How long has project management been around? Forever. Well, as long as people have been around. Project management isn’t new, but the history of project management is a relatively new development. It was only once the discipline had been codified that we could start to look back and identify key points in time that contributed to its development, such as the creation of the Gantt chart and the Agile Manifesto.
Let’s start at the beginning and sketch out the rich history of project management. But know that, though historic, project management isn’t a dusty relic of the past. It continues to grow and influence the way people do almost anything that has a start and a finish.
The Pre-History of Project Management
Before the profession of project management was defined, there were projects, but they didn’t share many of the foundations that hold up project management today. The pharaohs built the pyramids of Egypt around 2500 BC, and to this day we aren’t certain how they accomplished such a vast task. But records do show that there were managers, even back then, who were responsible for each of the four faces of the Great Pyramid.
More recently, the need for a more pronounced structure in construction, manufacturing and transportation in the 19th century led to the birth of project management as we recognize it today. Examples include the building of the Transcontinental Railroad and the rebuilding of the southern states after the devastation of the American Civil War.
While there might not have been task management, scope or workload considerations at the time, there was certainly leadership at play, and there must have been some budget, even if open-ended, and scheduling of some sort. But with practice came process and refinement.
The Modern History of Project Management
It wasn’t until the 1900s that project management as we know it began to take form. As projects became industrialized, the process to manage them also experienced a revolution.
The Principles of Scientific Management
In 1911, the publication of Frederic Taylor’s The Principle of Scientific Management, which he based on his work in the steel industry, was an attempt to help unskilled workers transition to new, more complex projects by simple learning techniques. He pioneered the need for incentive-based wage systems, and how to take advantage of time-saving techniques.
The Gantt Chart
Henry Gantt might be the father of modern project management. In 1917, he created the eponymous scheduling diagram. It was an innovation. He used a visual timeline to plot tasks as points with durations and linked them if they were dependent. That way, everyone could see the schedule more clearly.
The Gantt chart was the shot heard around the project management world. It was used in the building of the Hoover Dam in 1931, which was one of its first major implementations. Gantt charts continue to be used today and have transitioned to the digital world with online versions that make them easier to use.
ProjectManager has online Gantt charts that not only visualize the schedule on a timeline but link all four task dependencies, create milestones and allow you to assign tasks to your team. You can even filter for the critical path and set a baseline, which allows you to track your planned progress against your actual progress in real time. That helps project managers allocate resources to stay on schedule and not go over their budget. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
The American Association of Cost Engineers
Now called AACE International, AACE was formed by a collection of project managers and associated specialists in planning, scheduling, cost estimating and other related fields. It continues today as one of the leading professional societies of project managers and related fields. In 2006, they released the first integrated process for portfolio, program and project management with their Total Cost Management Framework.
The Critical Path
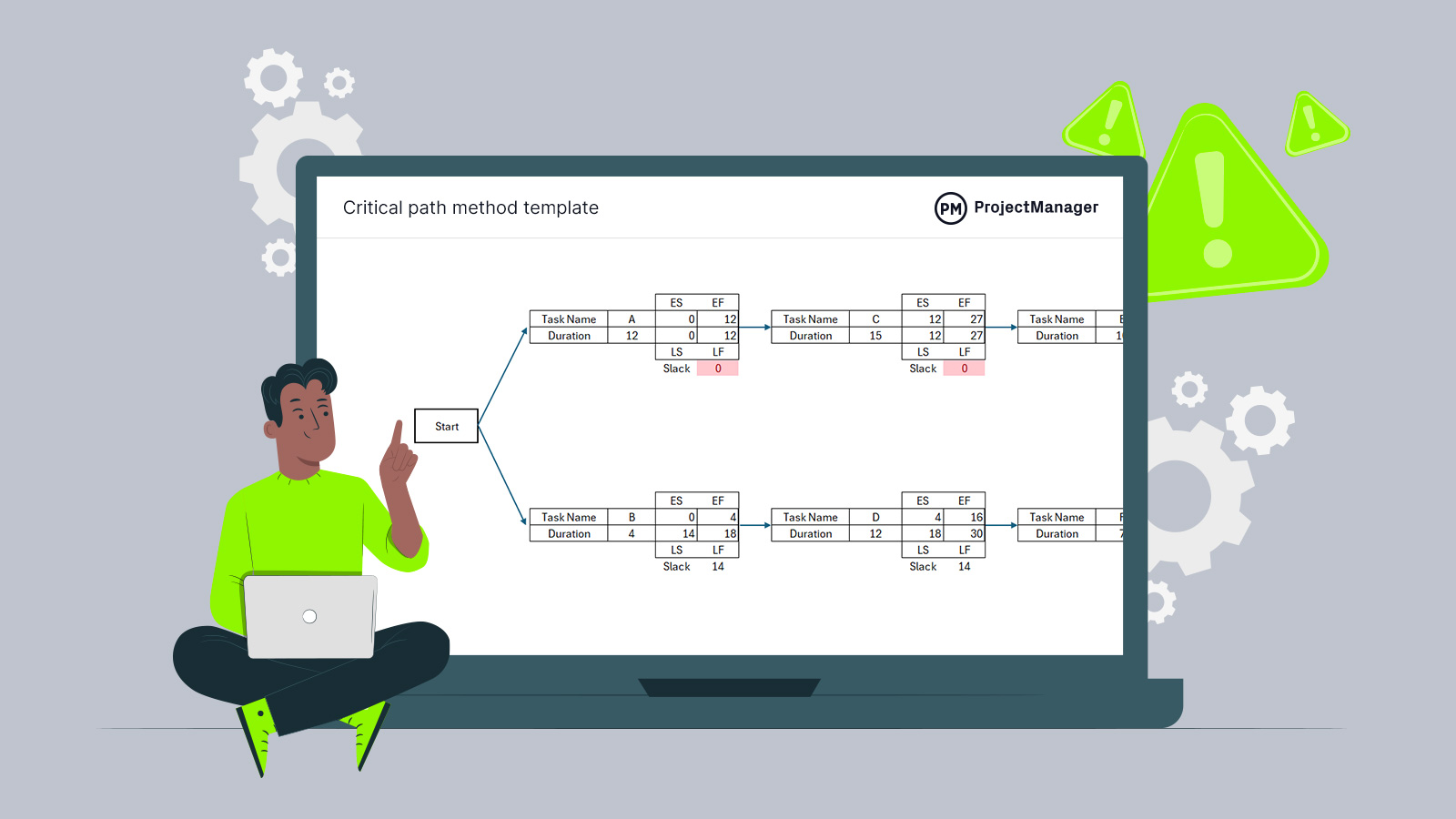
The critical path is a technique that’s used to predict how long a project will take. It analyzes which sequence of activities has the least amount of scheduling flexibility. The technique was developed by Dupont in 1957 to help work through the complexities of shuttering chemical plants for routine maintenance. The critical path proved so successful that it saved DuPont $1 million within the first year.
Get your free
Critical Path Template
Use this free Critical Path Template to manage your projects better.
Get the Template
Program Evaluation Review
In 1958, the United States Department of Defense’s US Navy Special Projects Office developed the Program Evaluation Review (PERT). It was developed as a method to analyze the tasks involved in completing a Polaris mobile submarine-launched ballistic missile project. It focused on the time needed to complete each task and identified the minimum amount of time required to finish the whole project.
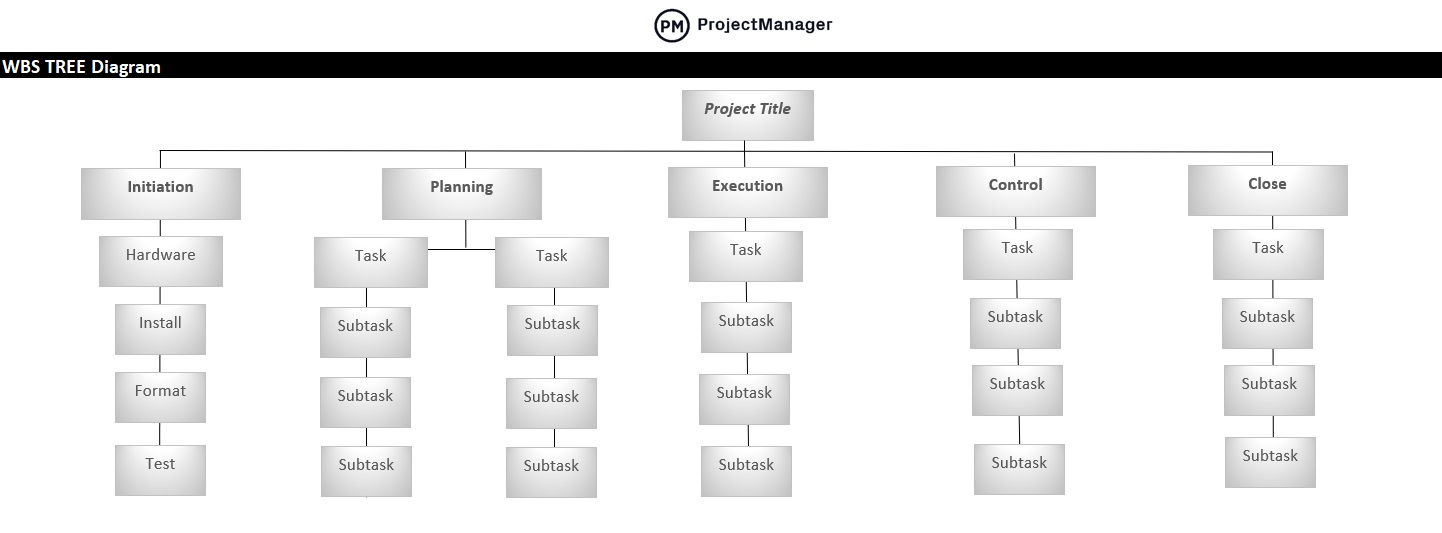
Work Breakdown Structure
Another commonly used method of project management, the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), first came about in the United States Department of Defense. The WBS is a complete hierarchical tree structure of the deliverables and tasks needed to complete a project. It was also part of the Polaris project. After the project was done, the Department of Defense published the WBS, and in 1962, mandated the procedure’s use for future projects.
The International Project Management Association
In 1965, the International Project Management Association (IPMA) was founded. It is the world’s first project management association. Founded in Vienna as a means for project managers to network, the organization is now registered in Switzerland and is compiled of 60 national and internationally oriented project management associations.
The Project Management Institute
The nonprofit Project Management Institute (PMI) was founded by five volunteers in 1969. Incorporated in Pennsylvania, it held its first symposium in Atlanta in 1969. It has since published A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK), which outlines the processes and knowledge areas of project management and became standard in 1998. PMI is also a certification body, offering both the Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) and the Project Management Professional (PMP).
Theory of Constraints
The management philosophy of the Theory of Constraints (TOC) was developed to help an organization meet its goals. The title comes from the idea that a manageable system is limited in achieving its goals by several constraints. It was first introduced by Dr. Eliyahu M. Goldratt in his 1984 novel The Goal. The theory was applied to the creation of Critical Chain Project Management.
Scrum
The agile software development model that incorporates multiple small teams working intensely and interdependently is known as Scrum, which was named as a project management style in 1986. The term comes from a paper first published in the Harvard Business Review called “The New New Product Development Game” by Takeuchi and Nonaka. Developed for software management, it has since moved into use with general projects.
Earned Value Management
The idea of an earned value concept isn’t new. It’s been around since the turn of the 1900s, but it came to prominence as a technique in project management by 1989. Earned Value Management (EVM) helps measure project performance by using a systematic project management process to find variances in projects based on the comparison of work performed and work planned. It’s a powerful predictor of cost and schedule control.
PRINCE
The UK government created Projects In Controlled Environments (PRINCE) as its standard for all information systems projects in 1989. It was revised in 1996 as PRINCE2 due to criticism that it was too unwieldy and rigid, and therefore only suited for large projects.
Critical Chain Project Management
In 1997, Eliyahu M. Goldratt developed Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM), which is based on the methods and algorithms of his Theory of Constraints. It keeps resources levelly loaded while remaining flexible to their start times, and switching between tasks when necessary to keep the project on schedule.
The Agile Manifesto
The use of iterative and incremental development methods traces back to 1957 with evolutionary project management, though adaptive software development didn’t emerge until the 1970s. But the widespread use of Agile as a project style was codified with the creation of the Agile Manifesto or the Software Development Manifesto, in 2001.
The history of project management is still being written. Whichever way it evolves, the one constant will be the need for the right tools to help project managers control every phase of their projects. ProjectManager is online project management software with real-time dashboards and online Gantt charts among other features. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

