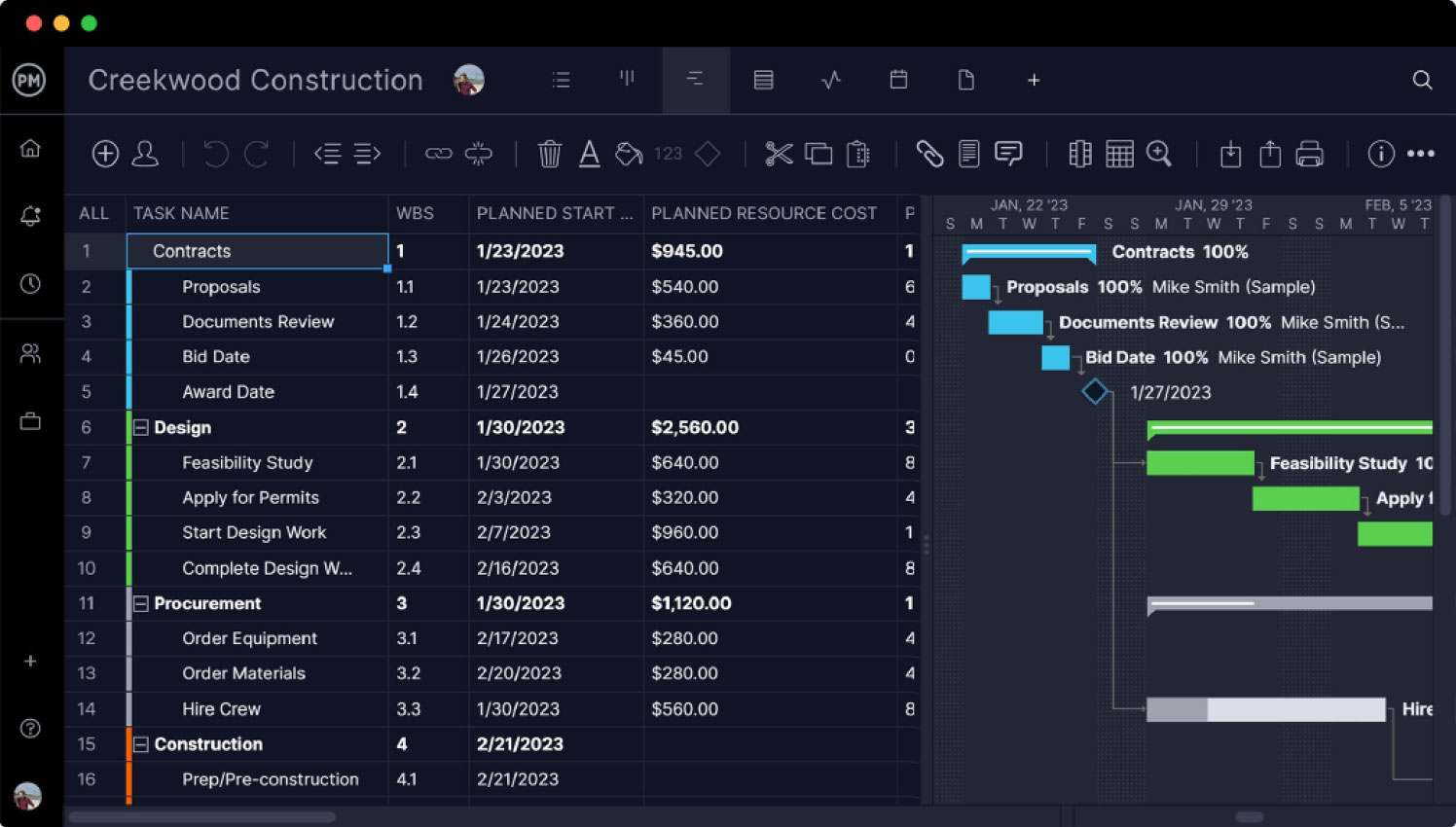
ProjectManager’s Gantt charts have two major parts. On the left side, there’s a spreadsheet that allows project managers to enter information that’ll be used to automatically generate a project timeline on the right side. This timeline won’t only show the project tasks but also milestones, task dependencies and due dates for project deliverables.
What ProjectManager Can Do to Help Your Project Design
Designing a project takes a lot of work, but using project management tools facilitates the process of creating an outline that details these various parts of the project. Besides using Gantt charts to organize your project design ideas into a project timeline, you can also use kanban boards to manage workflow using ProjectManager.
Plan Workflows With Kanban Boards
ProjectManager has a kanban feature that was created to visualize workflows. The project design phase involves collaboration among members of the project management team who will need to share files and communicate in real-time, which can be achieved with ProjectManager’s kanban boards that let project teams better communicate and structure the project design.
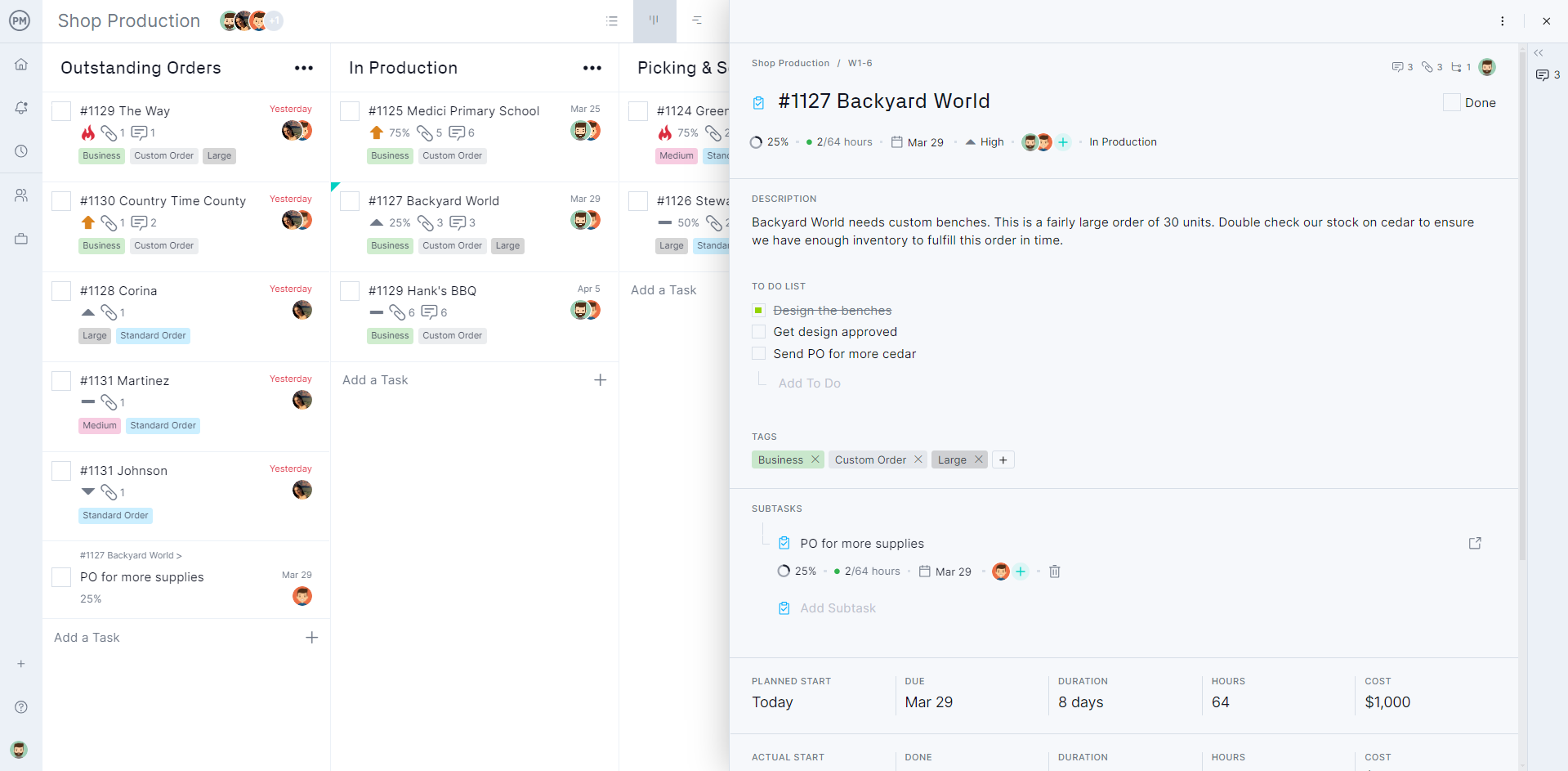
It’s easy to see how this process can serve you throughout the project design and as you collect more documents to define your project. Then, during execution, you can use ProjectManager’s real-time dashboards to keep track of the project’s progress.
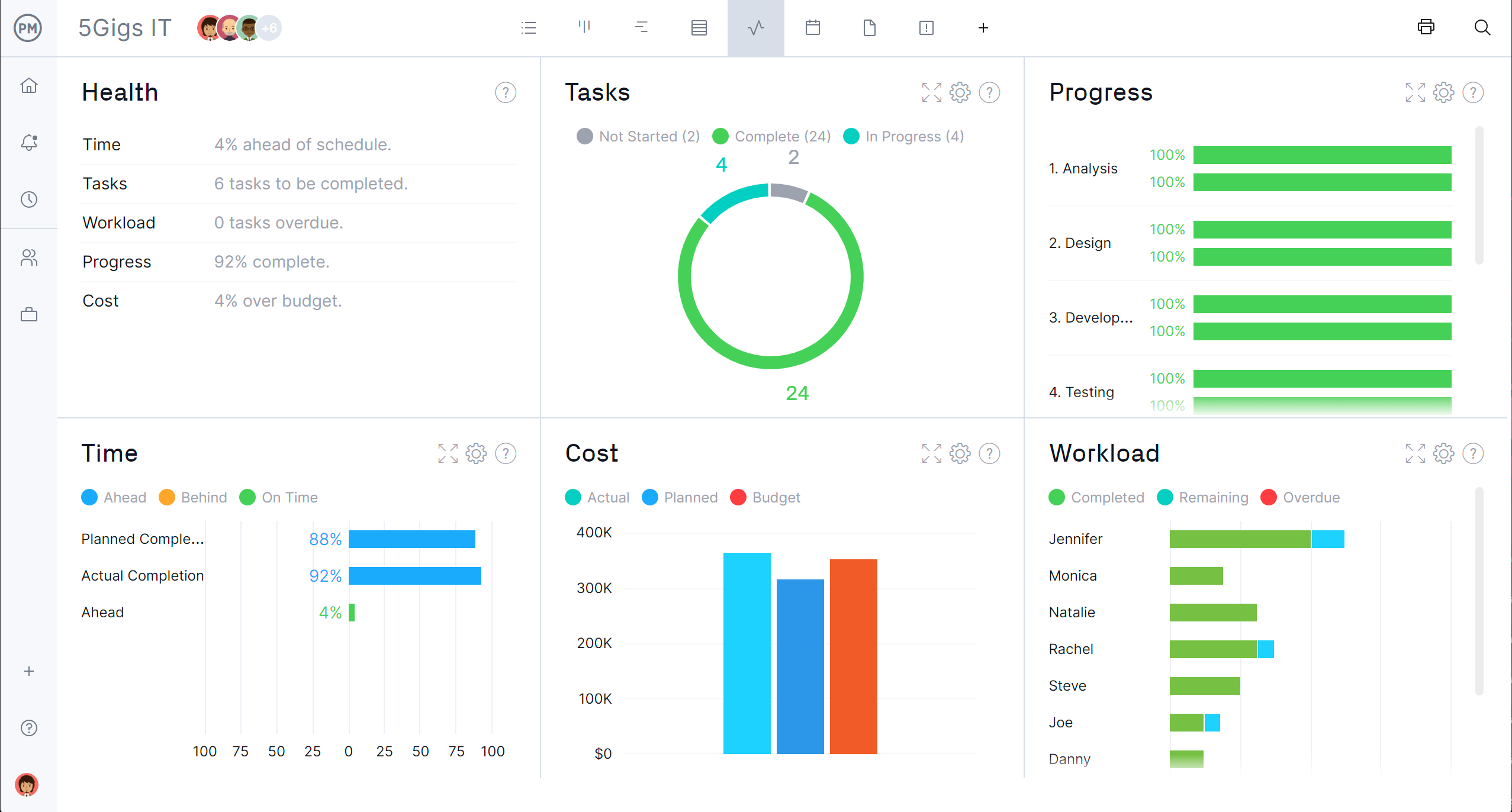
Track Projects With Real-Time Dashboards
ProjectManager’s real-time dashboards help project managers keep track of project costs, timelines and progress once the project design becomes a reality. These powerful dashboards can be used to track multiple projects in a portfolio. Six key metrics automatically update as changes are made across the software, making it easy to stay on track throughout your project or portfolio.
Related Project Management Content
- 10 Free Project Forms & Formats for Excel and Word
- Benefits of a Gantt Chart for Project Management: 8 Key Advantages
- Top Project Management Conferences for 2025, 2026 & 2027
- Project Financing Basics: How to Fund a Project
- Project Contingency: How to Get Projects Back On Track
- Introducción al Proceso de Diseño de Proyectos
Only robust project management software can handle all the data needed for a good project design. ProjectManager is an online tool that has features, such as the online Gantt chart, to help schedule, as well as others, to assist with budget and resource allocation. See how it can help you by taking this free 30-day trial.

